Embed presentation
Downloaded 26 times
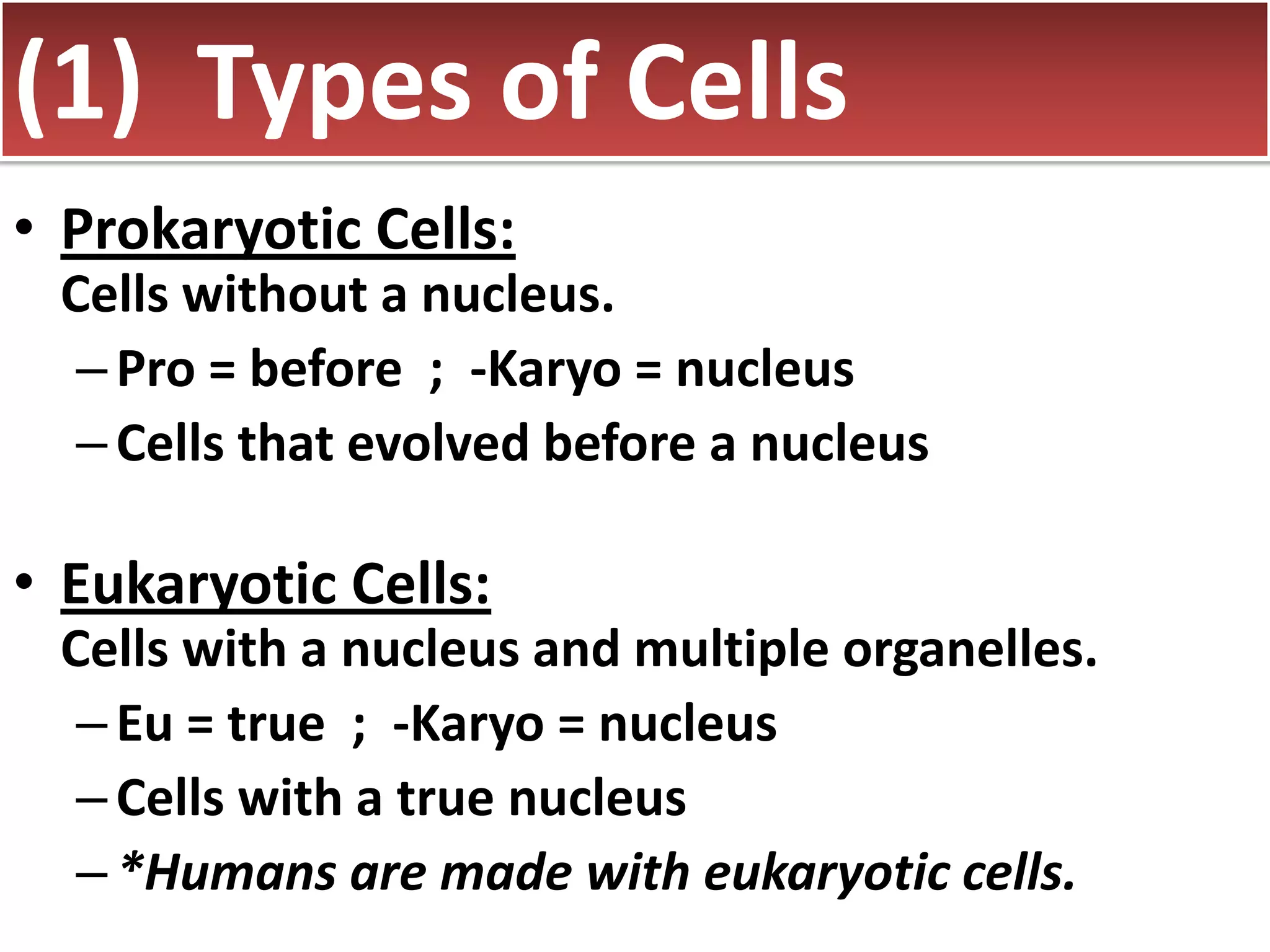

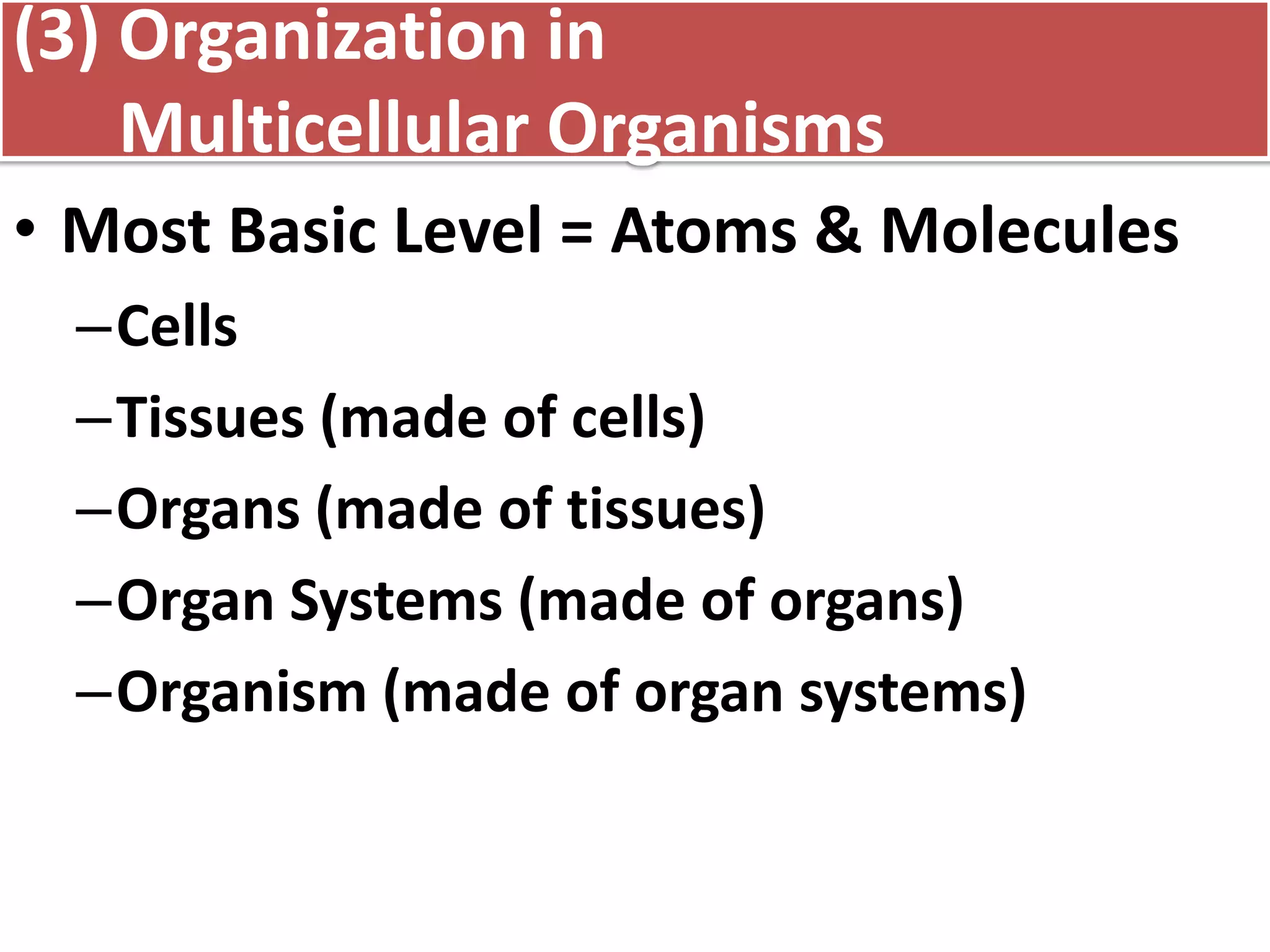
