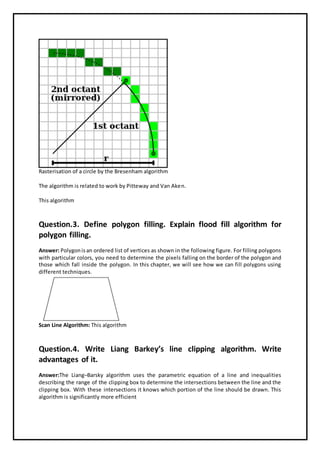
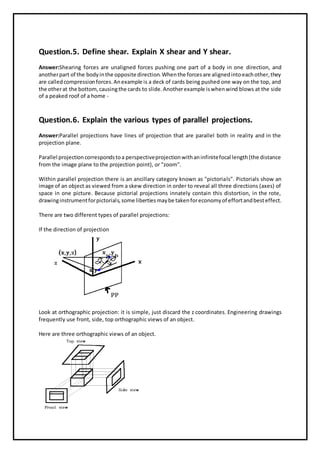
The document is a communication to students regarding assignment assistance for a BSc IT semester sixth course on computer graphics. It provides details about specific assignments, including topics like image processing, algorithms for drawing and clipping, polygon filling, and projection types. Students are encouraged to contact the provided email or phone number for fully solved assignments.