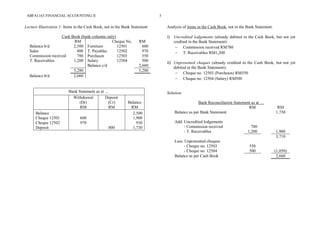
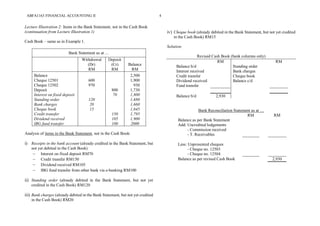
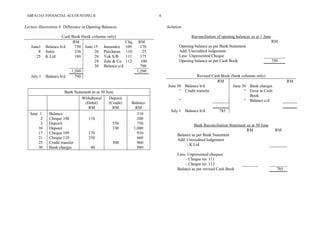
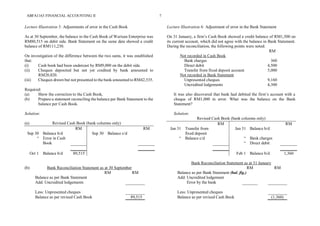
The document provides a detailed overview of bank reconciliation, including its purpose, processes, and common discrepancies between cash books and bank statements. Key concepts include identifying errors, updating the cash book, and preparing bank reconciliation statements, emphasizing the importance of monthly reconciliation for accurate bookkeeping. Various illustrations showcase practical examples of how to handle discrepancies and prepare reconciliation statements effectively.