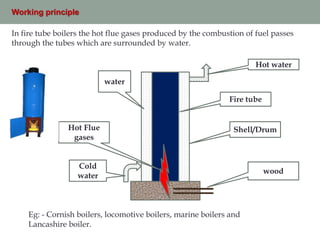
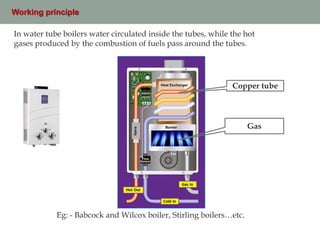
Boilers supply steam at constant pressure for various industrial applications. They work by heating water to its boiling point inside a closed vessel to produce steam. Boilers are classified based on how the hot gases and water circulate, the location of the furnace, water circulation method, orientation, and intended use. Common types include fire tube boilers where hot gases pass through tubes surrounded by water, and water tube boilers where water circulates inside tubes that hot gases pass around.