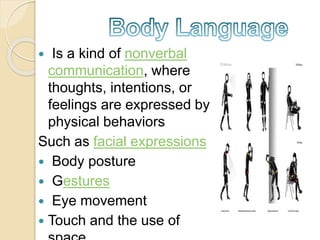
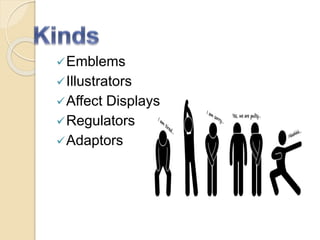
The document discusses body language and its importance in communication. It defines body language as nonverbal communication through physical behaviors like facial expressions, posture, gestures, eye movement, and touch. These signals can provide clues about a person's character, emotions, and reactions. The document also mentions that body language has both innate and learned cultural components and varies between cultures. It provides examples of different types of body language signals like kinesics, proxemics, haptics, eye contact, and handshakes. The document emphasizes that understanding one's own and others' body language can improve self-awareness, communication skills, and ability to establish relationships.