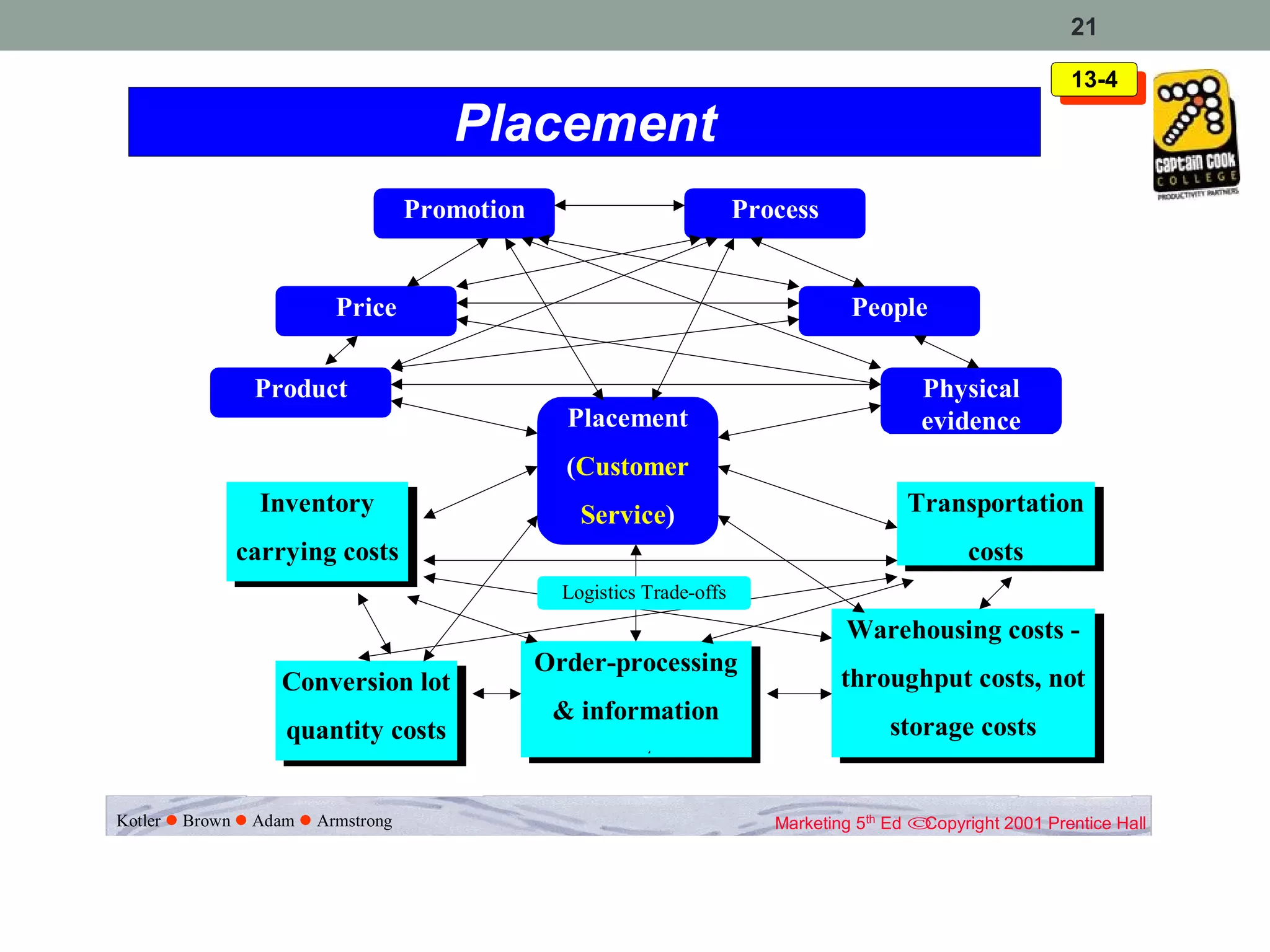
1. Place (also known as distribution) is the fourth element of the marketing mix, after product, price, and promotion. It involves getting the product to customers through appropriate distribution channels.
