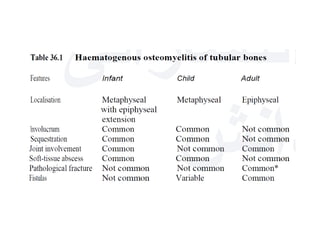
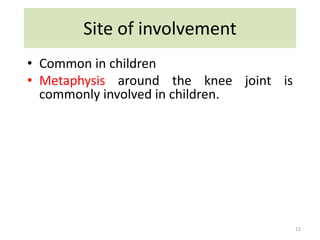
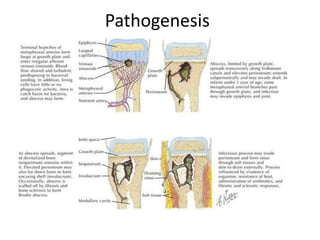
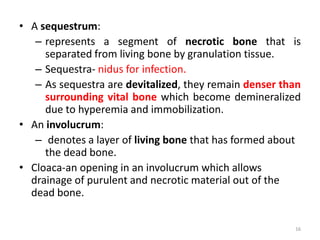
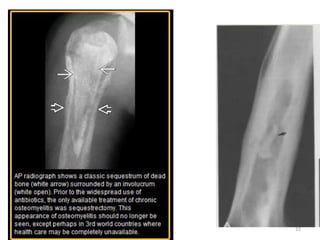
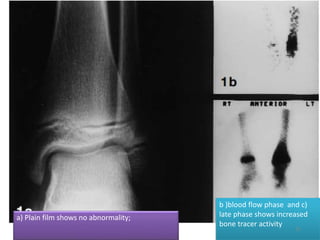
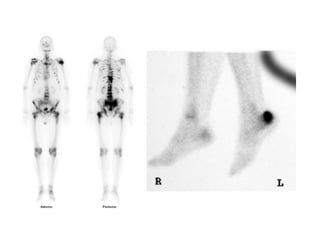
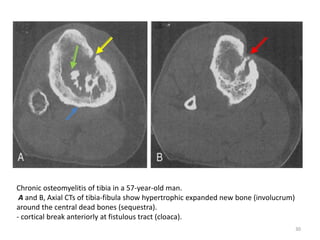
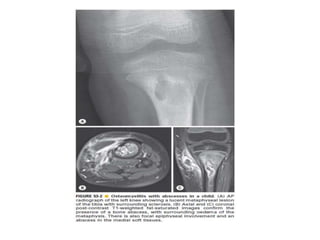
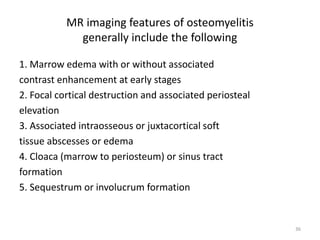
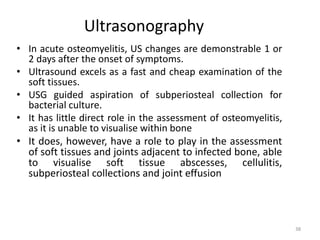
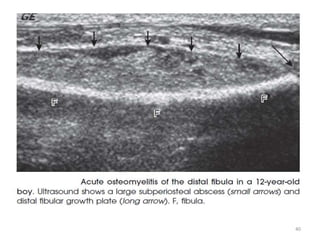
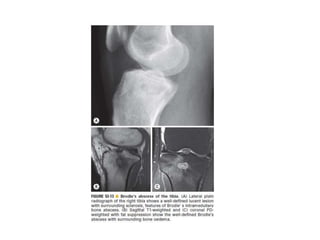
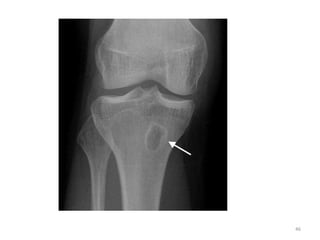
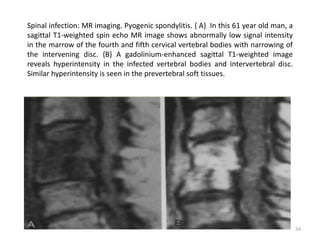
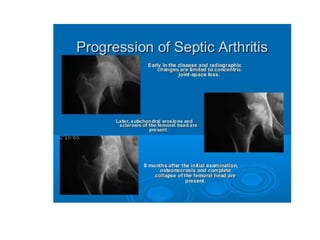
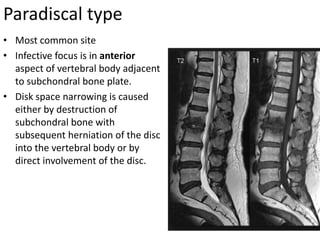
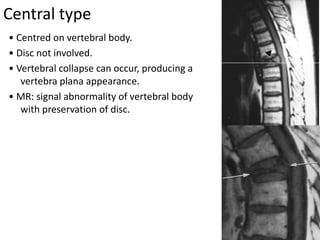
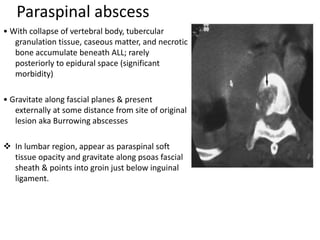
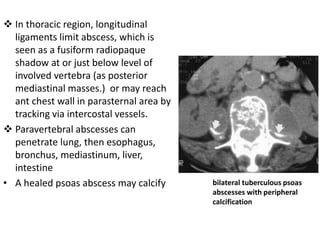
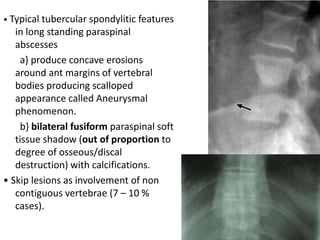
