Daily Lesson Log in Science 9 Fourth Quarter Physics
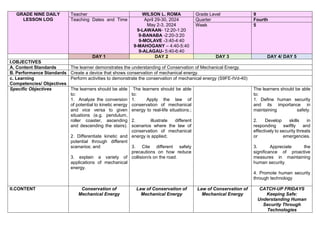
- 1. GRADE NINE DAILY LESSON LOG Teacher WILSON L. ROMA Grade Level 9 Teaching Dates and Time April 29-30, 2024 May 2-3, 2024 9-LAWAAN- 12:20-1:20 9-BANABA -2:20-3:20 9-MOLAVE -3:40-4:40 9-MAHOGANY – 4:40-5:40 9-ALAGAU- 5:40-6:40 Quarter Fourth Week 5 DAY 1 DAY 2 DAY 3 DAY 4/ DAY 5 I.OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards The learner demonstrates the understanding of Conservation of Mechanical Energy. B. Performance Standards Create a device that shows conservation of mechanical energy. c. Learning Competencies/ Objectives Perform activities to demonstrate the conservation of mechanical energy (S9FE-IVd-40) Specific Objectives The learners should be able to: 1. Analyze the conversion of potential to kinetic energy and vice versa to given situations (e.g. pendulum, roller coaster, ascending and descending the stairs). 2. Differentiate kinetic and potential through different scenarios; and 3. explain a variety of applications of mechanical energy. The learners should be able to: 1. Apply the law of conservation of mechanical energy to real-life situations.; 2. illustrate different scenarios where the law of conservation of mechanical energy is applied; 3. Cite different safety precautions on how reduce collision/s on the road. The learners should be able to: 1. Define human security and its importance in maintaining safety. 2. Develop skills in responding swiftly and effectively to security threats or emergencies. 3. Appreciate the significance of proactive measures in maintaining human security. 4. Promote human security through technology II.CONTENT Conservation of Mechanical Energy Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy Law of Conservation of Mechanical Energy CATCH-UP FRIDAYS Keeping Safe: Understanding Human Security Through Technologies
- 2. III.LEARNING RESOURCES A. REFERENCES 1.Teacher’s Guide pages TG: pp. 224 TG: pp. 225 2.Learner’s Materials pages LM: pp. 257-258 LM: pp. 259-260 3.Textbook pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resources (LR) Portal https://docs.google.com/doc ument/d/1D3Mf4LSBEwK8 DGKjaOL3vH4BO8vIaGFPr y5dNIj_IBI/edit B.Other Learning Resources IV.PROCEDURES A. Reviewing previous lesson or presenting the new lesson ELICIT Identify whether the following has Potential or Kinetic Energy. Write the number in each corresponding column. If the activity is classified as potential energy, indicate the specific type of potential energy. ELICIT Classify whether the description pertains to Potential Energy (PE) or Kinetic Energy (KE). Write PE or KE in the space provided. __________1. Energy possessed by a moving tricycle. __________2. An energy of motion, observable as the movement of an object, particle, or set of particles. __________3. Energy due to the position of an object __________4. Energy waiting to be used ELICIT B. Establishing a purpose for the lesson. ENGAGE There are lots of energy present in the environment. ENGAGE Energy transformation is common to any objects or appliances who perform work. ENGAGE ENGAGE Are you ready to learn the importance of sensors in preventing road crashes?
- 3. What are the changes in the forms of mechanical energy? How do we describe energy transformation on pendulums? On a roller coaster? C. Presenting examples/ instances of the new lesson ENGAGE Introduce the following concept UNLOCKING OF TERMS: Kinetic Energy: energy in motion. KE = 1/2mv2 Potential Energy: stored energy PE = mgh Gravitational potential energy: energy of the object due to its position above Earth. ENGAGE Introduce the following concept UNLOCKING OF TERMS Mechanical Energy: Combination of potential and kinetic energy ME = KE + PE ENGAGE ENGAGE Distribute the reading materials. D. Discussion of new concepts and practicing new skills #1 EXPLORE Activity : Little Shop of Toys Materials: Any material available Instructions: 1. Students may trace energy input from the chemical energies of their hands converted into mechanical energy as their hands work to operate toys and EXPLORE Activity 1: Hep Hep Hooray! Materials : Instructions: 1. In a real hydroelectric power plant, the tail water level is fixed at the bottom of a water channel or penstock with openings to control the volume and flow rate of water that leaves the dam and enters the power plant containing the EXPLORE EXPLORE Reading Time!
