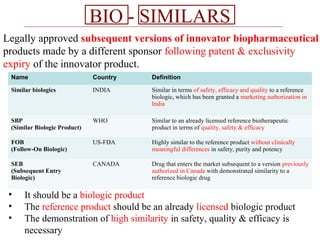
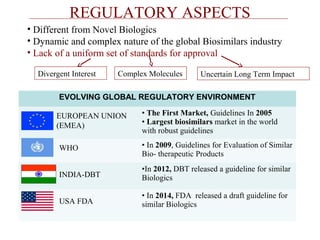
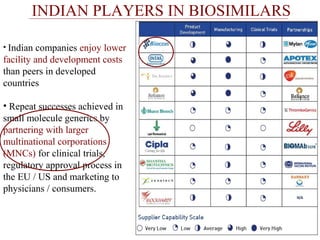
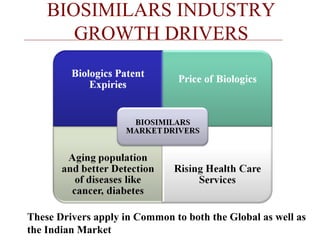
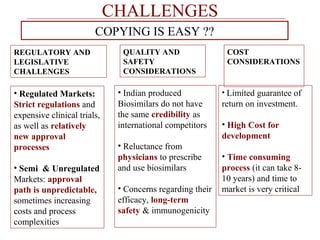
This document discusses biosimilars in India and the opportunities and challenges in the biosimilars industry in India. It defines biosimilars and provides an overview of the global and Indian biosimilars market and regulatory landscape. The key opportunities for India include providing affordable treatment options and commercial benefits from lower cost manufacturing. However, challenges include regulatory hurdles, concerns around quality and safety, high development costs, and physician reluctance to prescribe biosimilars.