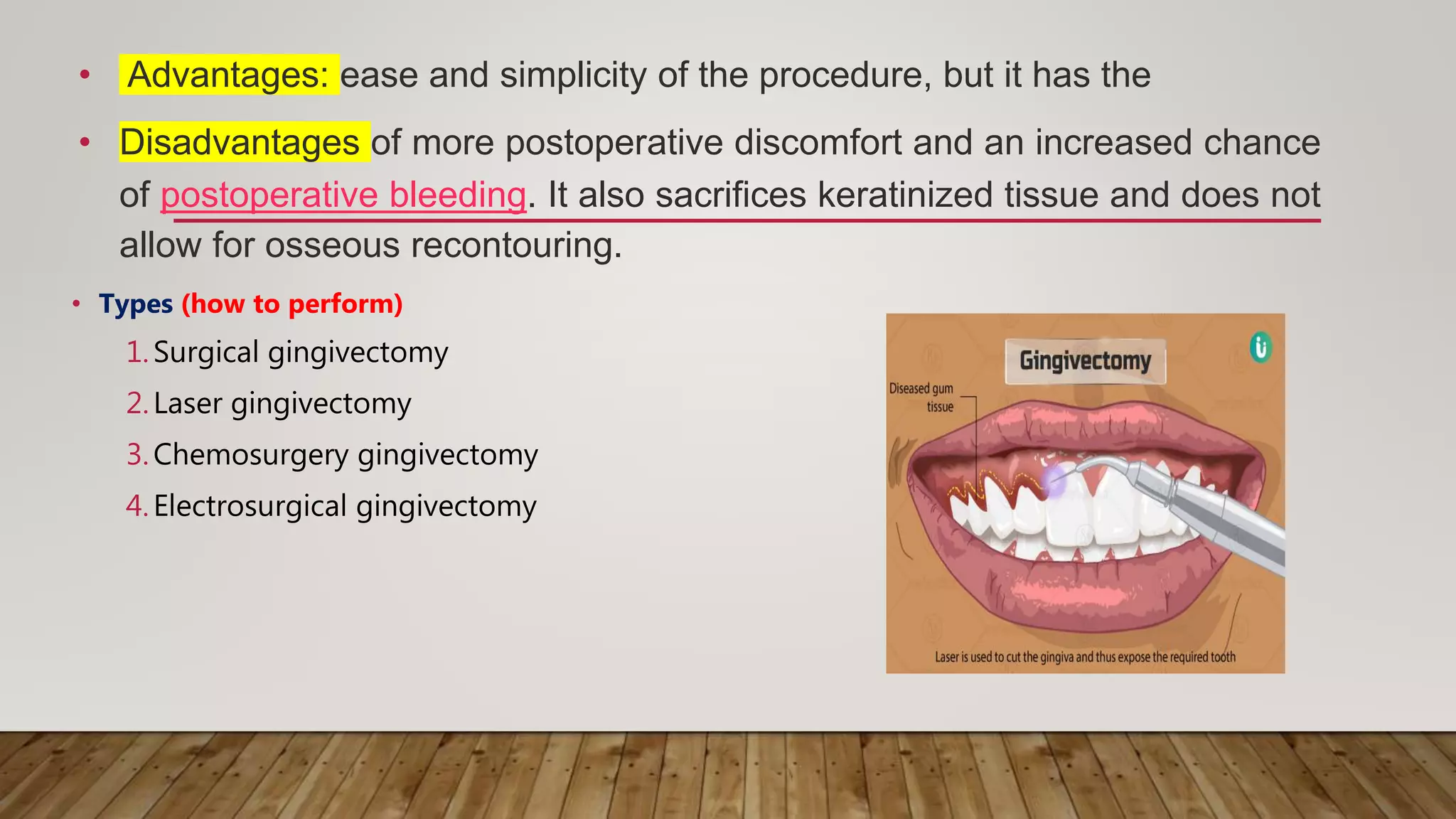
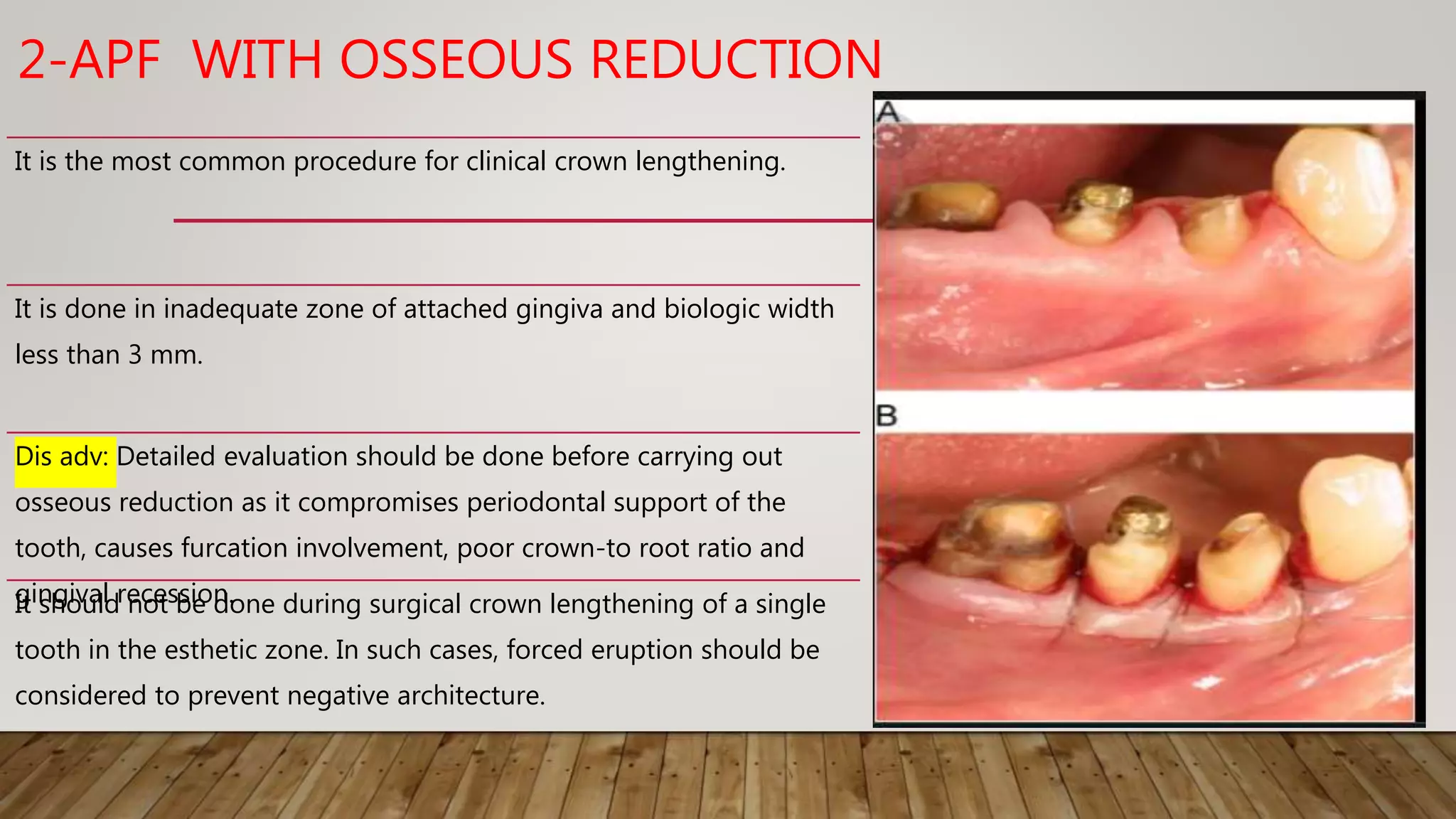
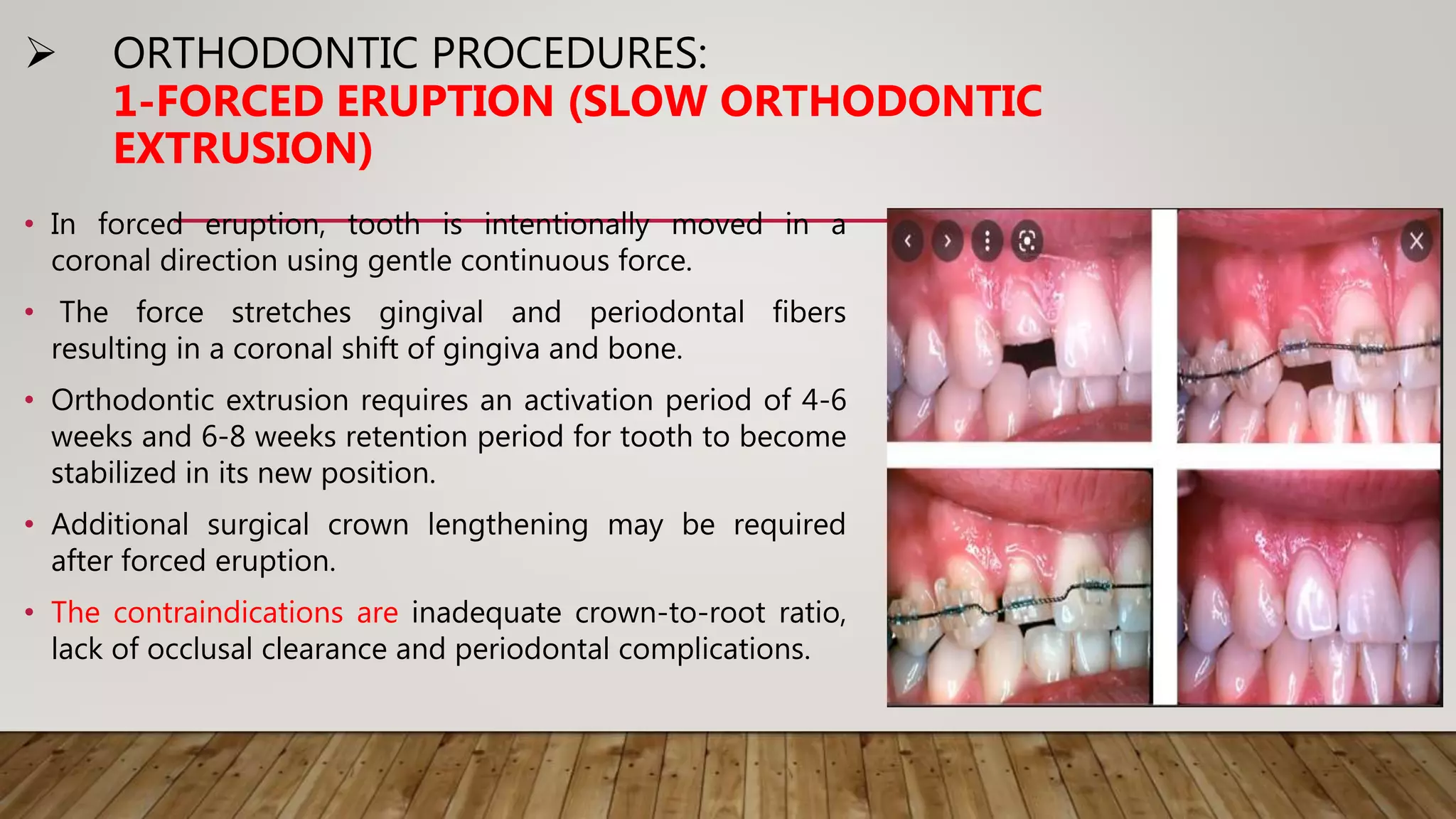
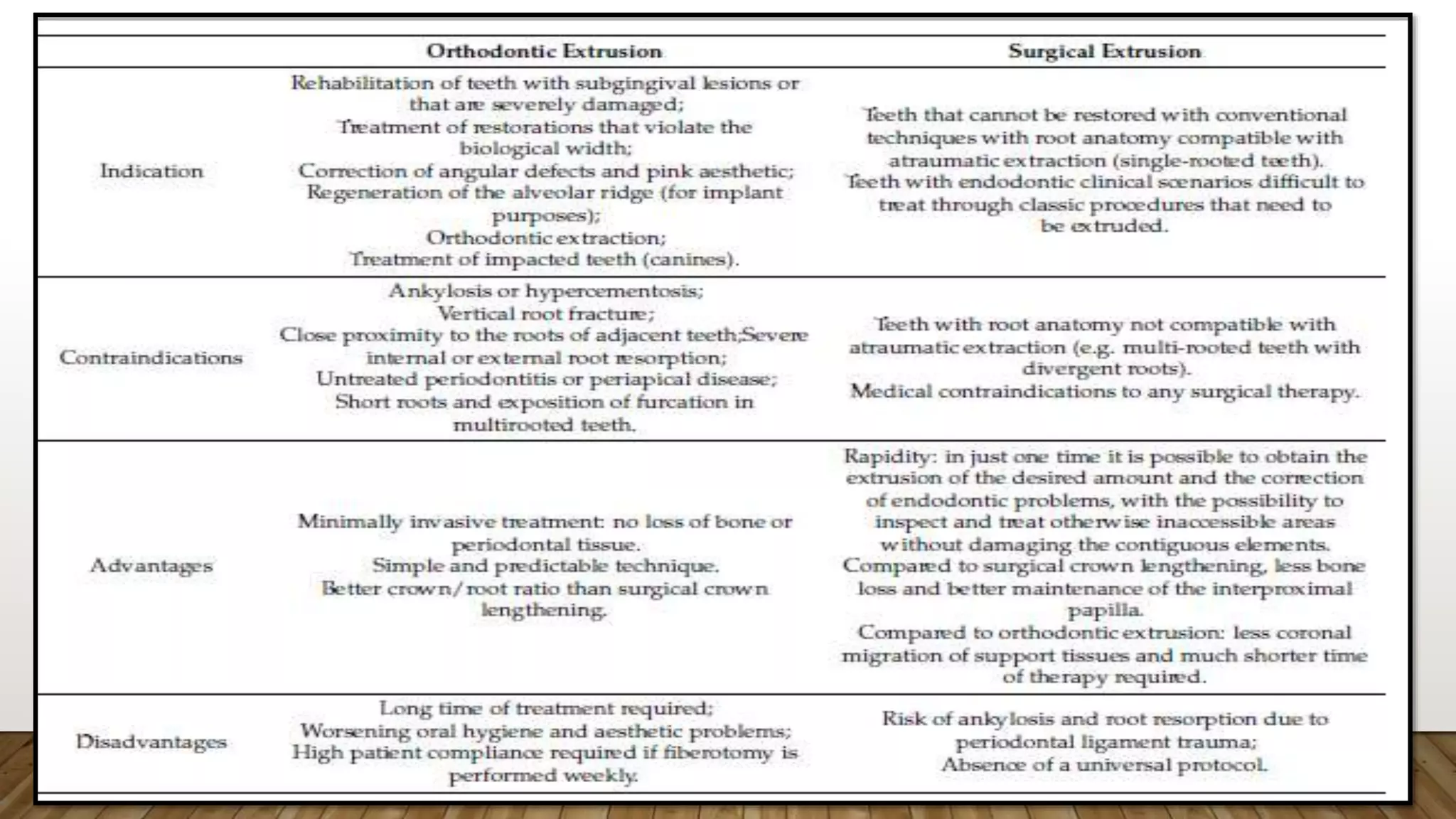
