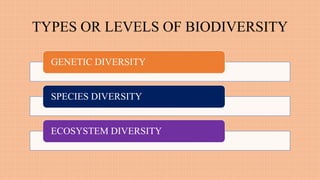
Biodiversity, defined by E.O. Wilson in 1985, refers to the variety and variability of life forms within different ecosystems and is essential for ecological processes, human survival, and agricultural productivity. Different levels of biodiversity include genetic, species, and ecosystem diversity, each playing a crucial role in maintaining stable environments. However, biodiversity faces significant threats from habitat destruction, poaching, man-wildlife conflicts, and pollution, resulting in numerous endangered species globally, including 154 in India.