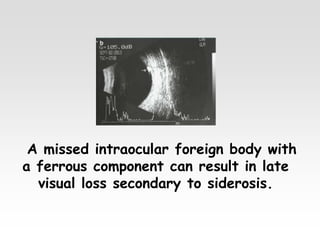
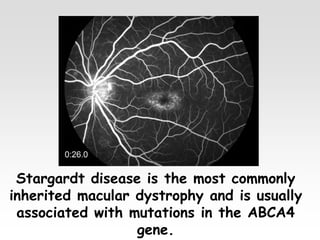
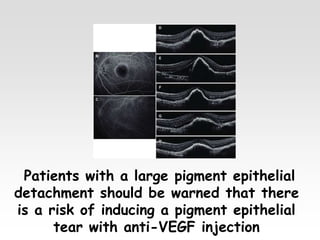
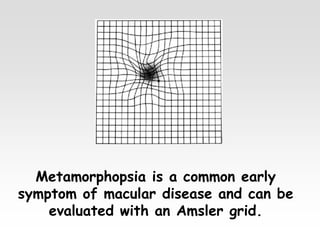
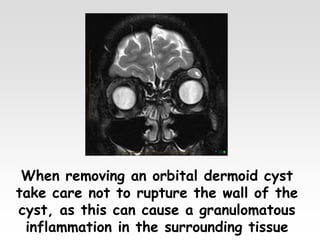
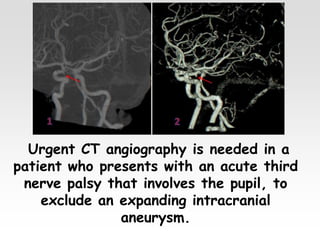
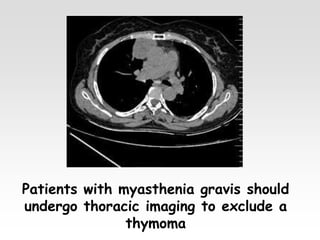
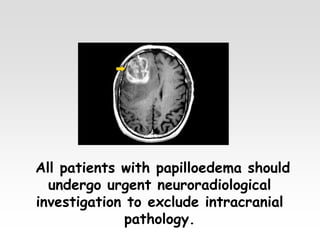
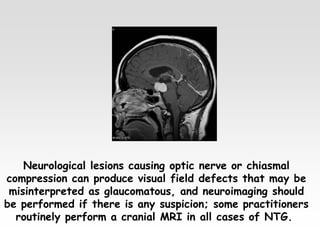
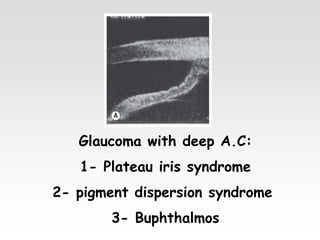
The document provides brief summaries of key points related to various ophthalmic and neurological conditions and treatments. Some of the main topics covered include: identifying intraocular foreign bodies; evaluating optic neuritis and macular dystrophy; investigating non-responders to anti-VEGF treatment for AMD; warning about risks of pigment epithelial tears with anti-VEGF injections; using Amsler grids to evaluate metamorphopsia; avoiding cyst rupture during dermoid cyst removal; investigating sinus infections with orbital cellulitis; needing urgent CT angiography for acute third nerve palsies involving the pupil; testing hearing and corneal sensation for sixth nerve palsies; investigating for thymoma with myasthenia gravis; needing