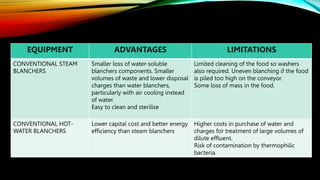
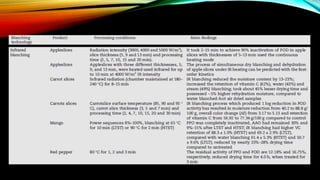
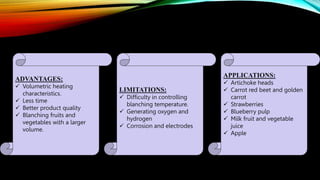
This document discusses various methods of blanching foods, including traditional hot water and steam blanching as well as emerging techniques like microwave, infrared, and ohmic blanching. Blanching involves briefly heating foods to inactivate enzymes and microbes. It helps preserve quality during processing and storage by slowing degradation. The document outlines the purposes of blanching, factors that influence blanching effectiveness like time and temperature, and how different techniques compare in terms of advantages, limitations, and applications. Finally, the effects of blanching on nutrient, color, flavor, and texture retention in foods are summarized.