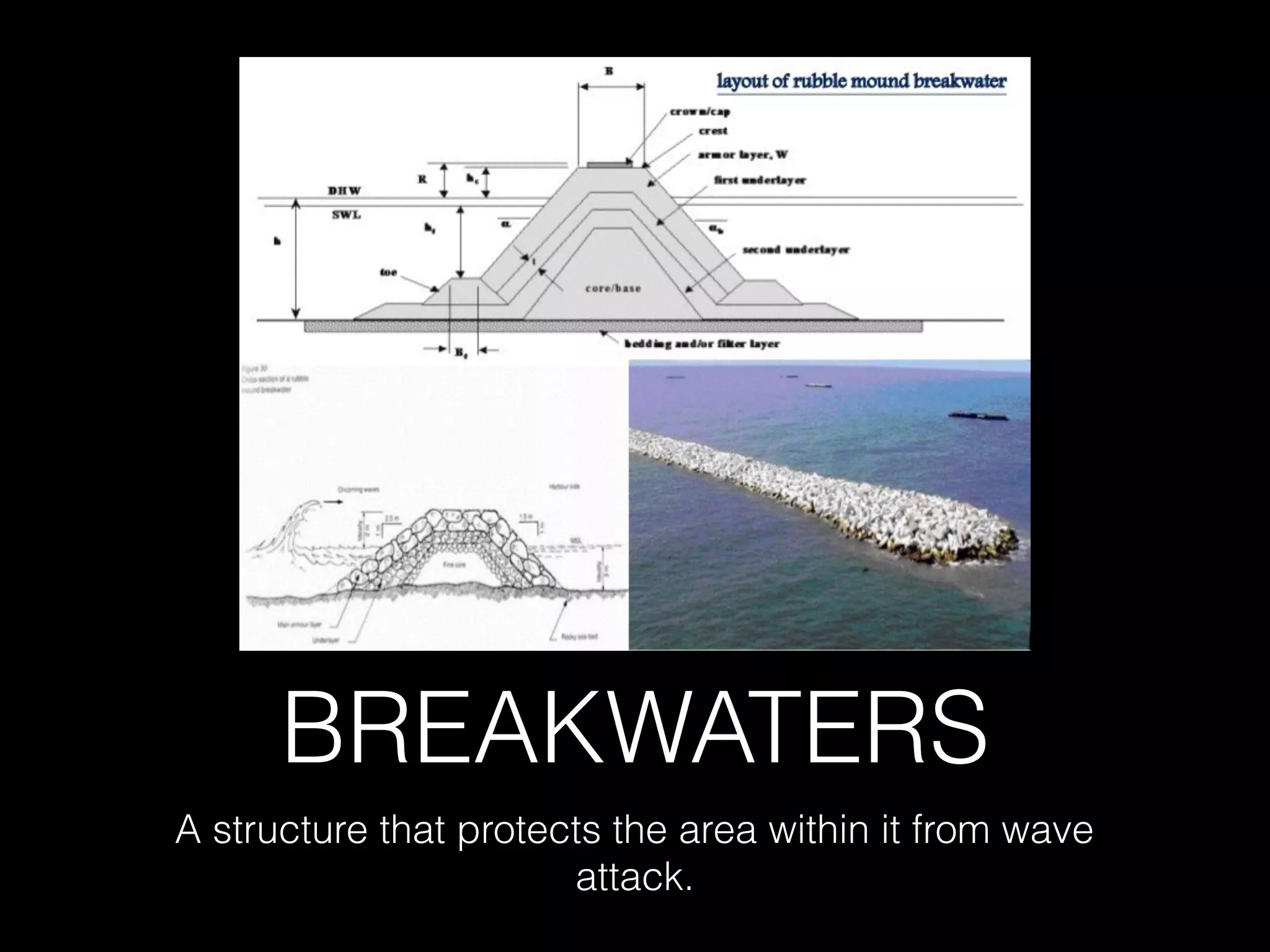
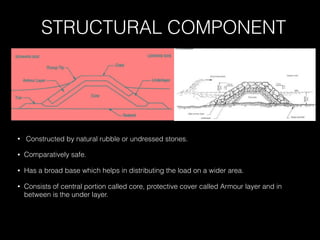
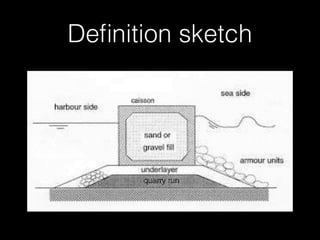
The document discusses different types of breakwaters used to protect coastal areas from wave attack. It describes rubble mound breakwaters, vertical-wall breakwaters, and floating breakwaters. Rubble mound breakwaters are constructed from natural rubble or stone and dissipate wave energy through breaking. Vertical-wall breakwaters use a vertical wall structure and reflect wave energy. Floating breakwaters are removable structures constructed from caissons or pontoons that are anchored but less effective against long waves. The document provides details on the characteristics, uses, advantages, and disadvantages of each type of breakwater.