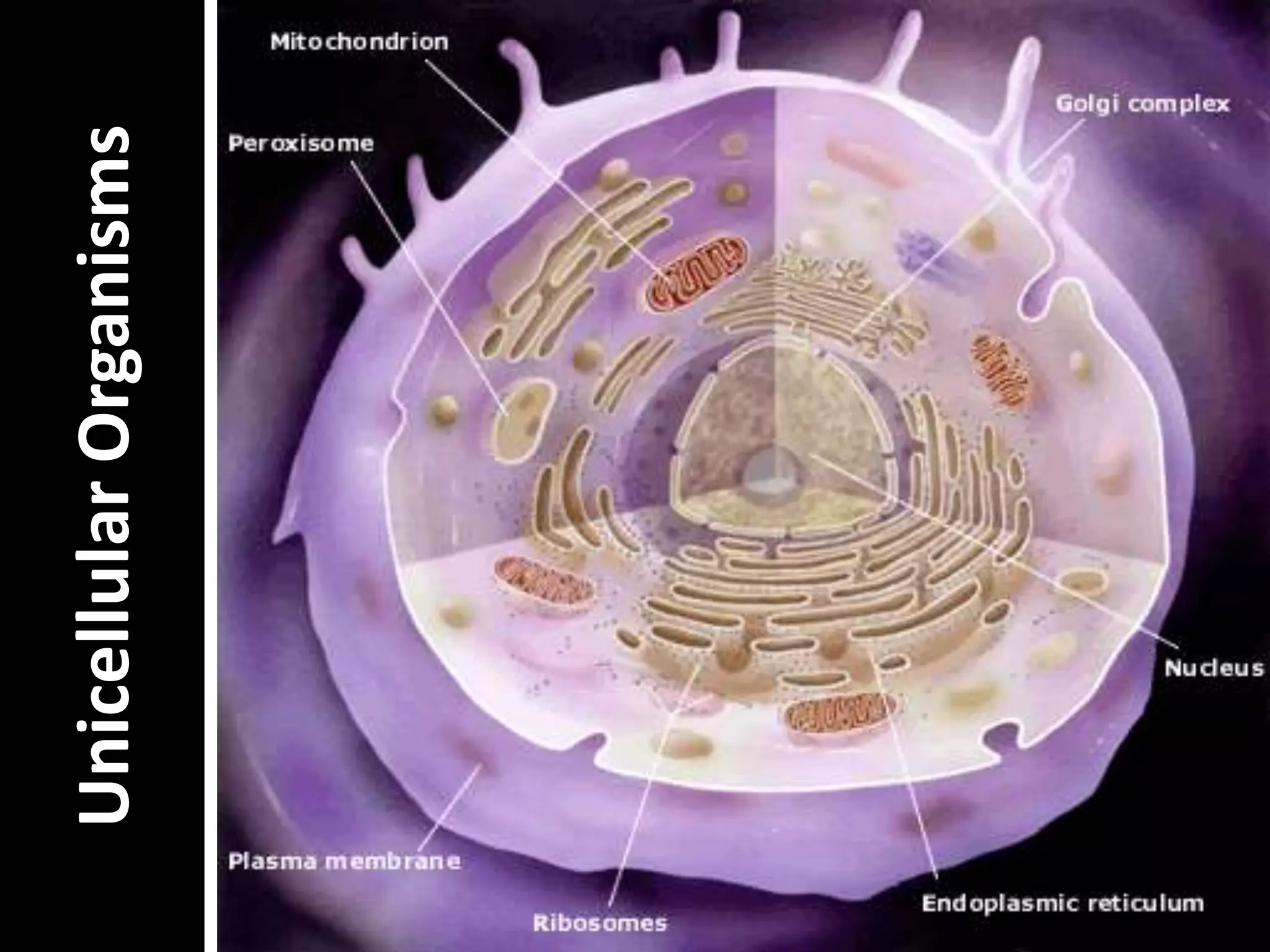
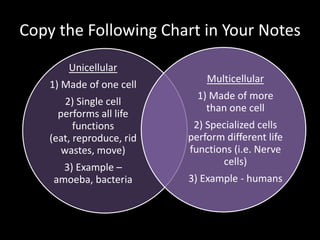
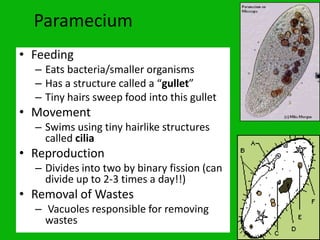
The document discusses unicellular and multicellular organisms. It defines unicellular organisms as made of only one cell and able to perform all life functions like eating, moving, reproducing, and eliminating waste on their own. Multicellular organisms are made of more than one cell and have specialized cell types that each perform different life functions. Examples of unicellular organisms include amoebas and bacteria, while humans and other animals are multicellular. The document provides details on how specific unicellular organisms like amoebas, paramecium, and euglena eat, move, reproduce, and eliminate waste.