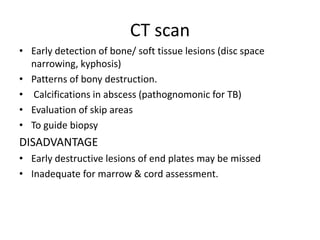
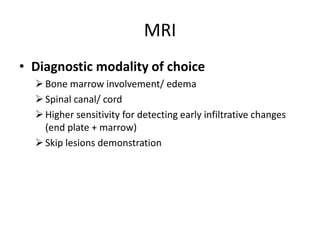
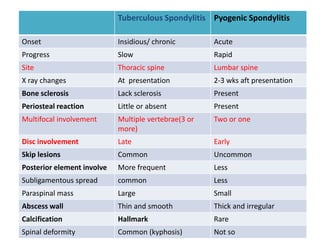
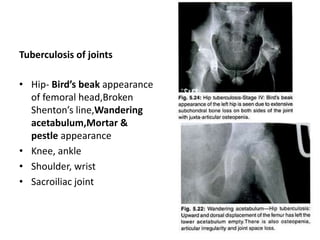
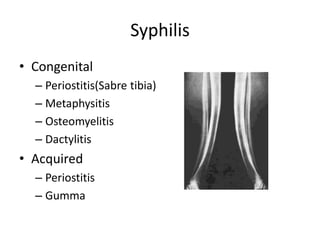
This document discusses bone and joint infections. It begins by classifying infections as either pyogenic (bacterial), tuberculous, or other causes. Osteomyelitis is defined as a bone infection that can be caused by bacteria, fungi, parasites or viruses. Symptoms of osteomyelitis can be acute, subacute, or chronic. Common sites of bone infection in children are the metaphysis around the knee. Imaging plays an important role in diagnosis, with plain radiography, CT, MRI, bone scans, and ultrasound all discussed. Biopsy may be needed to confirm infection and identify the organism. Brodie's abscess, a characteristic subacute pyogenic bone infection, is also mentioned.