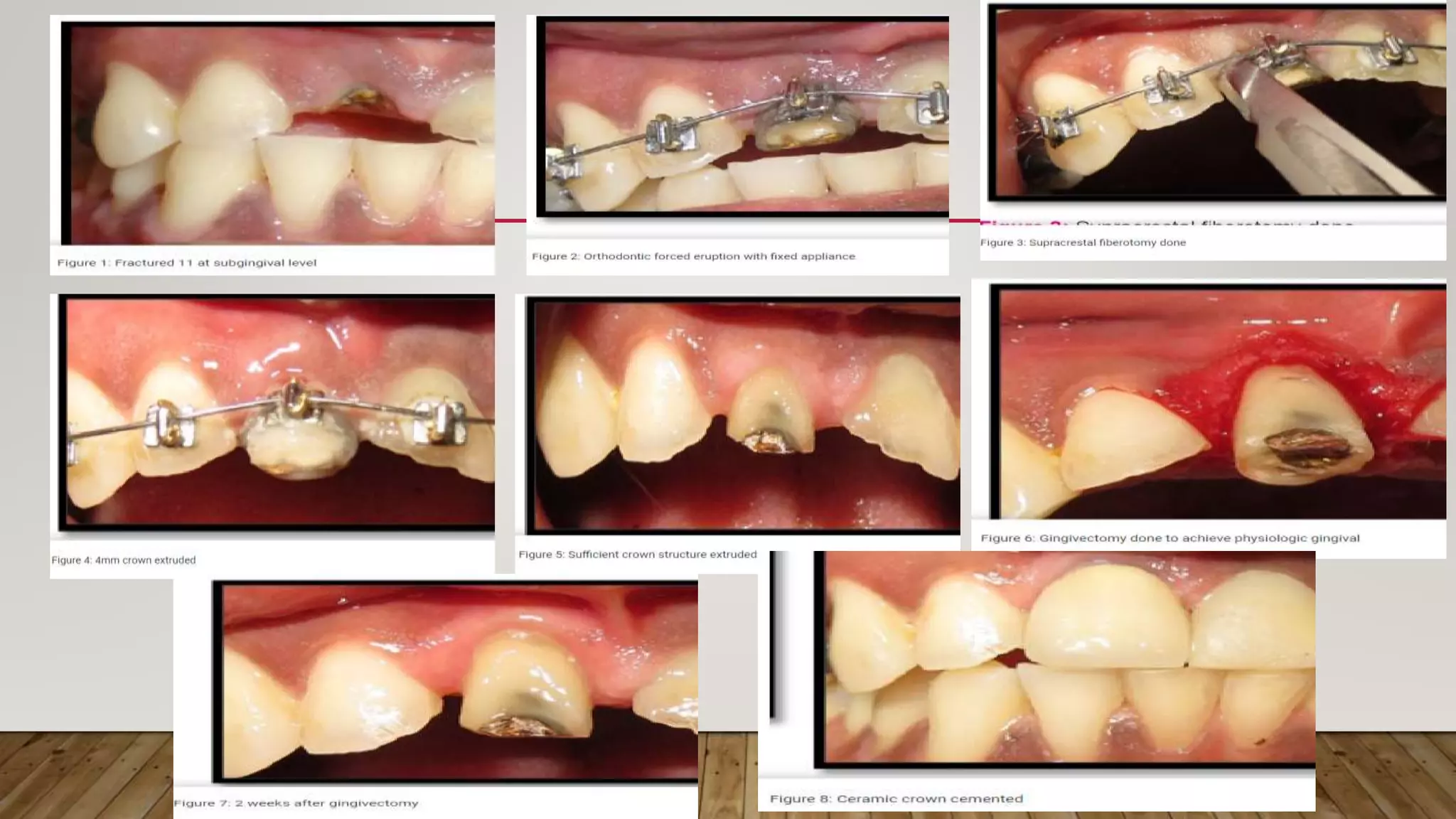
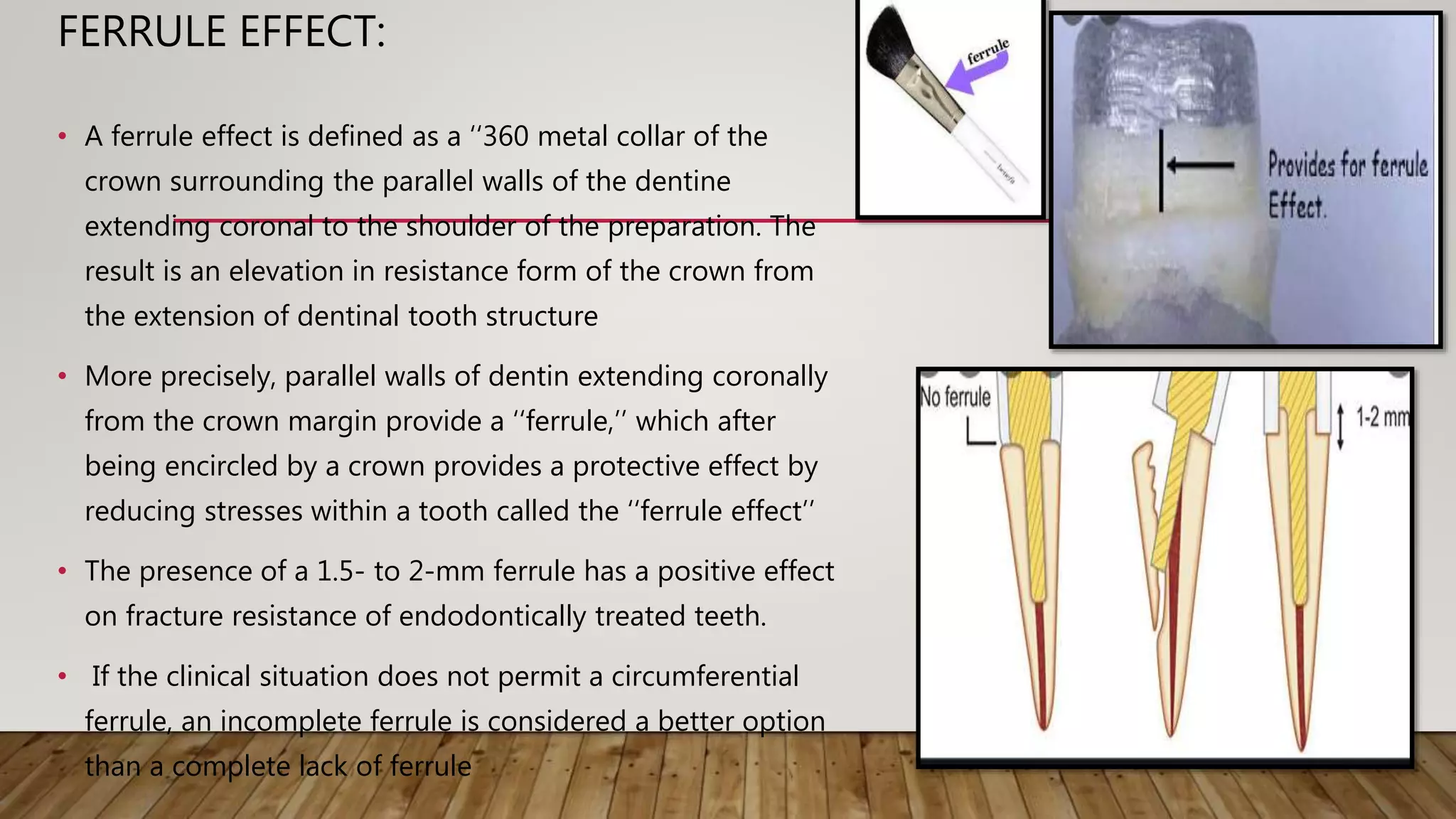
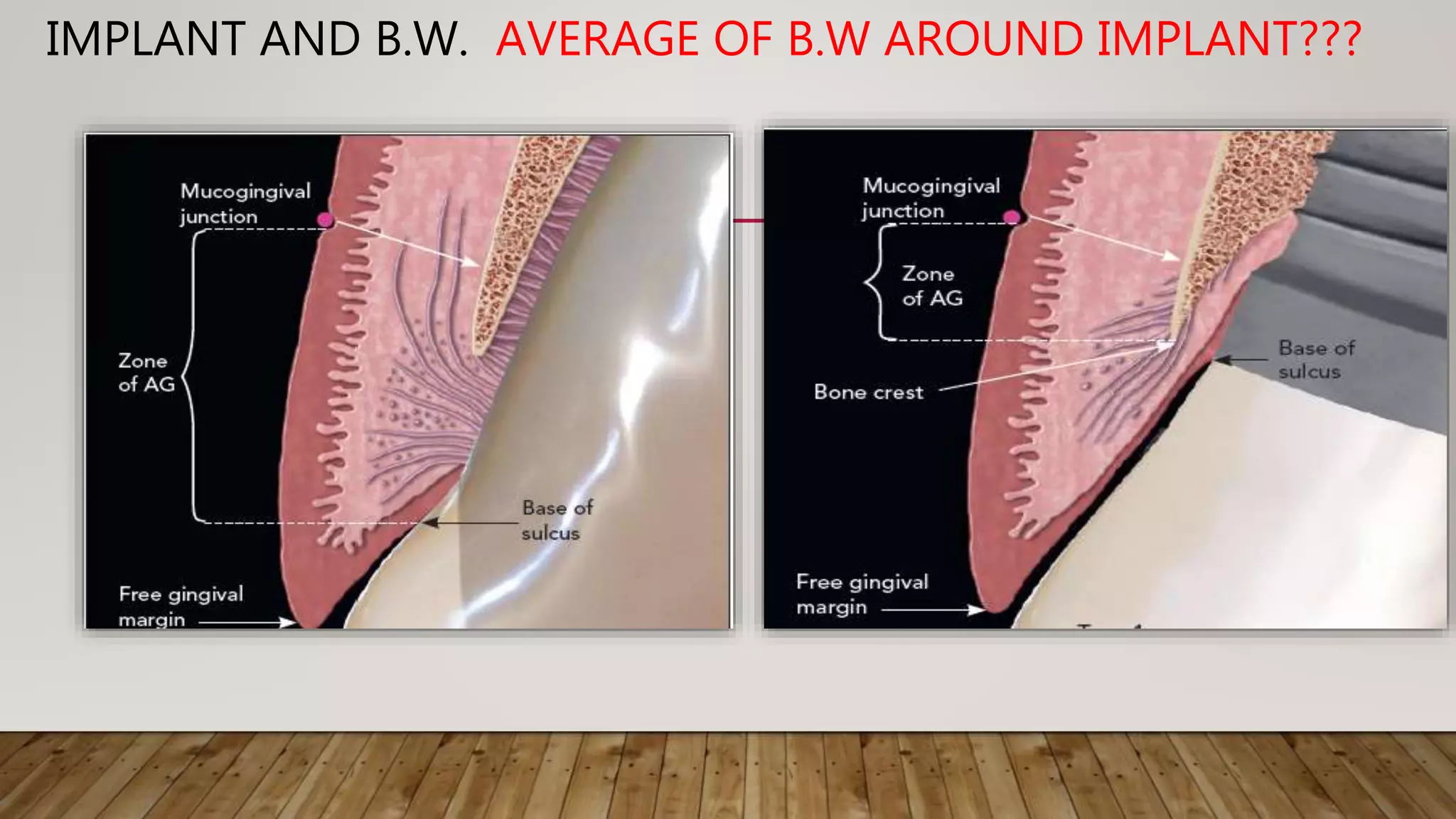
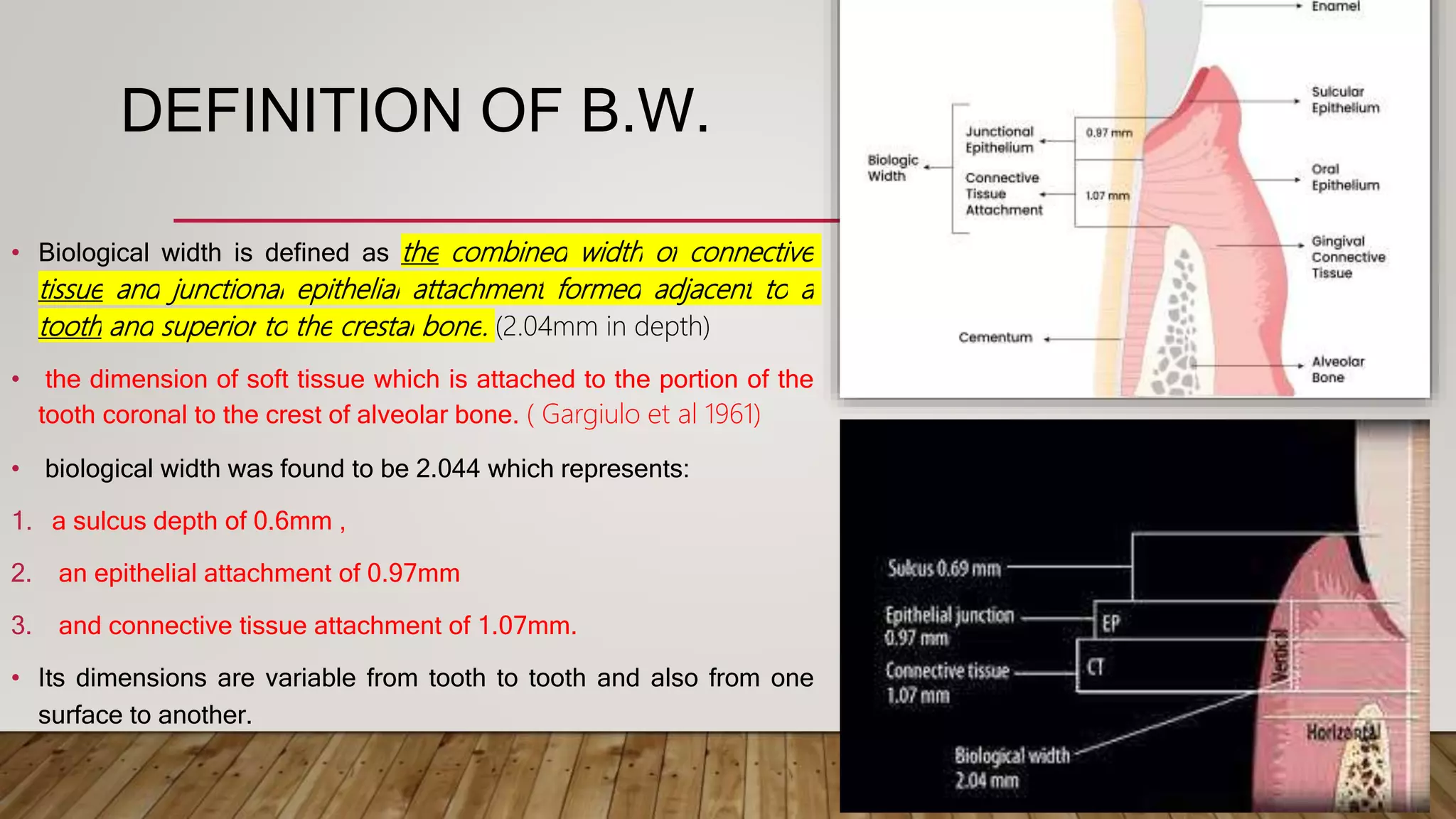