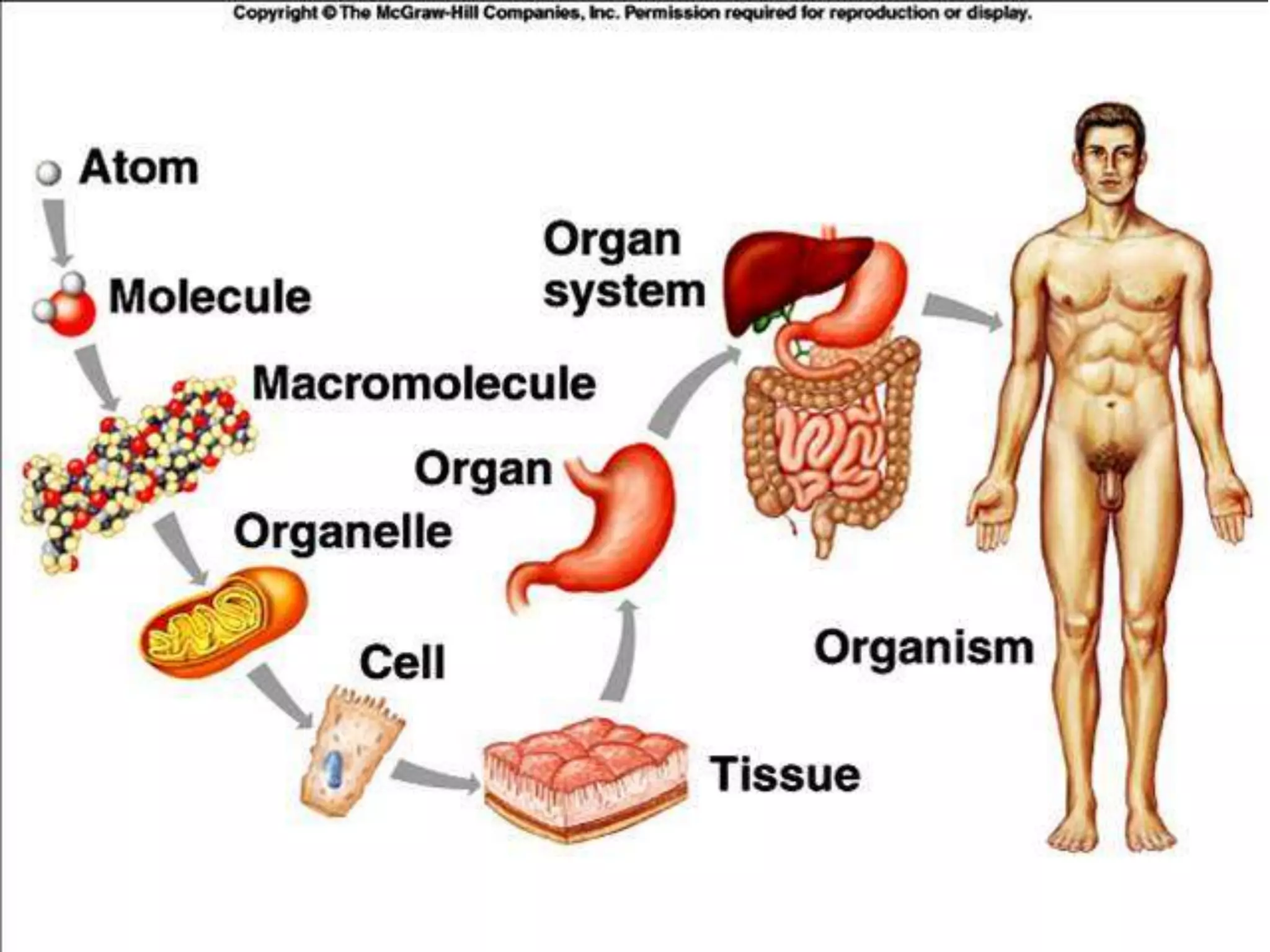
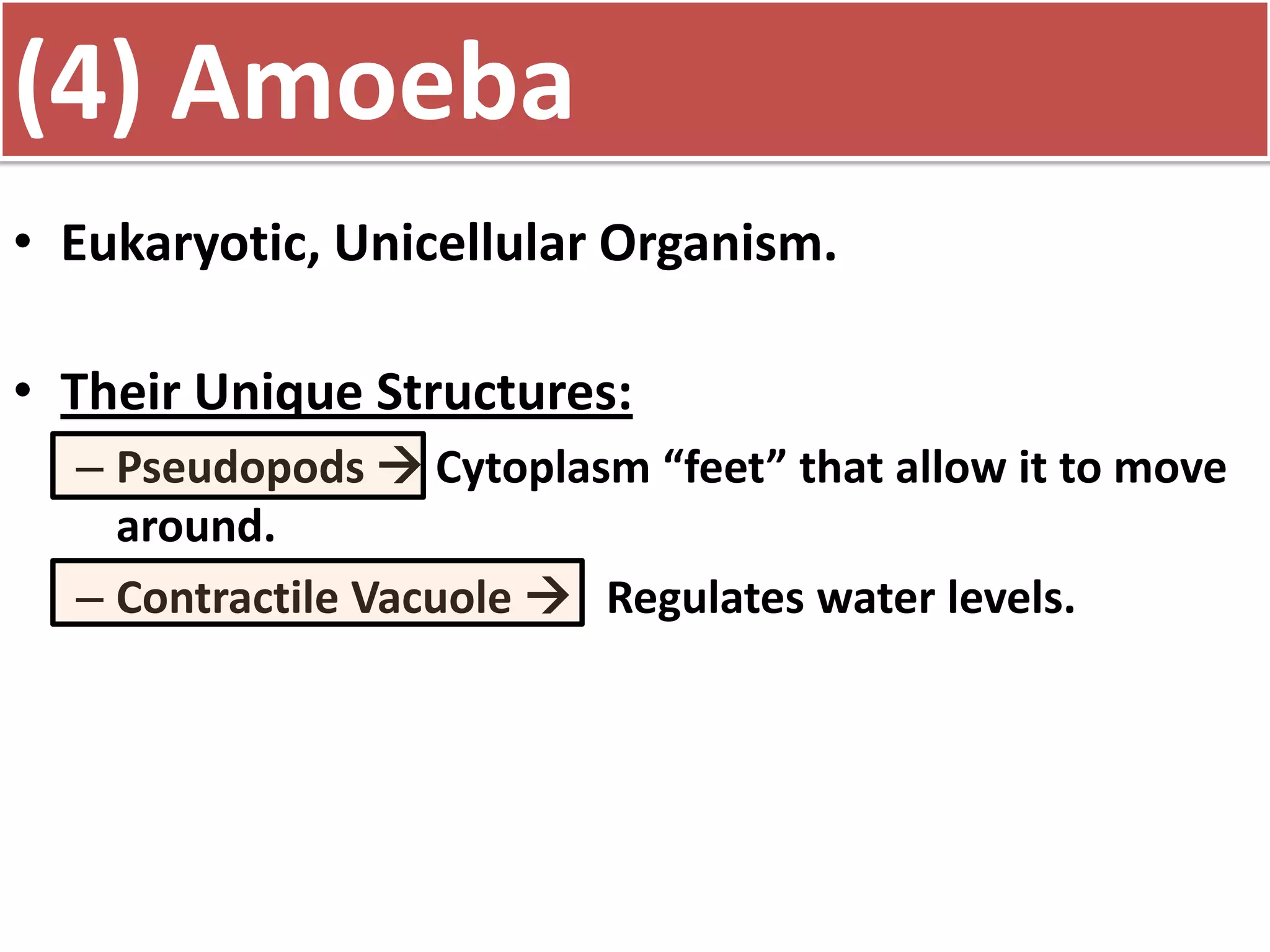

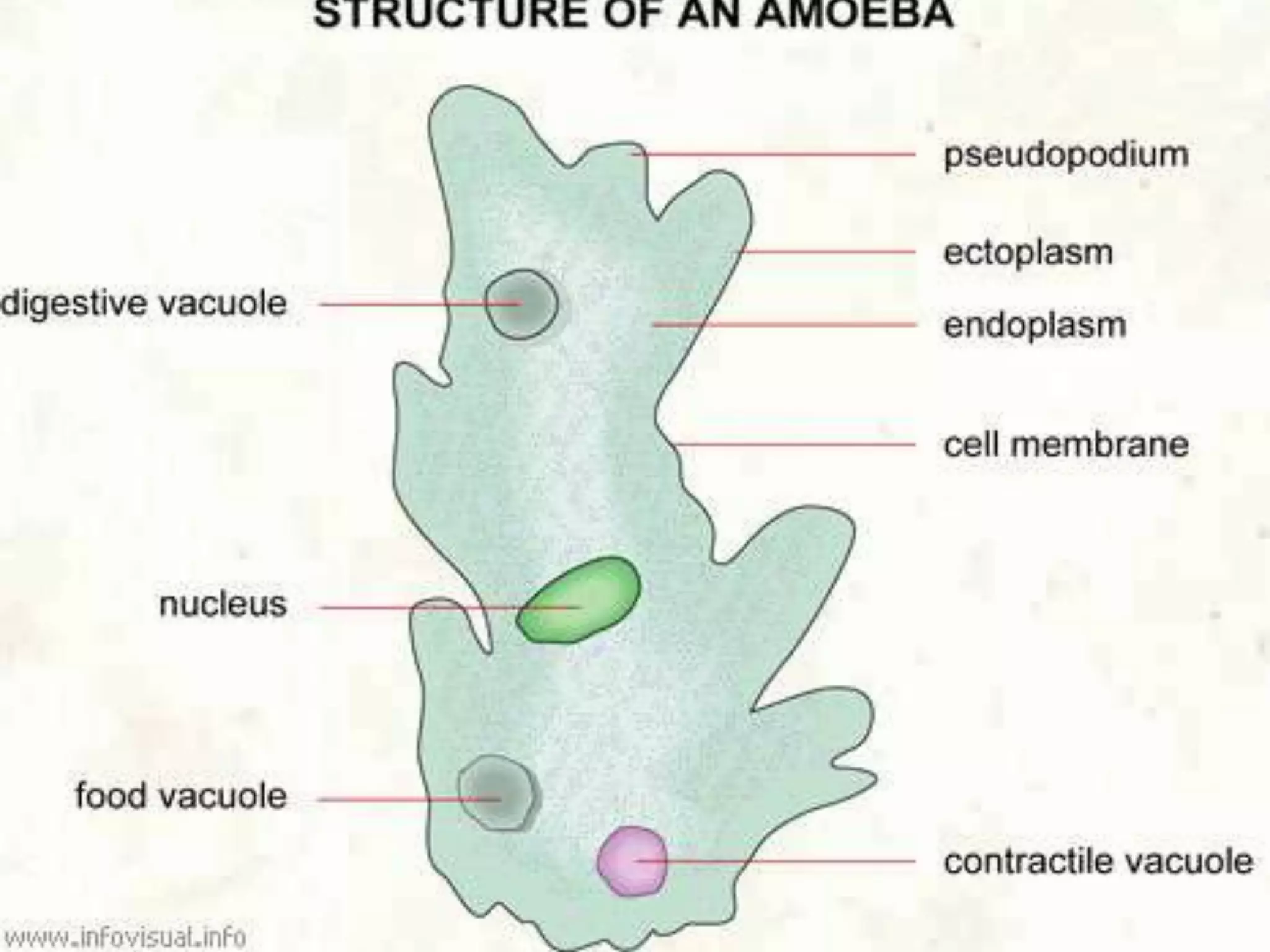
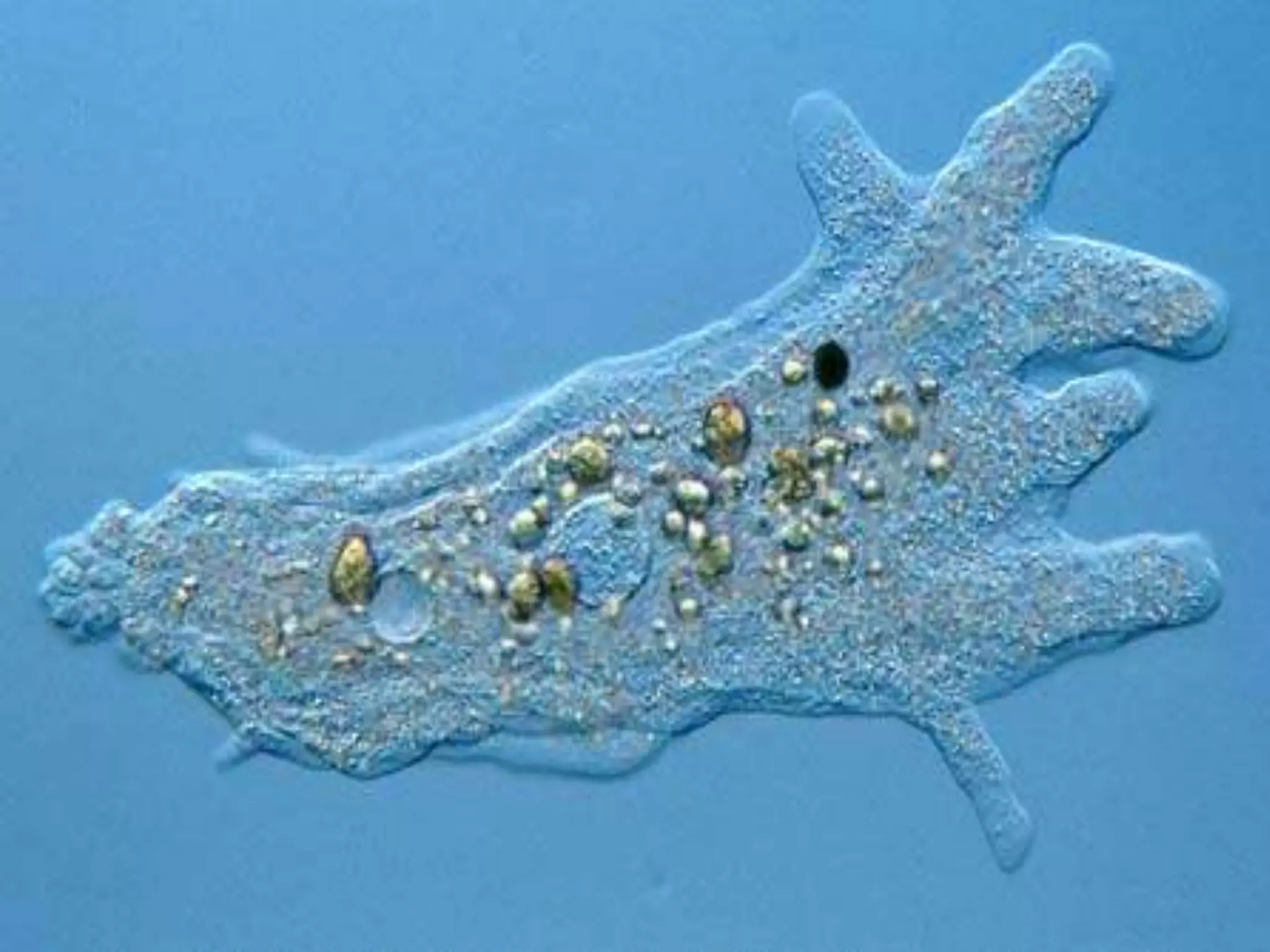
