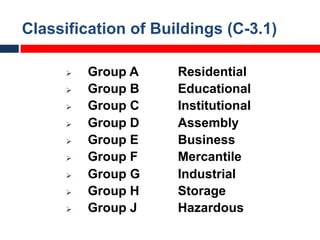
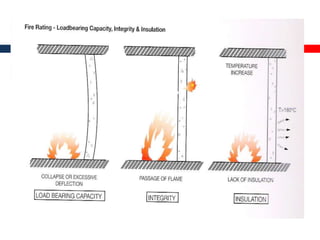
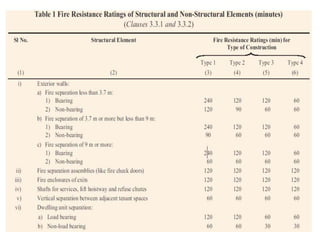
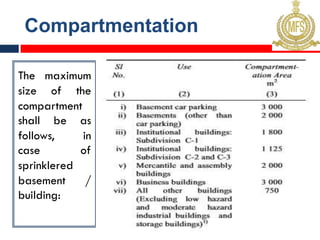
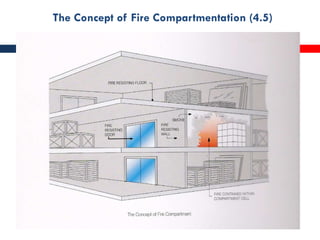
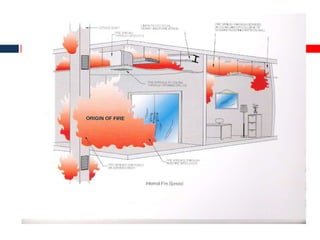
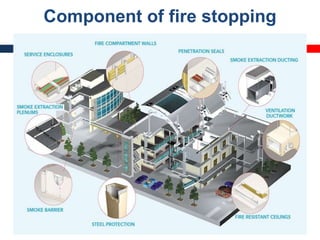
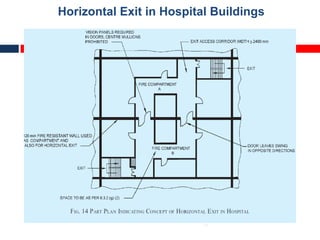
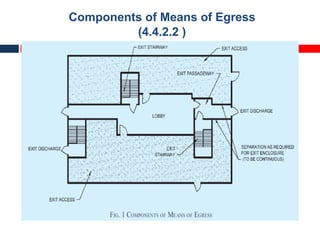
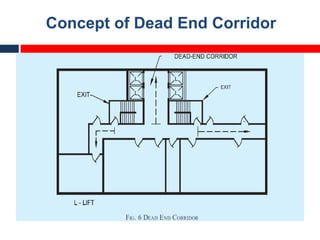
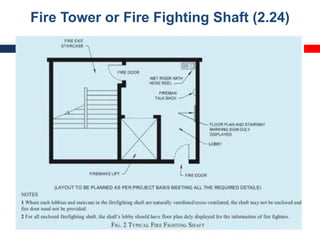
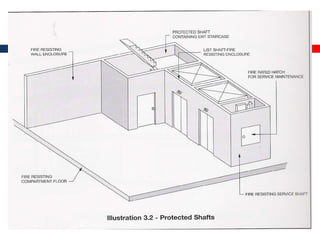
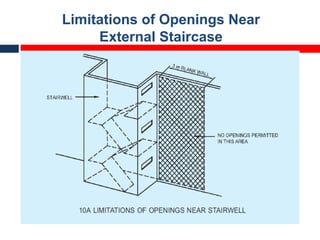
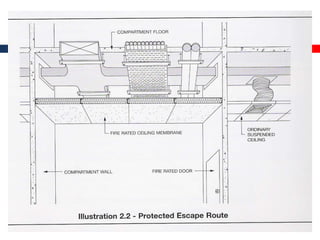
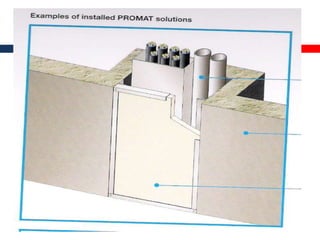
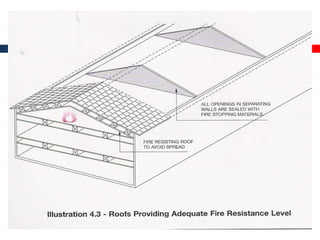
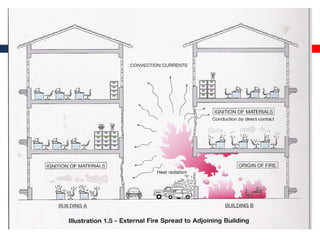
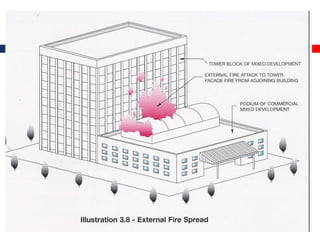
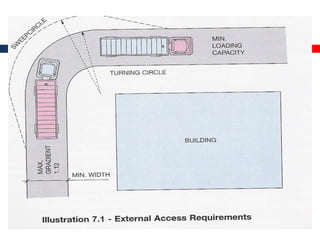
This document outlines fire resistant design and construction guidelines from the Directorate of Maharashtra Fire Service. It discusses classifying buildings based on occupancy and types of construction. It also covers provisions around fire resistance, prevention, and protection. The goal is to ensure structural safety, health safety, fire safety, and life safety through proper planning, design, construction, and maintenance of buildings in accordance with the National Building Code of India. This includes compartmentalization, openings, electrical installations, ventilation, means of egress, and other passive fire protection measures.