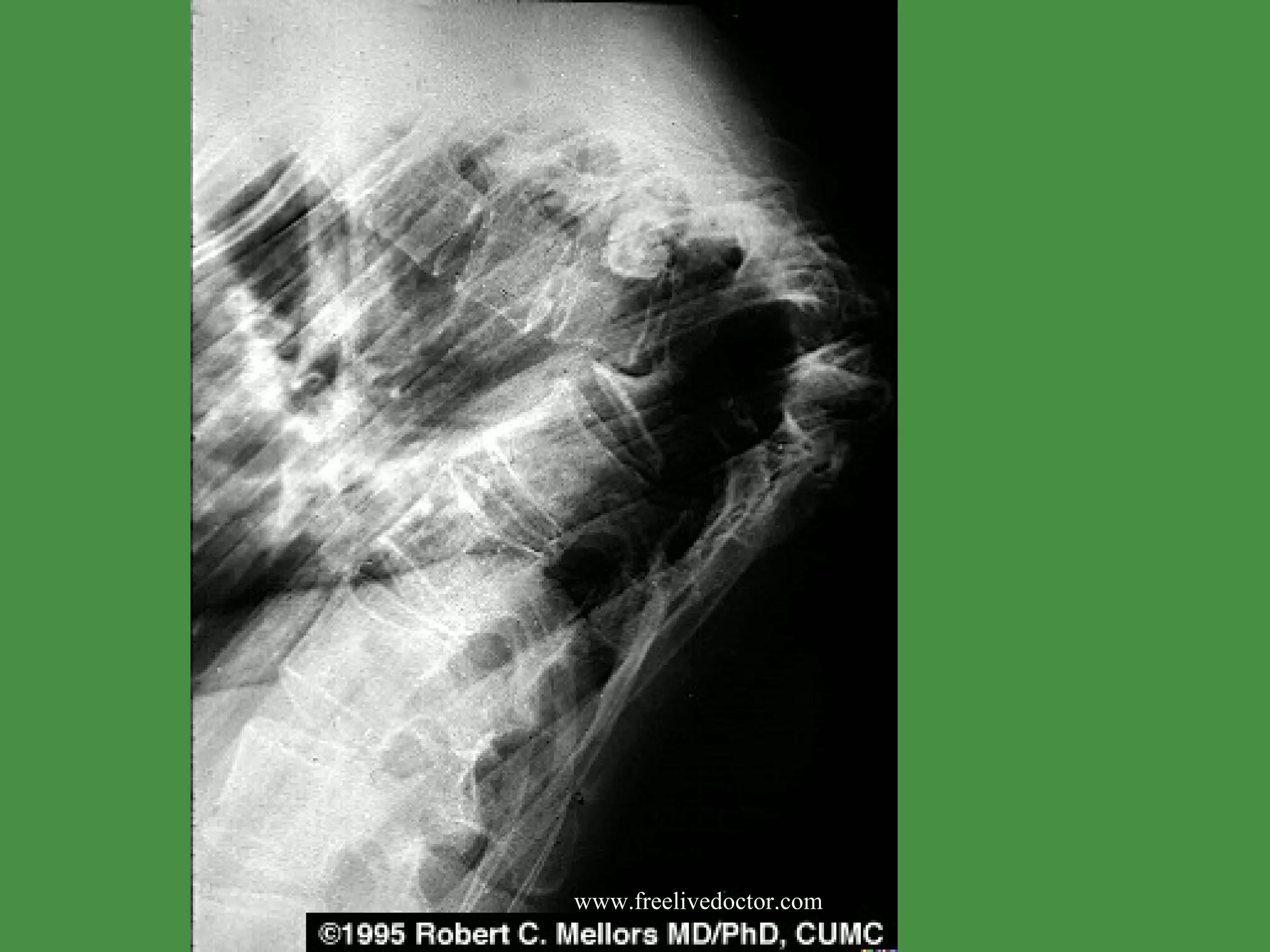
The document discusses several bone disorders and degenerative conditions, including osteoporosis, osteomalacia, rickets, osteomyelitis, tuberculosis osteomyelitis, syphilitic osteomyelitis, and Paget's disease. It provides details on the causes, clinical presentation, diagnostic methods, and treatment for each condition. The document also covers basic bone biology, structure, cells, proteins, mineralization, and calcium homeostasis.