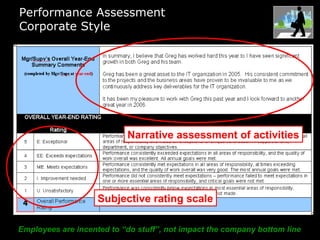
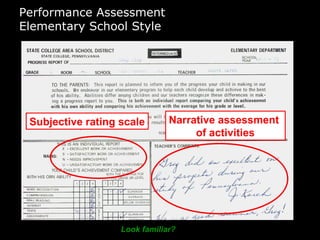
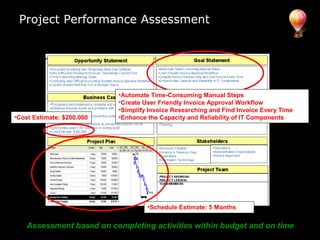
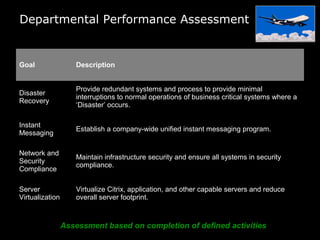
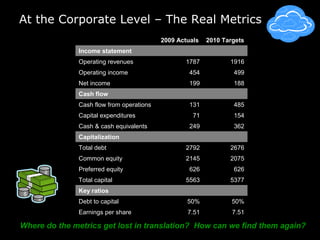
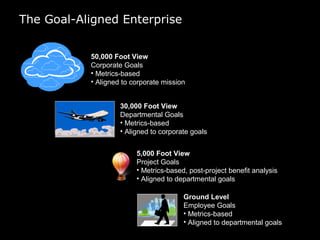
In 2009, an energy wholesaler's IT department initiated a successful, grassroots value delivery program that yielded significant cash impacts without heavy top-down involvement. The document outlines a strategic framework for aligning corporate, departmental, and employee goals with measurable metrics to enhance performance. Key recommendations include breaking down high-level goals into actionable sub-goals across all organization levels to foster accountability and improve efficiency.