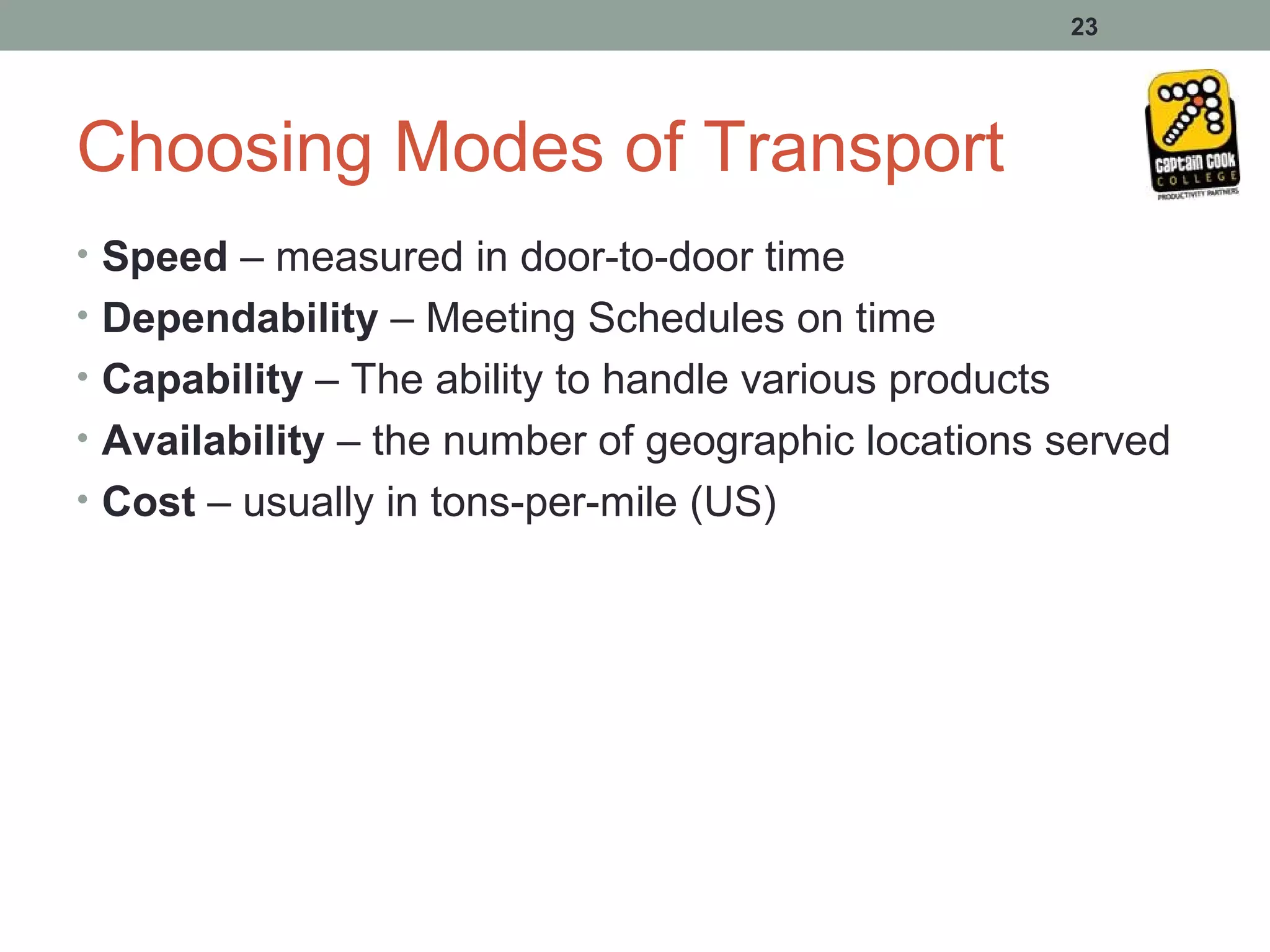
2. Physical placement involves planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of materials from origin to points of use to meet customer needs profitably. Marketing logistics networks and demand chain management coordinate supplier, manufacturer, and customer flows.