- 4. objects. Some examples of toys to use: 1. Yoyo 2. Friction Toy Car 3. Deflated Balloon turbine and generating units. The water that rotates the turbines returns to the body of water below the dam. 2. Some groups may opt to modify the activity by using only the hole on the 5- cm level for the different heads of flow due to different head water levels. This way the elevation of the exit openings relative to the turbine is constant for different flow heads. This model reflects more closely realistic water storage levels that differ over a period of time. E. Discussion of New concepts and practicing new skills #2 F. Developing Mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment 3) EXPLAIN Guide Questions: 1. What does the toy or object do? 2. What energy changes take place as this toy or object operates? 3. What form does the stored energy start out in? 4. What form does the stored energy turn into? 5. In summary, what made each object begin moving and what made each object stop? EXPLAIN Guide Questions: 1. For each method, what forms of energy will be involved in the process? Trace the transformations of energy. 2. What mechanical energy transformations took place when water got projected out of the holes? 3. What was the effect of the stored water’s head of flow to its range? EXPLAIN EXPLAIN After Reading, let the students write a short reflection about the topic.
- 5. The energy that is received or given off by an object can change into different forms as it is transferred or used when work is done and accompanied mostly by heat dissipated into the air or other forms of energy such as light, sound. The input energy coming from the energy source, is stored in an object and when used can be transferred or transformed into a used (work) and unused (heat) energy output. For any mechanical process that occurs inside an isolated system and involves only conservative forces, the total mechanical energy is conserved. This means that the total mechanical energy remains constant in time. G. Finding Practical Applications of Concepts and Skills in Daily Living ELABORATE Ask: What happens to some of the energy as it performs transformation from one energy into another? ELABORATE Ask: In a swing, when is the potential energy at its highest? Lowest? In which point the kinetic energy at its highest? Lowest? ELABORATE H. Making generalizations and abstractions about the lesson EXTEND Ask: Why do we need to transform energy? EXTEND Ask: If you ride a roller coaster, what do you feel if the coaster is going down? Going up? EXTEND I. Evaluating Learning EVALUATE Multiple Choice: Read each question carefully. Choose the BEST EVALUATE MULTIPLE CHOICE Directions: Read the statement carefully. Choose EVALUATE
- 6. answer from the options provided. 1. What is the energy of a motorcycle moving slowly at the top of a hill? A. entirely kinetic B. entirely potential C. entirely gravitational D. both kinetic and potential 2. Which event is explained in the sequence of energy changes shown in the diagram below? A. a headlight is on B. a turbine spins C. electric current powers a flat iron D. gasoline burns to run a jeepney 3. In the Agus VI Hydroelectric Power (HEP) Plant, which energy transformation takes place? A. nuclear energy to heat to electrical energy B. heat to mechanical energy to electrical energy. C. electrical energy to mechanical energy to electrical energy. D. gravitational to potential energy to kinetic energy to electrical energy 4. Which event does NOT describe potential energy being changed into kinetic energy? the BEST answer from the options provided. 1. Which sequence of energy transformation best describes what happens when you switch on your battery-run radio? Sound Energy Energy C. Energy Energy 2. Which among the forms of energy is considered a potential energy? A. chemical energy B. radiant energy C. sound energy D. thermal energy 3. Which of the following happens to the coconut that falls freely? A. Gains both potential energy and kinetic energy. B. Loses both potential energy and kinetic energy. C. Gains potential energy and loses kinetic energy. D. Loses potential energy and gains kinetic energy.
- 7. A. A box sliding down a ramp. B. A mango falling from a crate. C. A pen spring being compressed. D. A stretched rubber band got loosened. 5. Which event illustrates the direct transformation of potential to kinetic energy? A. A Kalesa moves from rest. B. A basketball player catches a flying ball. C. Kathy’s arrow is released from its bow. D. The spring mechanism of a toy is rotated until it locked. 4. A torchlight fell from a watch tower. The potential energy of the torchlight at the highest point compared to its kinetic energy at the lowest point is _______ A. lesser. B. equal. C. greater. D. not related. 5. The potential energy of a 1- kg object on top of a hill is 18 J. What is its velocity in m/s just before it hits the bottom of the hill? A. 36 B. 18 C. 6 D. 3 Additional Activities for application of remediation Activity 3 Fill in the Table Study the different activities which can be easily performed and then explain how energy is conserved. Since the Total mechanical energy is the sum of the Potential and kinetic energy, complete the table by finding the Total mechanical energy.
- 8. V.REMARKS VI.REFLECTION No of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation who scored below 80% Did remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson No. of learner who continue to require remediation Which of my teaching strategies work well? Why did these works? What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? What innovation or localized materials did I use/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Prepared by: Checked by: Monitored by:
- 9. WILSON L. ROMA ANTONETTE M. DIZON NELIZA G. REYES Teacher I Master Teacher I HT III, Science Department Noted by: RUBY U. DE JESUS Principal IV