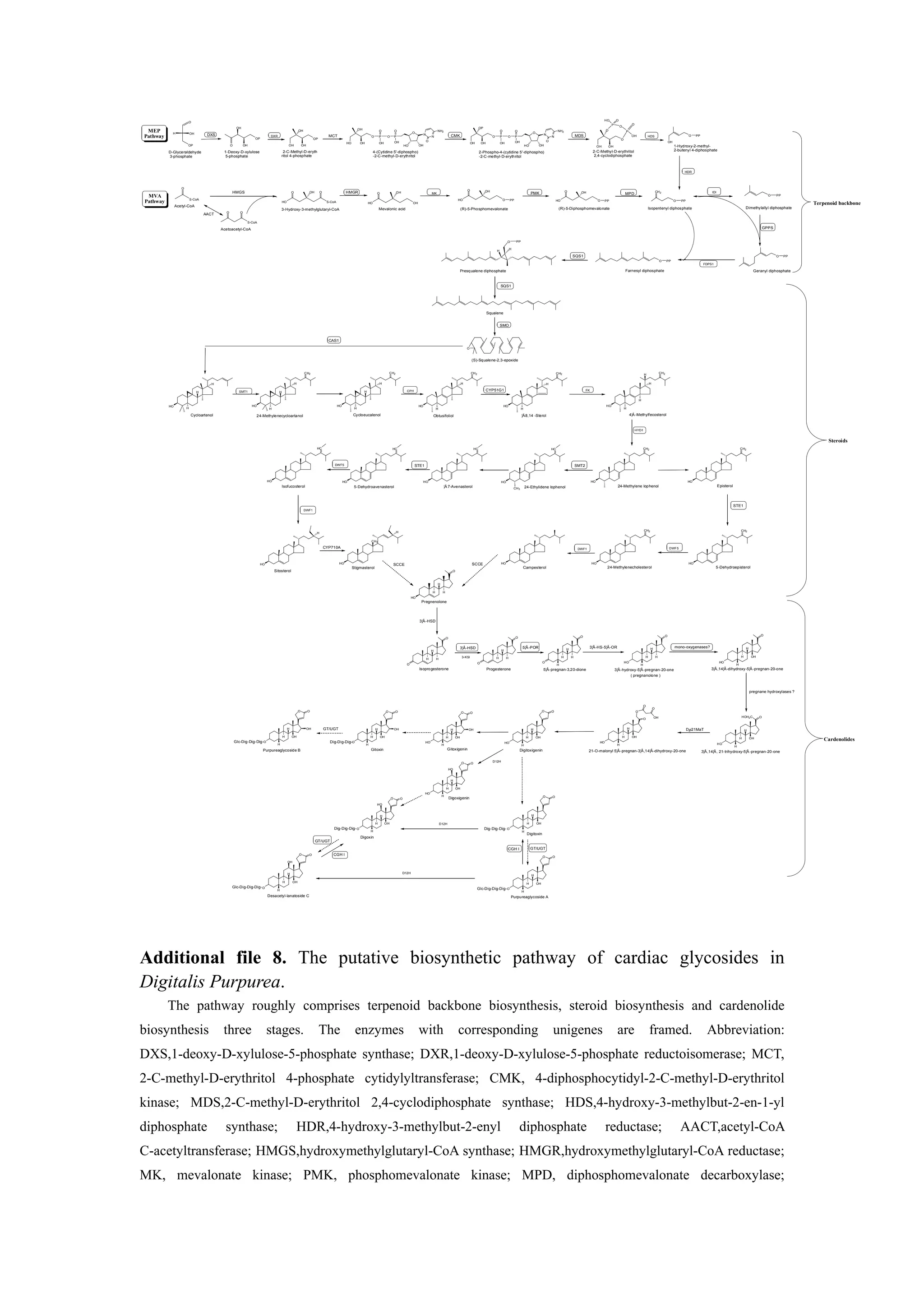
This document outlines the putative biosynthetic pathway of cardiac glycosides in Digitalis purpurea. The pathway involves three main stages: terpenoid backbone biosynthesis, steroid biosynthesis, and cardenolide biosynthesis. The terpenoid backbone biosynthesis involves the mevalonate (MVA) pathway and 2-C-methyl-D-erythritol 4-phosphate (MEP) pathway. The steroid biosynthesis involves enzymes that convert acetyl-CoA to various sterols. The cardenolide biosynthesis stage involves enzymes that modify sterols to produce cardenolide compounds through hydroxylation, acetylation, and glycosylation reactions. Key enzymes are identified for each stage of the pathway.