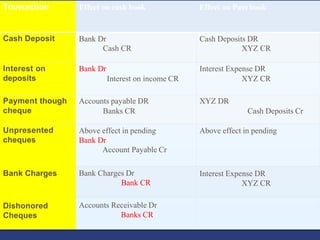
This document provides information about bank reconciliation in accounting. It begins with an introduction and then discusses the purpose of bank reconciliation statements, reasons for differences between cashbook and bank statement balances, and the reconciliation process. The reconciliation process involves 5 steps: 1) identify outstanding checks, 2) identify deposits in transit, 3) analyze the bank statement for unrecorded transactions, 4) check for errors, and 5) compare adjusted balances. The document also provides an example reconciliation and explains adjusting entries related to the reconciliation.