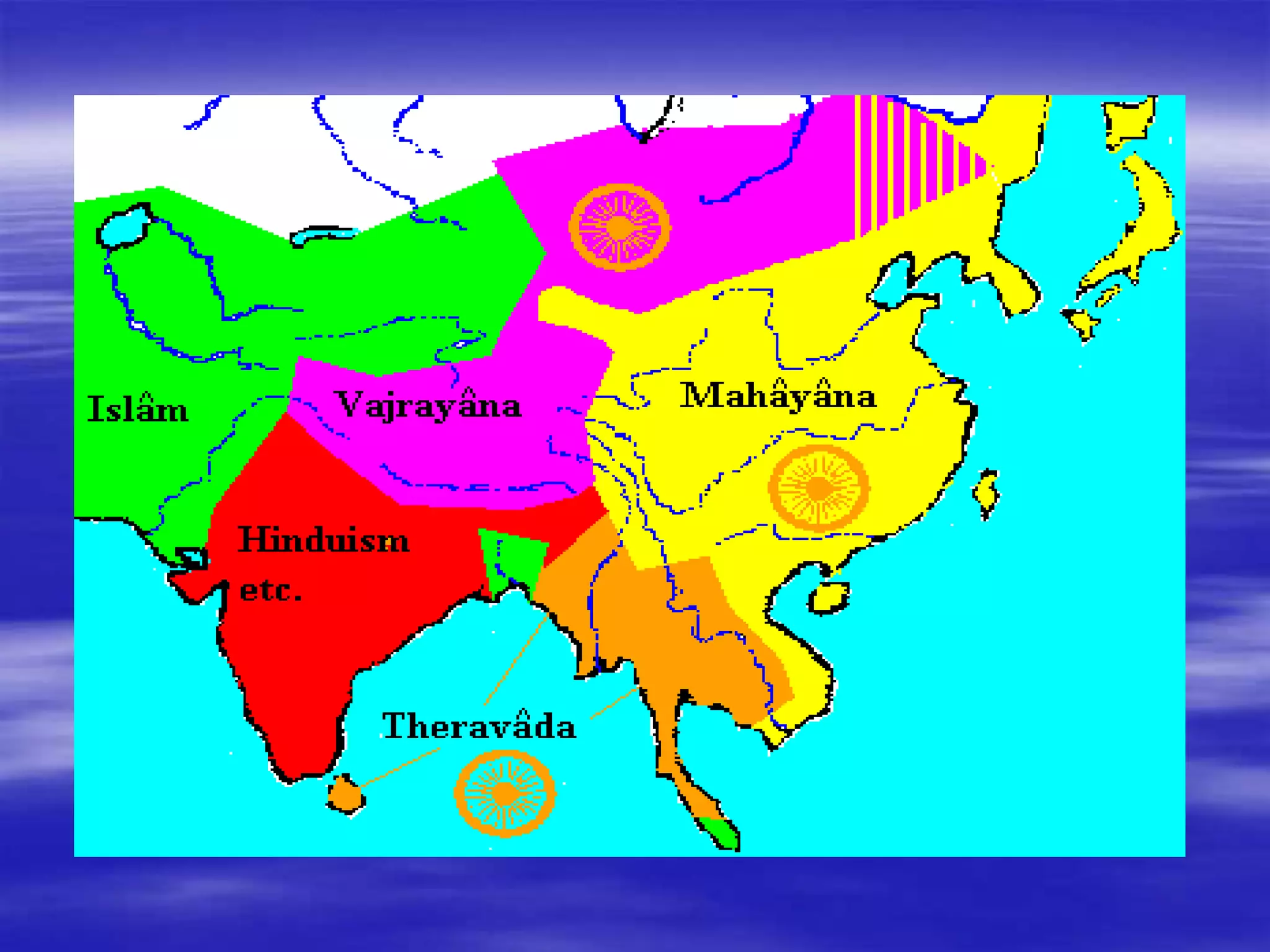
Buddhism was founded in India by Siddhartha Gautama, known as the Buddha, who achieved enlightenment and taught the Four Noble Truths about suffering. Buddhism does not believe in gods but reveres enlightened beings known as bodhisattvas. The core teachings of Buddhism are recorded in sacred texts like the Tripitaka and Sutras. Buddhism spread across Asia through missionary work and trade, establishing monasteries, and some traditions began worshipping the Buddha as a god. It challenged the Hindu caste system and aspects of violence and intolerance.