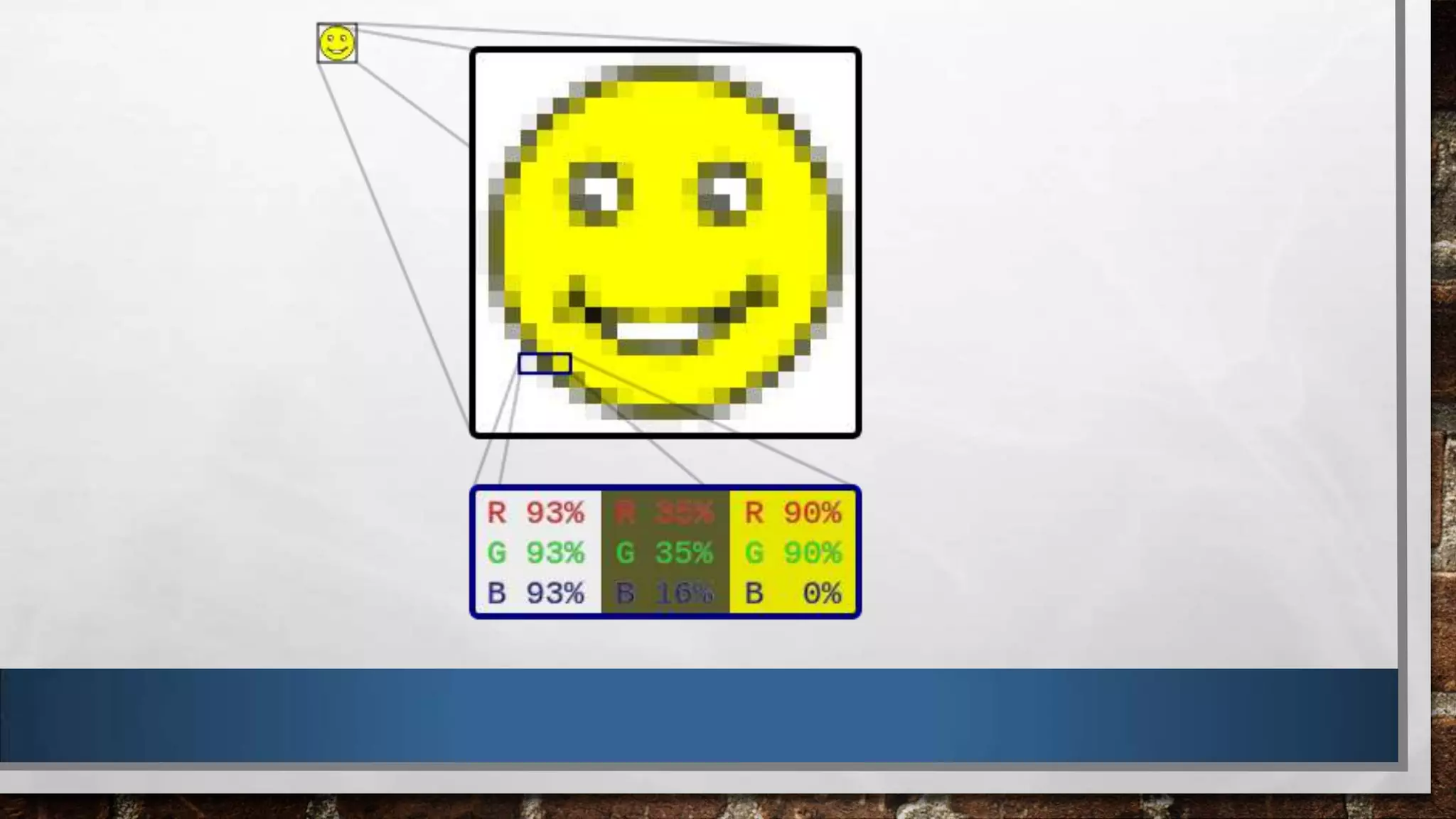
Digital graphics can be either vector or bitmap. Vector graphics use mathematical expressions to build images from points, lines and curves, allowing them to be scaled without losing quality. Bitmap graphics are made up of pixels and are resolution-dependent, meaning they cannot be scaled up without losing quality. Key factors that impact image quality include compression, resolution, and whether the image is meant for print or screen output. Proper file naming and organization are also important for effective storage and management of digital graphics assets.