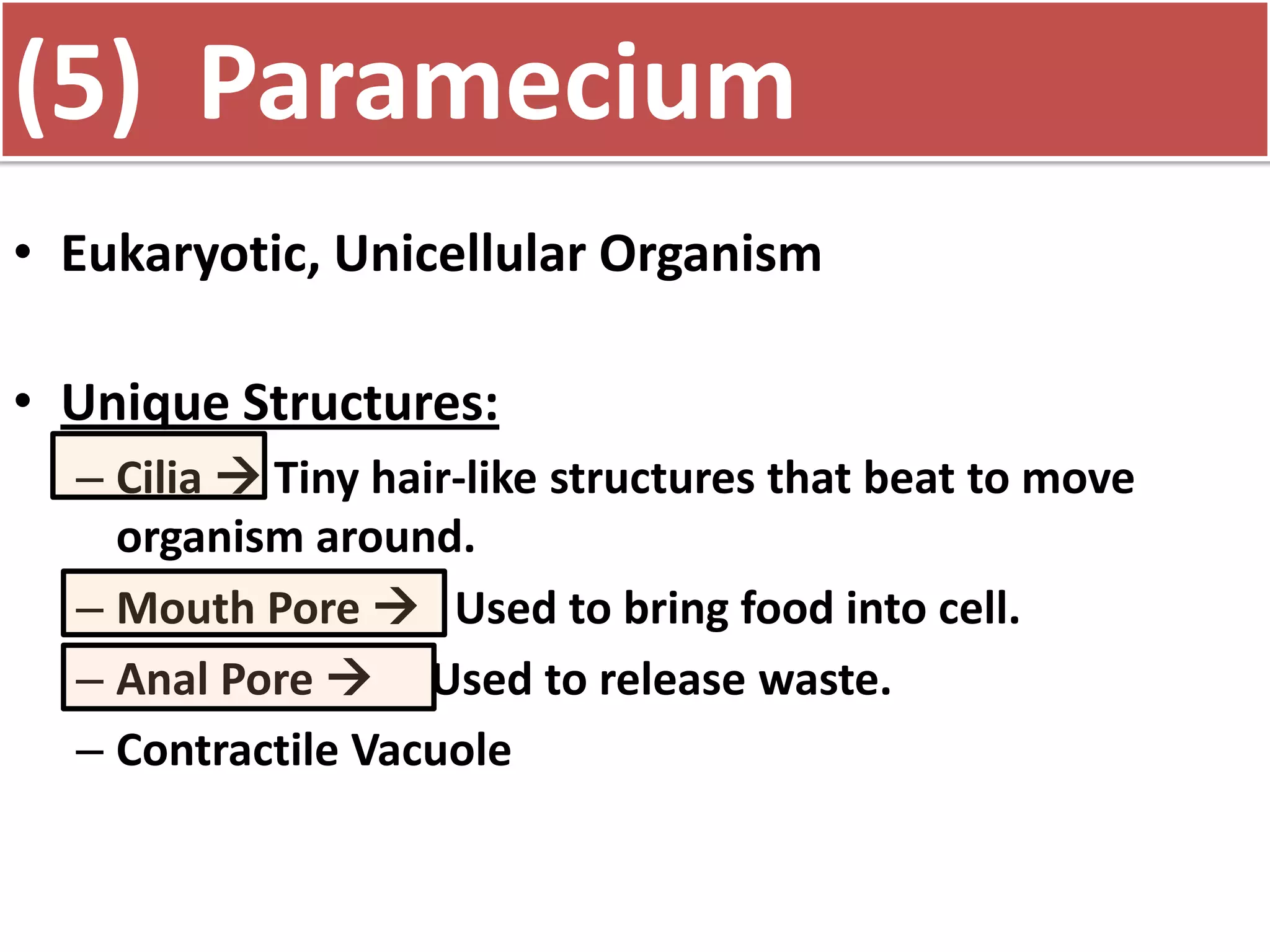
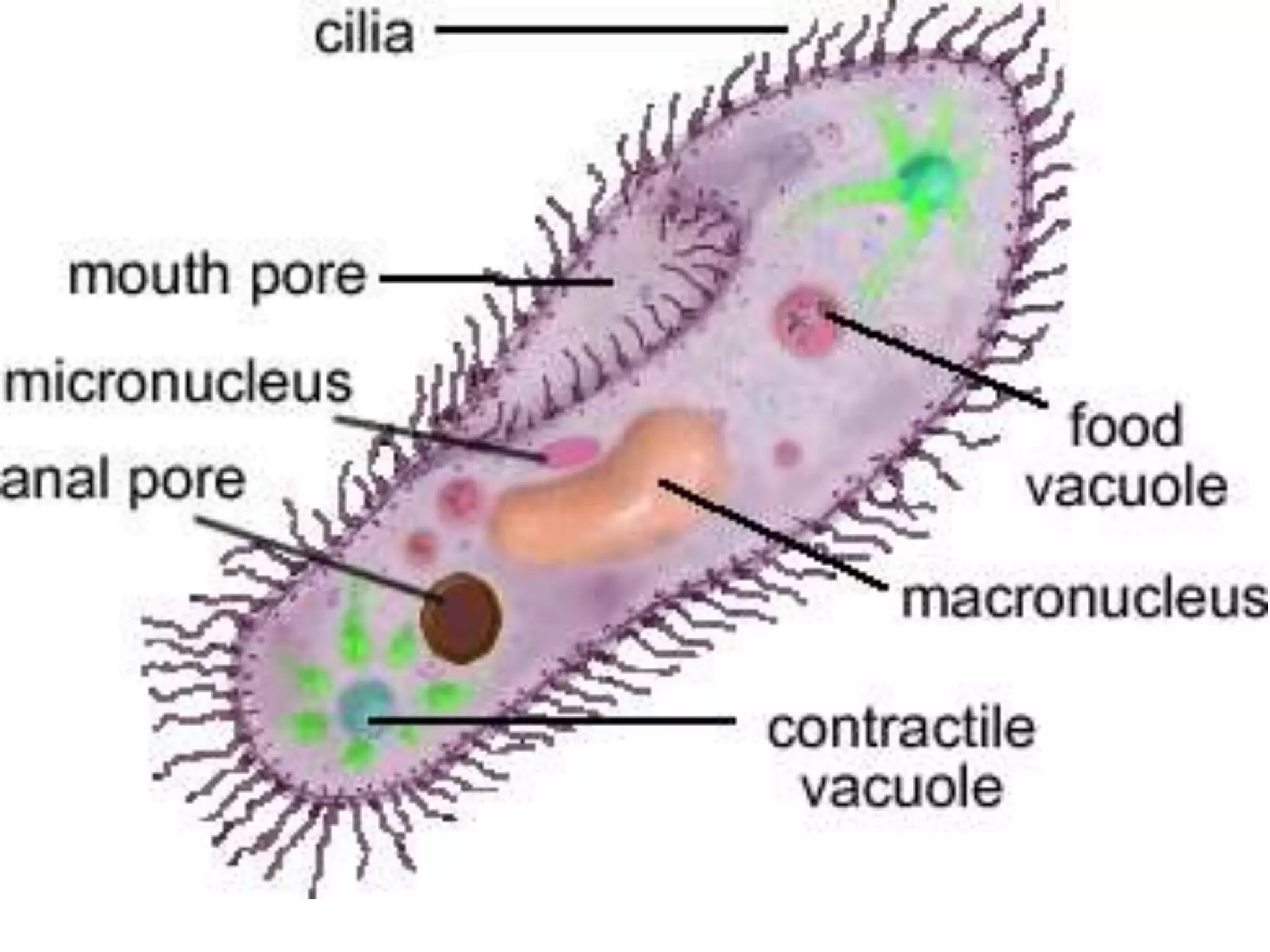
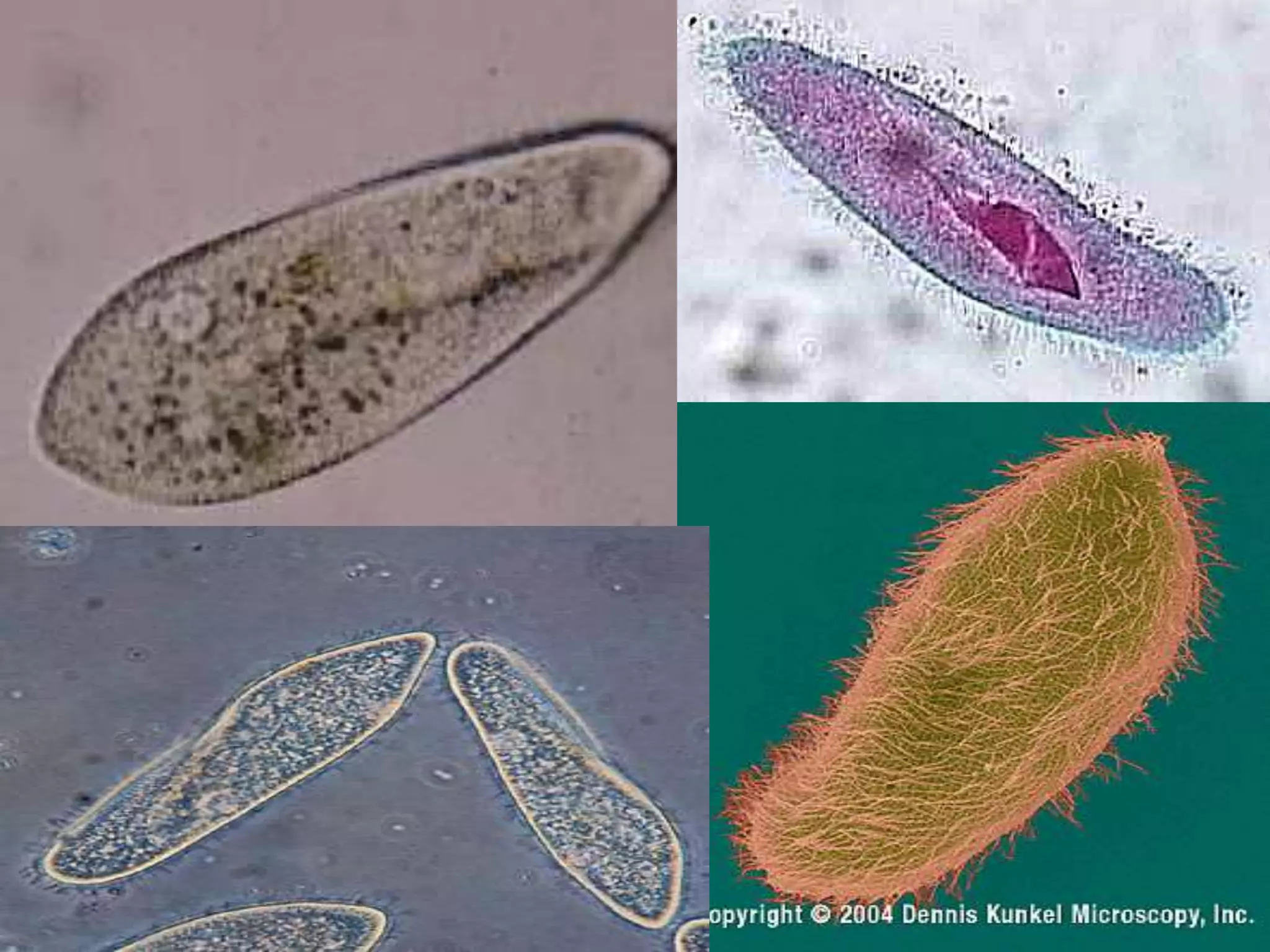
