1. Biological evolution can be examined through fossils and dating techniques like relative dating and absolute dating.
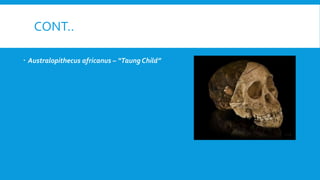
2. Early hominins like Australopithecus africanus had traits of both humans and apes and evidence shows they could walk upright but were also adapted for climbing.
3. Later species in the genus Homo include Homo habilis, Homo erectus, and Homo floresiensis and archaic humans like Neanderthals, Denisovans, and Cro-Magnon that were ancestral to modern humans.