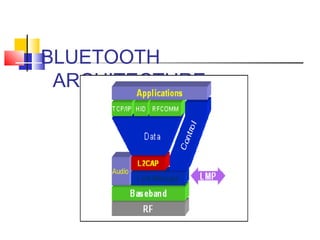
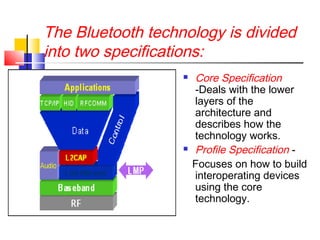
Bluetooth is a low-cost, short-range wireless technology designed to replace cables and connect devices over distances of 10-100 meters. It has evolved from its origin in Scandinavia, allowing multiple devices to form a network called a piconet, offering advantages like eliminating wires and facilitating communication, while facing challenges such as a short range and security issues. The future of Bluetooth is promising, with ongoing improvements in speed, range, and security to meet growing demands.