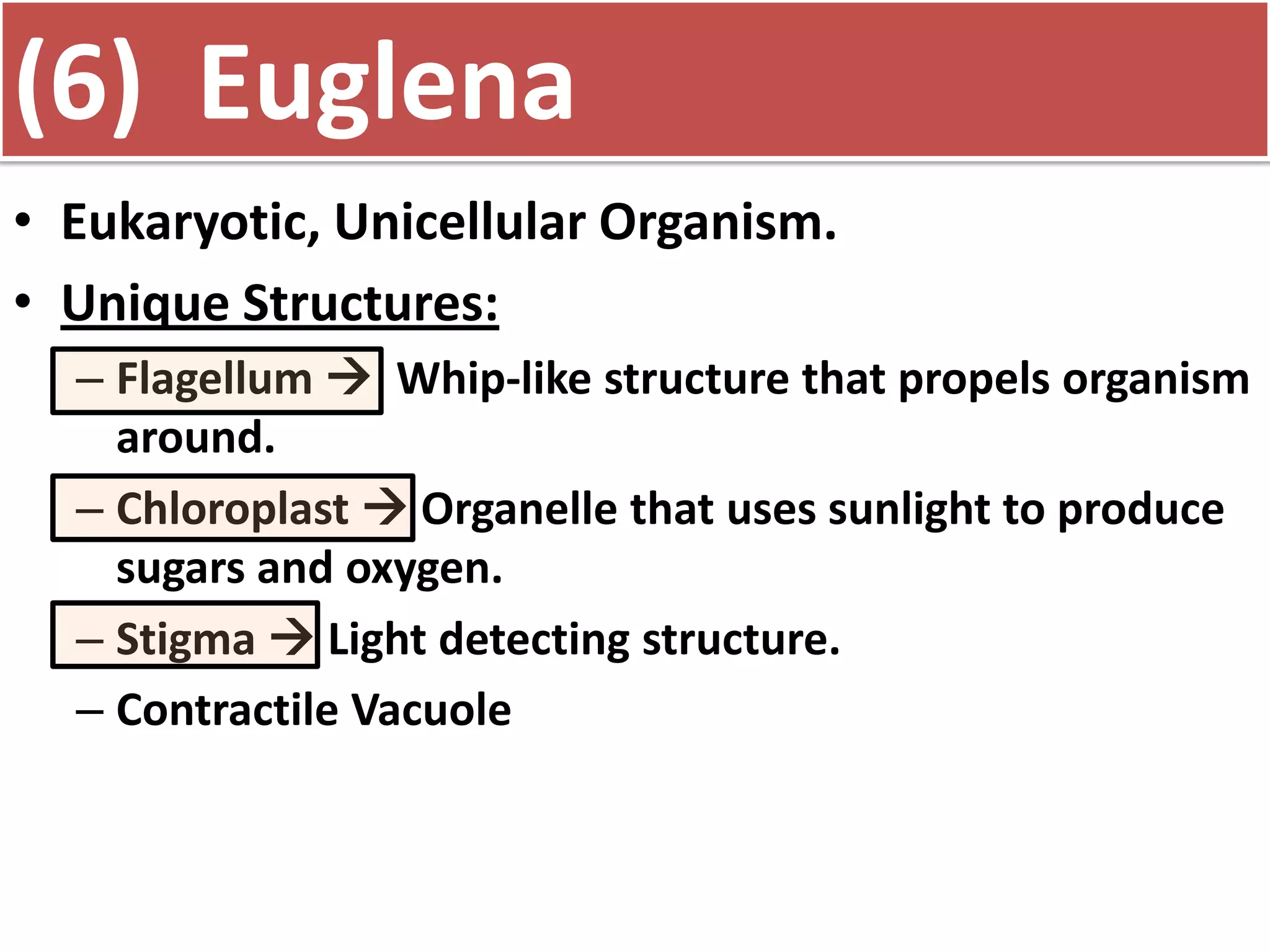
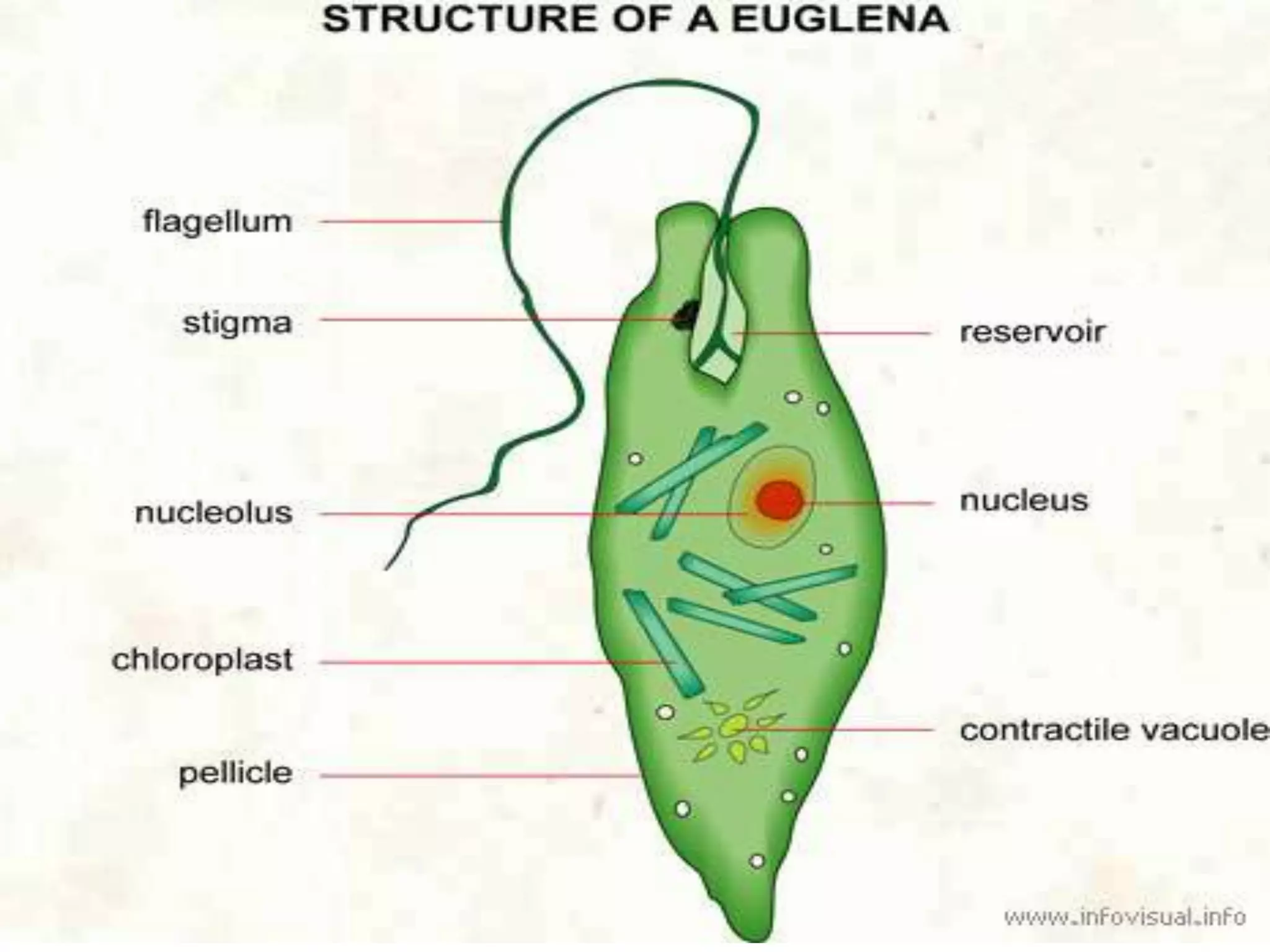
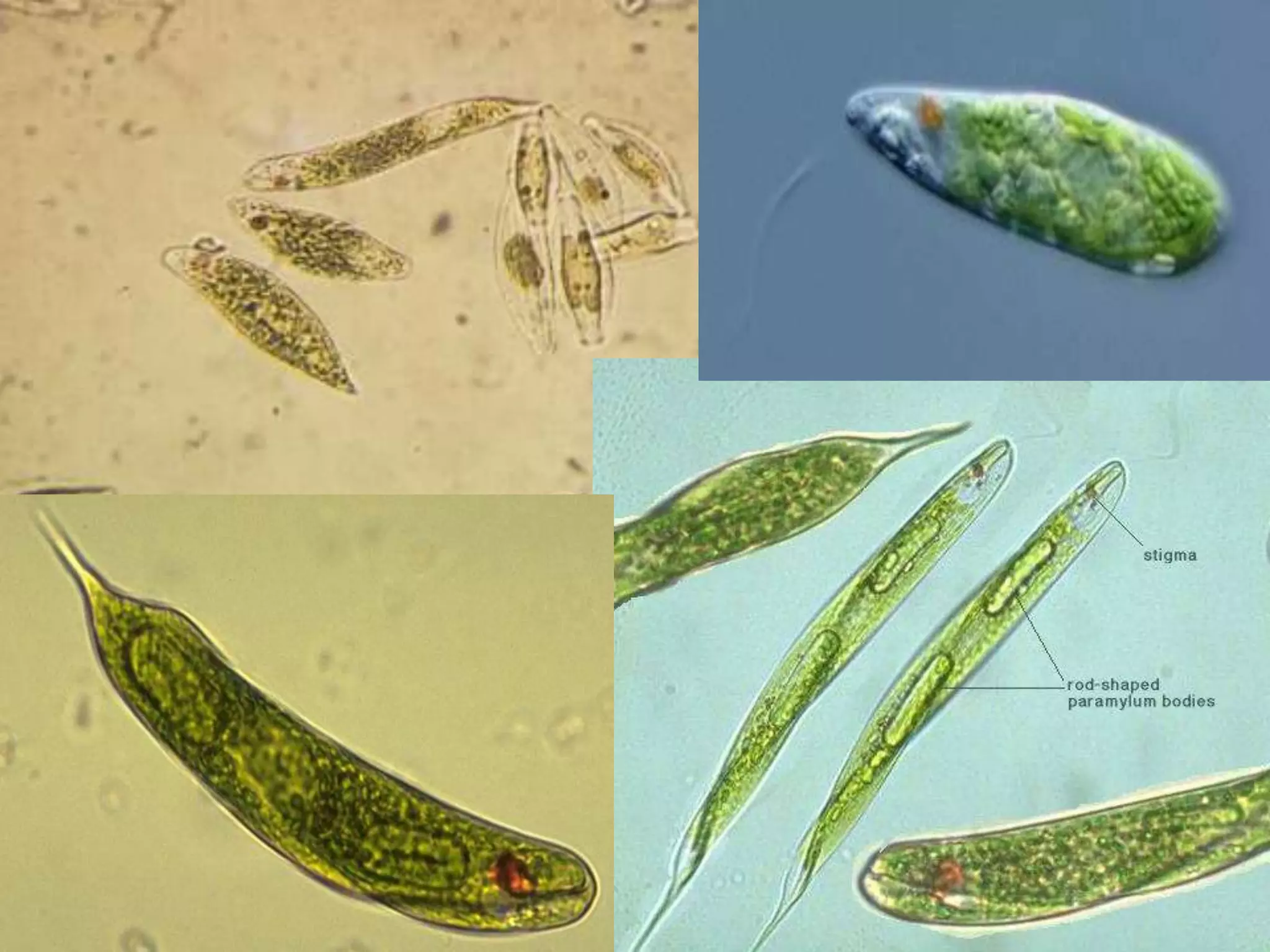
This document discusses different types of cells and organisms. It covers prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, unicellular and multicellular organisms, and the organization of cells into tissues, organs, organ systems and organisms. Specific unicellular eukaryotes are also described, including amoebas, paramecium and euglena. Amoebas move using pseudopods and regulate water levels using a contractile vacuole. Paramecium uses cilia to move and has a mouth and anal pore. Euglena uses a flagellum to move and contains chloroplasts to photosynthesize.














