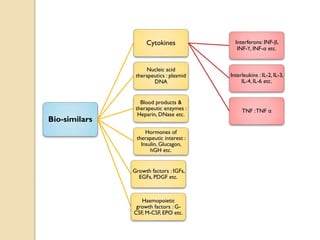
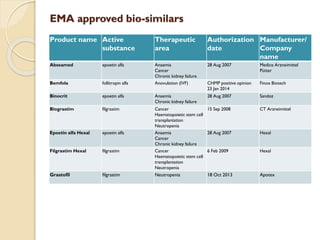
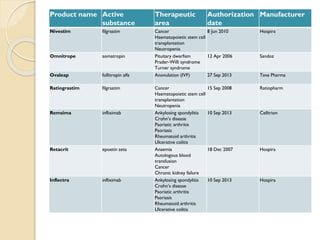
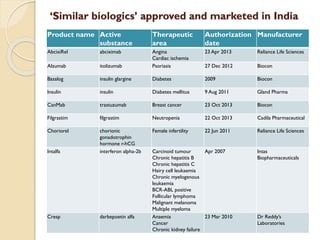
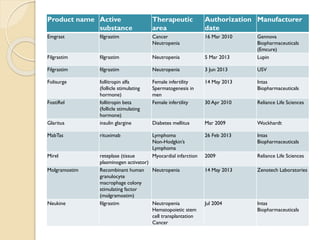
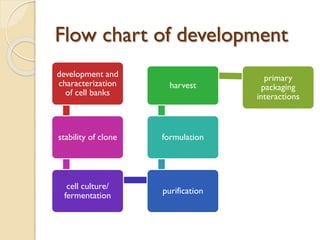
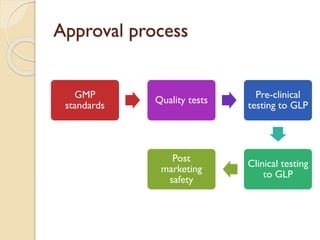
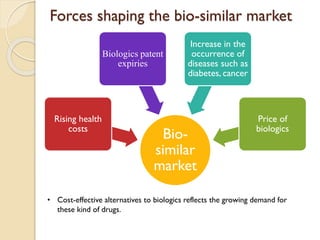
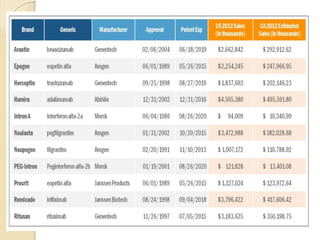
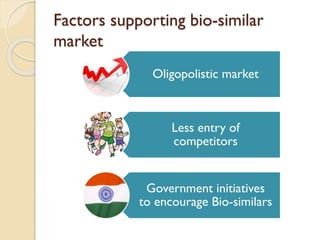
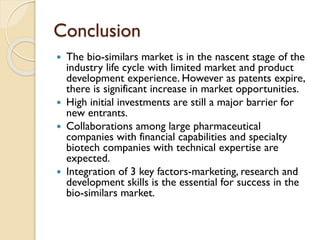
This document provides an overview of biosimilars in India. It discusses definitions of biosimilars according to various regulatory agencies like WHO, FDA, and EMA. It also covers the Indian regulatory guidelines and approval process for biosimilars. The document lists some examples of approved biosimilars in Europe and India and the companies that manufacture them. It describes the development and approval process for biosimilars in India and notes they must demonstrate similarity to a reference product through characterization studies and less testing than the originator product.