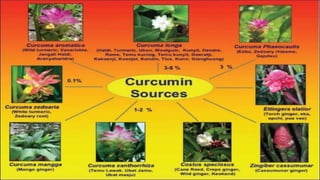
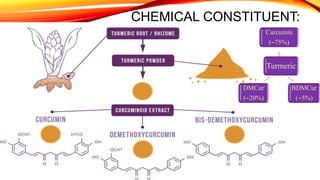
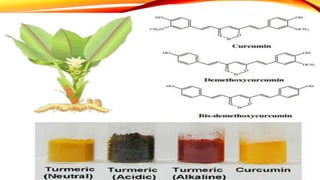
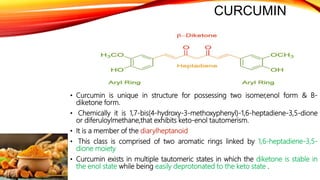
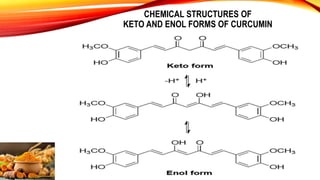
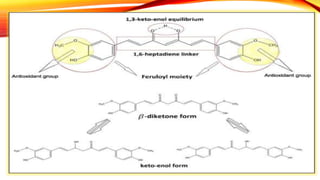
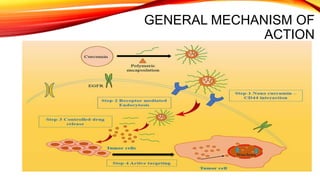
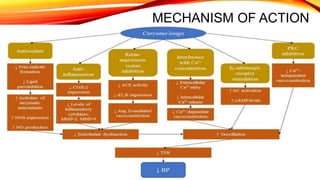
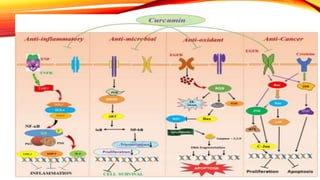
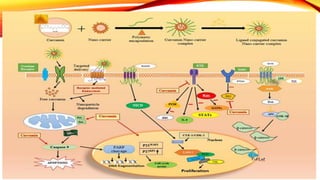
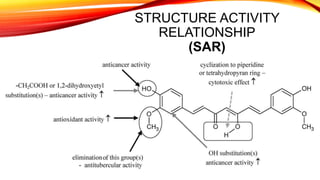
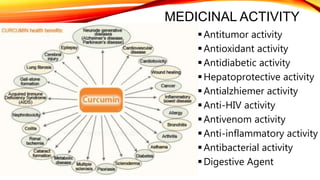
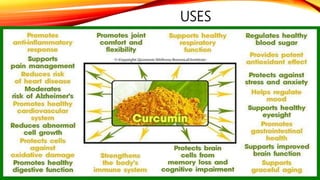
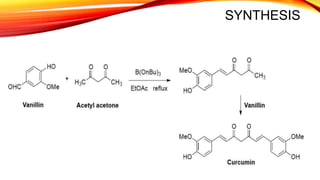
This document discusses curcumin, the active constituent of turmeric (Curcuma longa Linn.) that is used for its antitumor properties. It describes how curcumin is extracted from turmeric using a solvent extraction method. The key chemical constituents of turmeric include curcumin (~75%), demethoxycurcumin (~5%), and bisdemethoxycurcumin (~20%). Curcumin has a unique chemical structure that allows it to exist in both keto and enol forms. The document explores curcumin's mechanism of action and various structure-activity relationships, including how modifications to its aromatic rings and diketone chain can influence its biological activity.