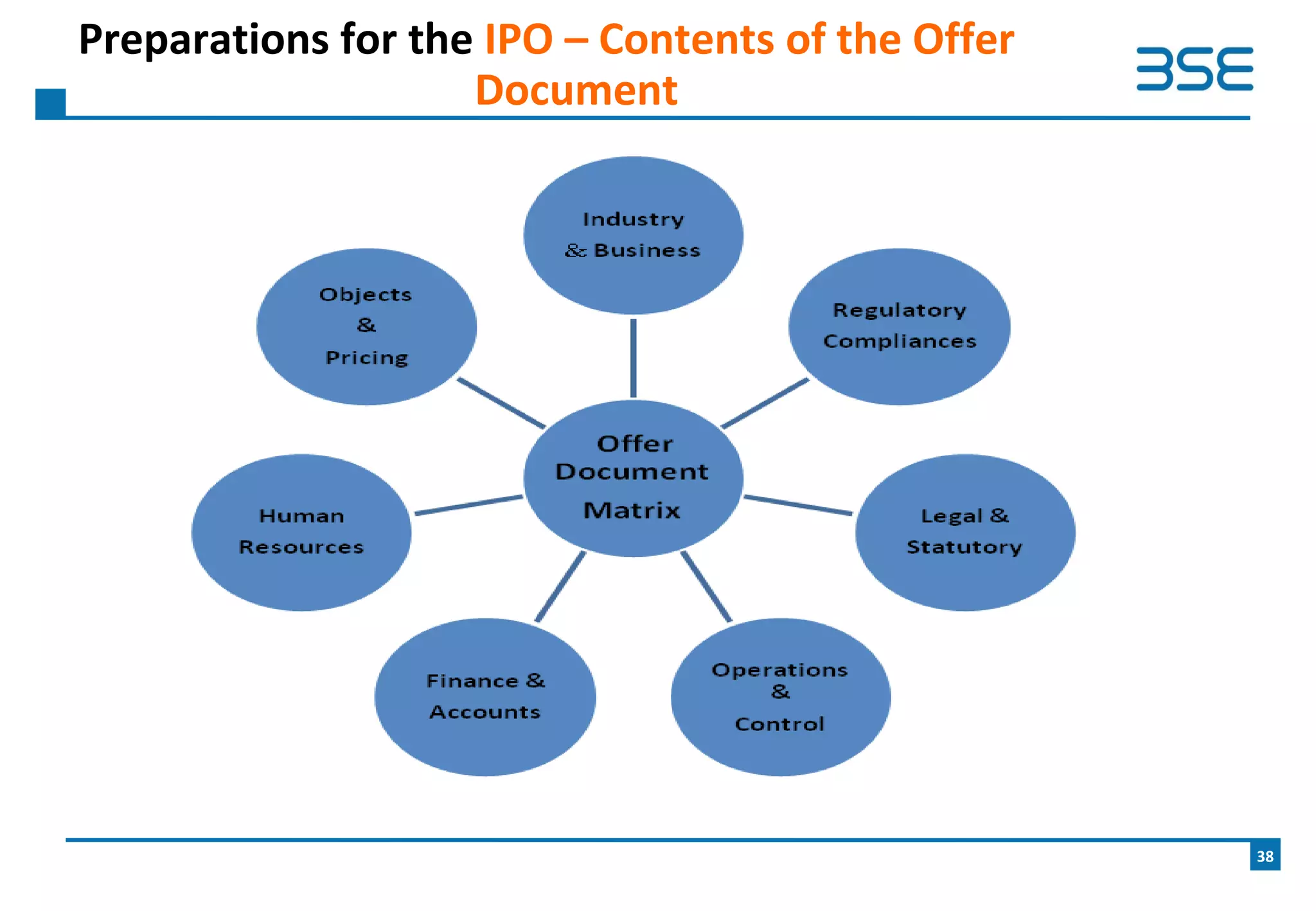
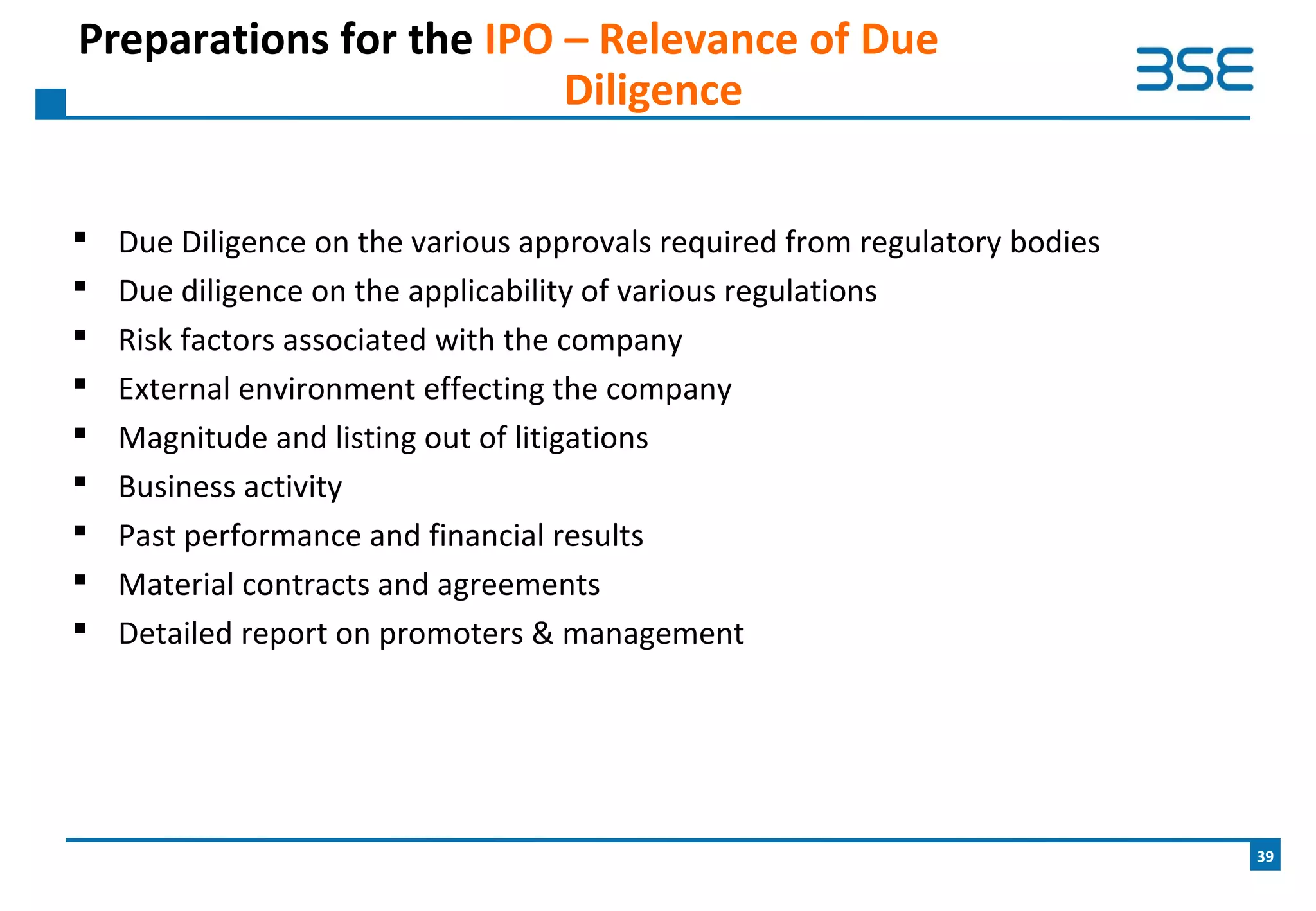
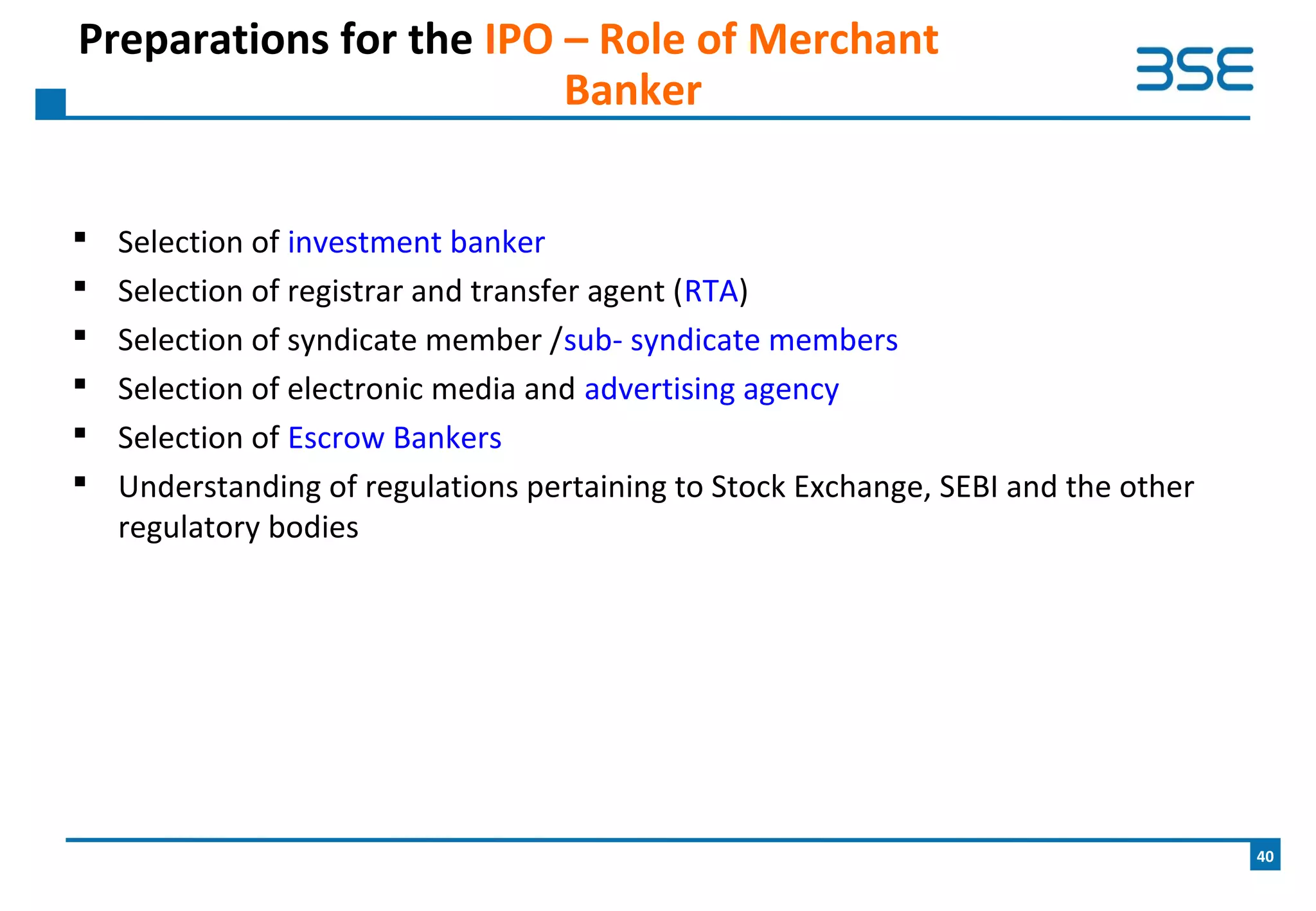
The document provides an overview of the upcoming BSE SME Exchange, which will provide a dedicated platform for small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in India to list and raise capital. Some key points include:
- BSE has received regulatory approval to launch the SME Exchange, leveraging its existing equity trading platform.
- Listing requirements and compliance norms are simplified for SMEs compared to the main board.
- The exchange aims to help SMEs access funding for growth while providing investors an opportunity to invest in early-stage companies.
- Key aspects include 100% underwriting of issues, mandatory market making for 3 years, and simplified listing procedures.