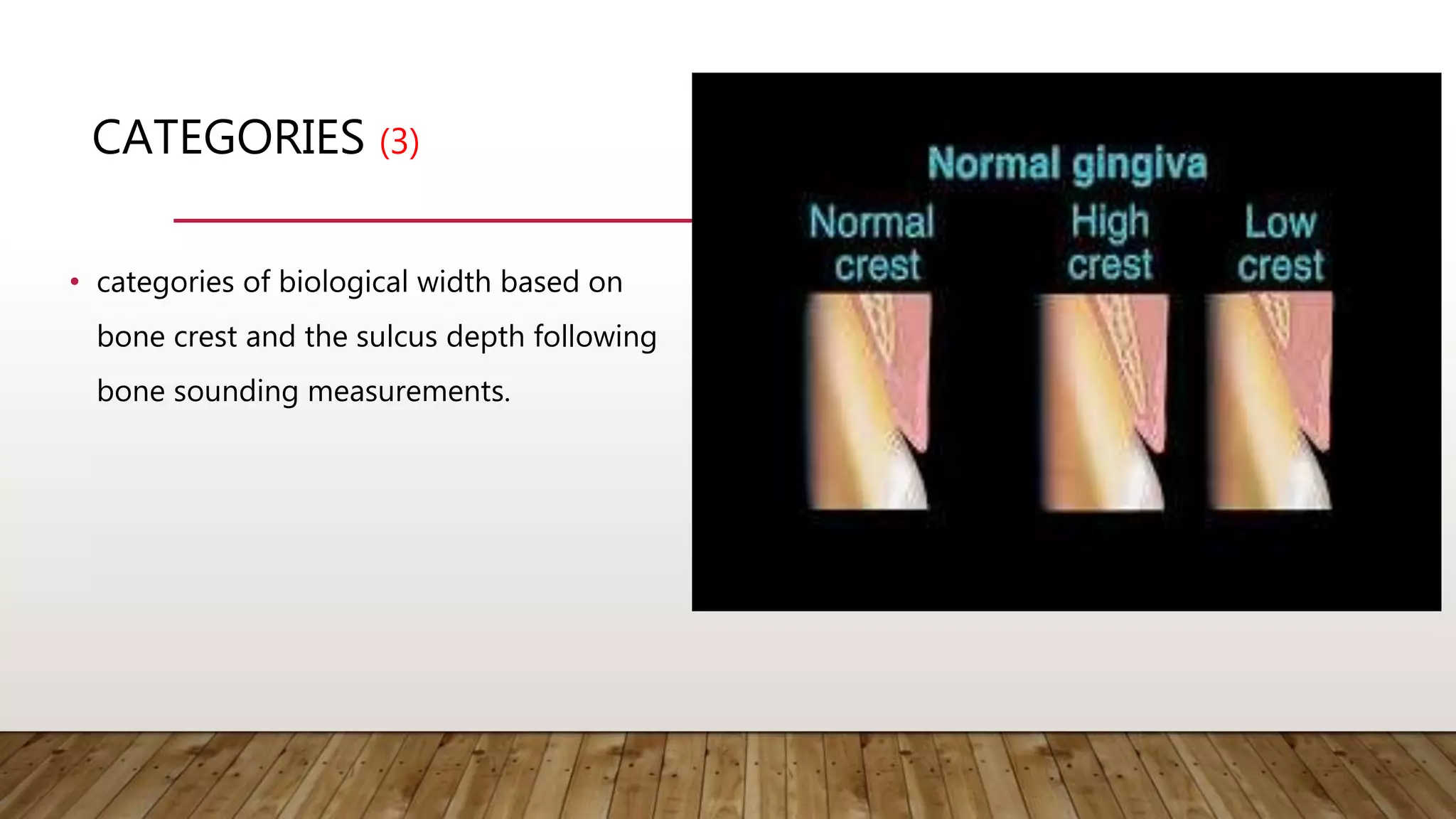
This document discusses biological width, which refers to the combined width of connective tissue and epithelial attachment adjacent to a tooth above the alveolar bone crest. The biological width was found to be approximately 2.04mm on average. Maintaining the biological width is important for periodontal health. There are several factors that can impact the biological width, such as the location and finish of restorative margins, gingival displacement techniques, crown contours, and subgingival debris. Violations of the biological width can be evaluated clinically and radiographically. Various techniques exist to correct biological width violations, including surgical crown lengthening procedures and orthodontic extrusion methods.


























