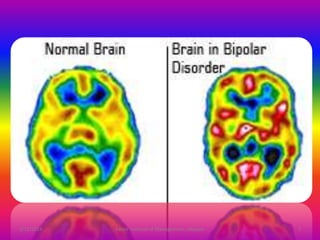
Bipolar disorder is a mental condition characterized by alternating periods of mania and depression. During mania, an individual feels abnormally happy, energetic, or irritable and makes poorly thought out decisions. Depression causes crying, poor eye contact, and a negative outlook. Bipolar disorder is diagnosed based on self-reported experiences and observations by professionals, and can be treated with psychotherapy and medications like lithium, which helps prevent relapses.