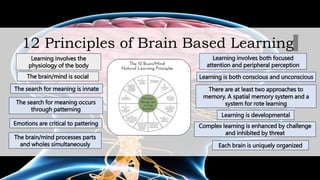
Brain-based learning is an instructional approach grounded in neuroscience research about how the brain learns naturally. Key principles include the social nature of learning, the importance of emotions, and the need for a challenging yet safe learning environment. Effective teaching practices derived from these principles emphasize immersive experiences and active processing of information.