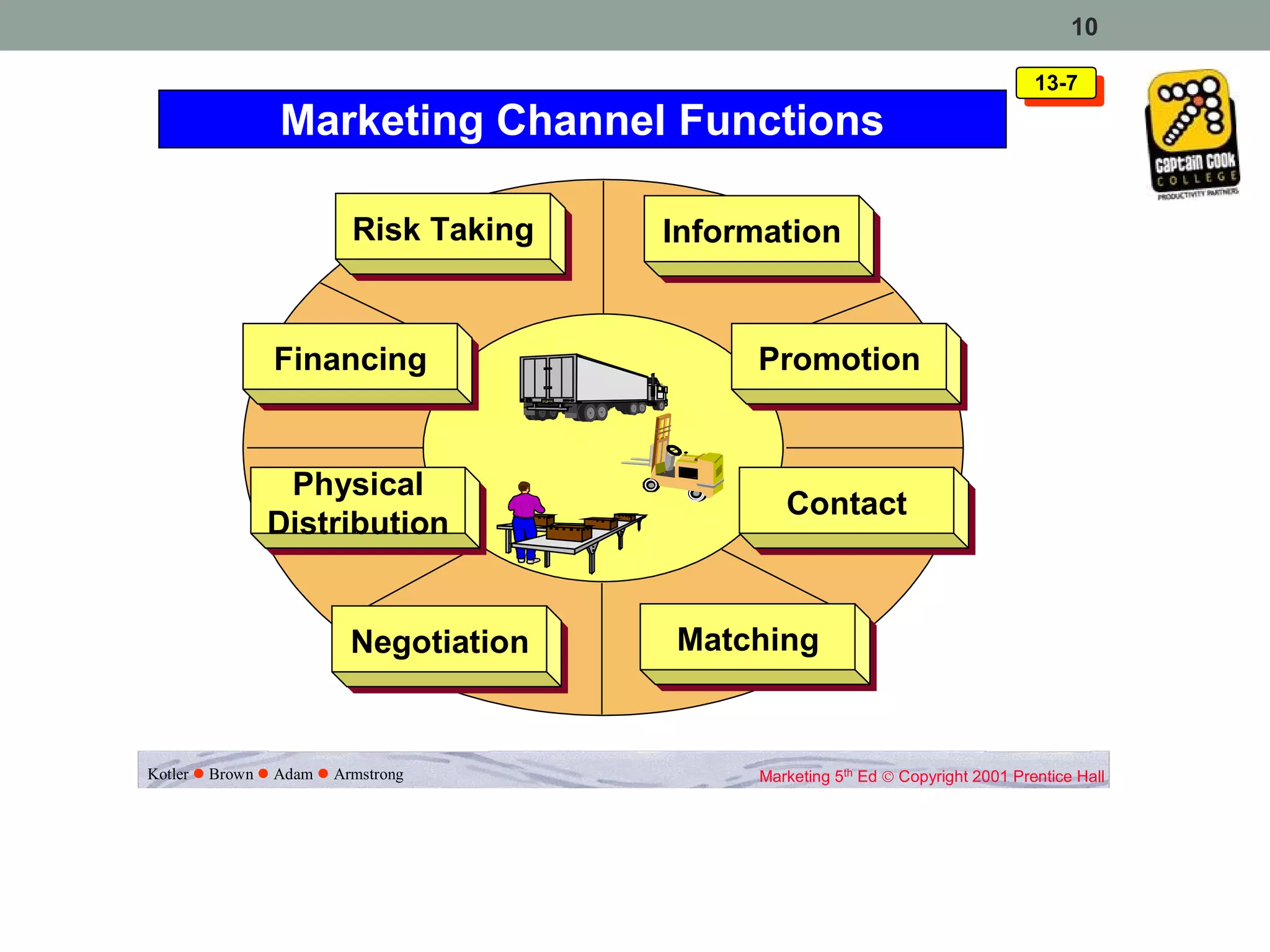
3. Marketing channels involve interdependent organizations that make a product available to consumers. Channel functions include information sharing, promotion, negotiation, physical distribution, financing, and risk taking.