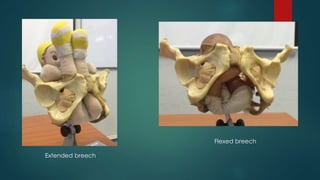
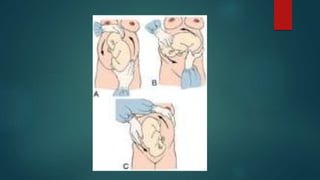
Breech presentation occurs when the fetus is positioned longitudinally with the buttocks or feet closest to the cervix. This is the most common malpresentation and is more likely to occur earlier in gestation. Predisposing factors include maternal fibroids or uterine anomalies, and fetal abnormalities like anencephaly. Management options include external cephalic version (ECV) to rotate the fetus, vaginal delivery if the breech is extended or flexed, or elective cesarean section. ECV has a higher success rate in multiparous women and is performed after 37 weeks to reduce cesarean delivery. Vaginal breech delivery requires experienced assistance and careful fetal monitoring due to risks of cord pro