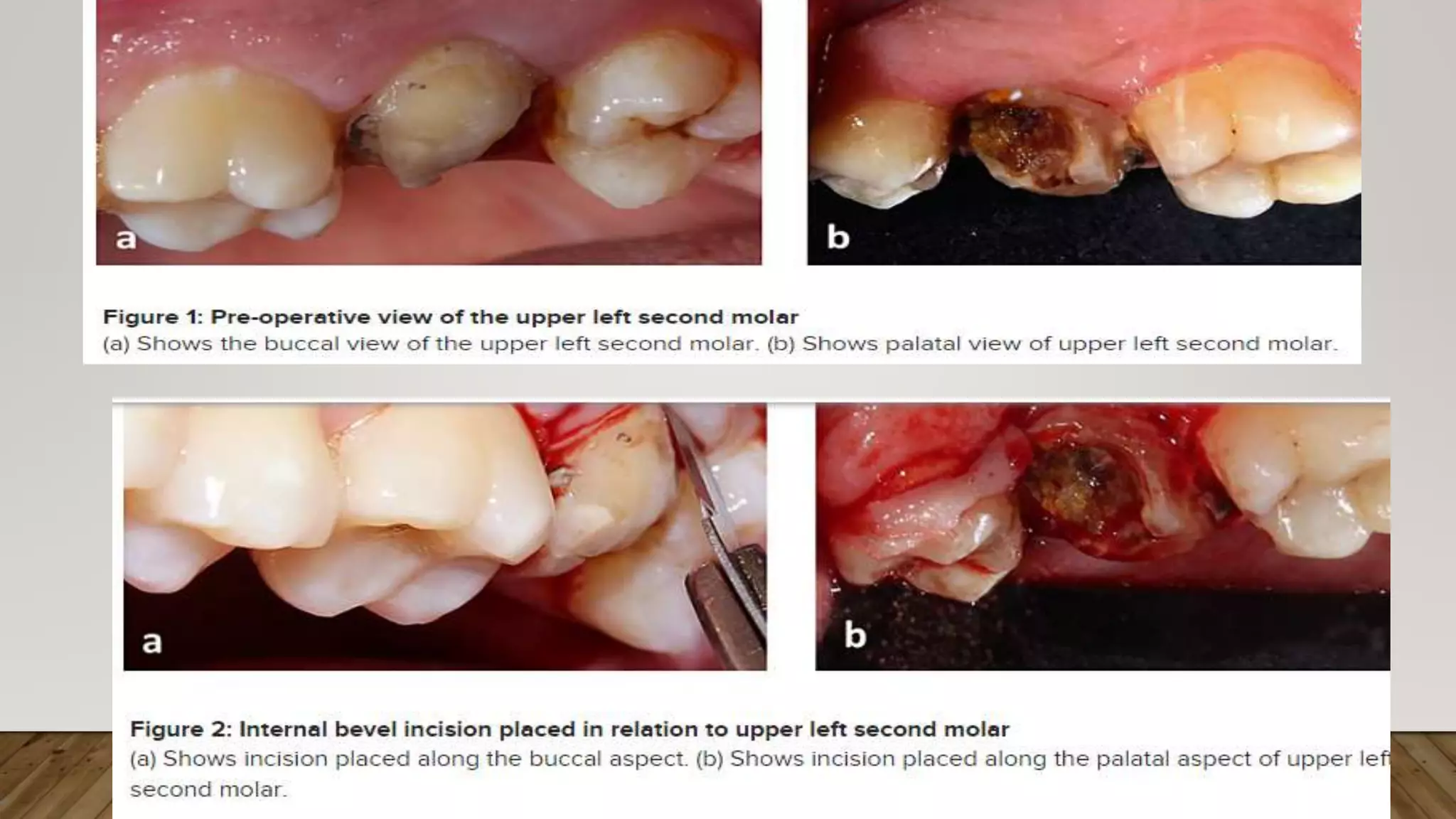
![The most apical point of the gingival sulcus was
assessed by probing [Figure 1].
To highlight the soft tissue structures on the radiograph, the auxiliary elements used were
gutta percha and lead foil because of their opaque nature. After probing, gutta percha was cut
to the sulcus depth [Figure 2, 3],
The lead foil was cut appropriately [Figure 4]
and then positioned over the gingival surface,
aligned with the long axis of the tooth.
The paralleling device was placed in such a way that
the film was positioned on the lateral vestibule
When the patient fixes teeth on the bite block fig 5
The radiographs thus obtained were digitized using
a scanner fig 6. The images were imported to
Adobe Photoshop CS2.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologicalwidth-220205091054/75/Biological-width-30-2048.jpg)