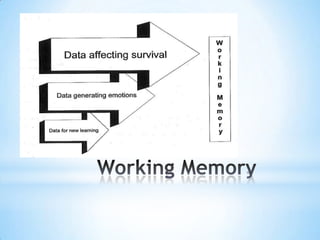
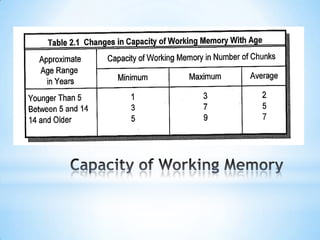
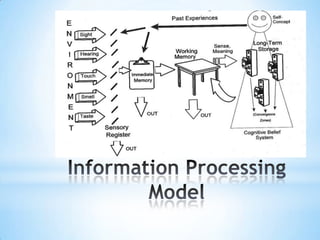
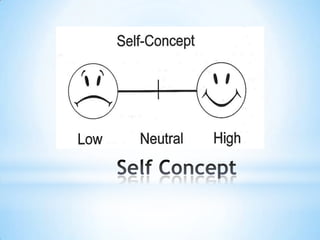
The document discusses how the brain processes information and what educators can do with this knowledge. It explains that the thalamus screens incoming information for importance. It also notes that motivation, meaning, closure, and testing long term storage can improve learning and retention. Finally, it suggests educators reflect on how they can apply these brain insights to improve their instructional methods.