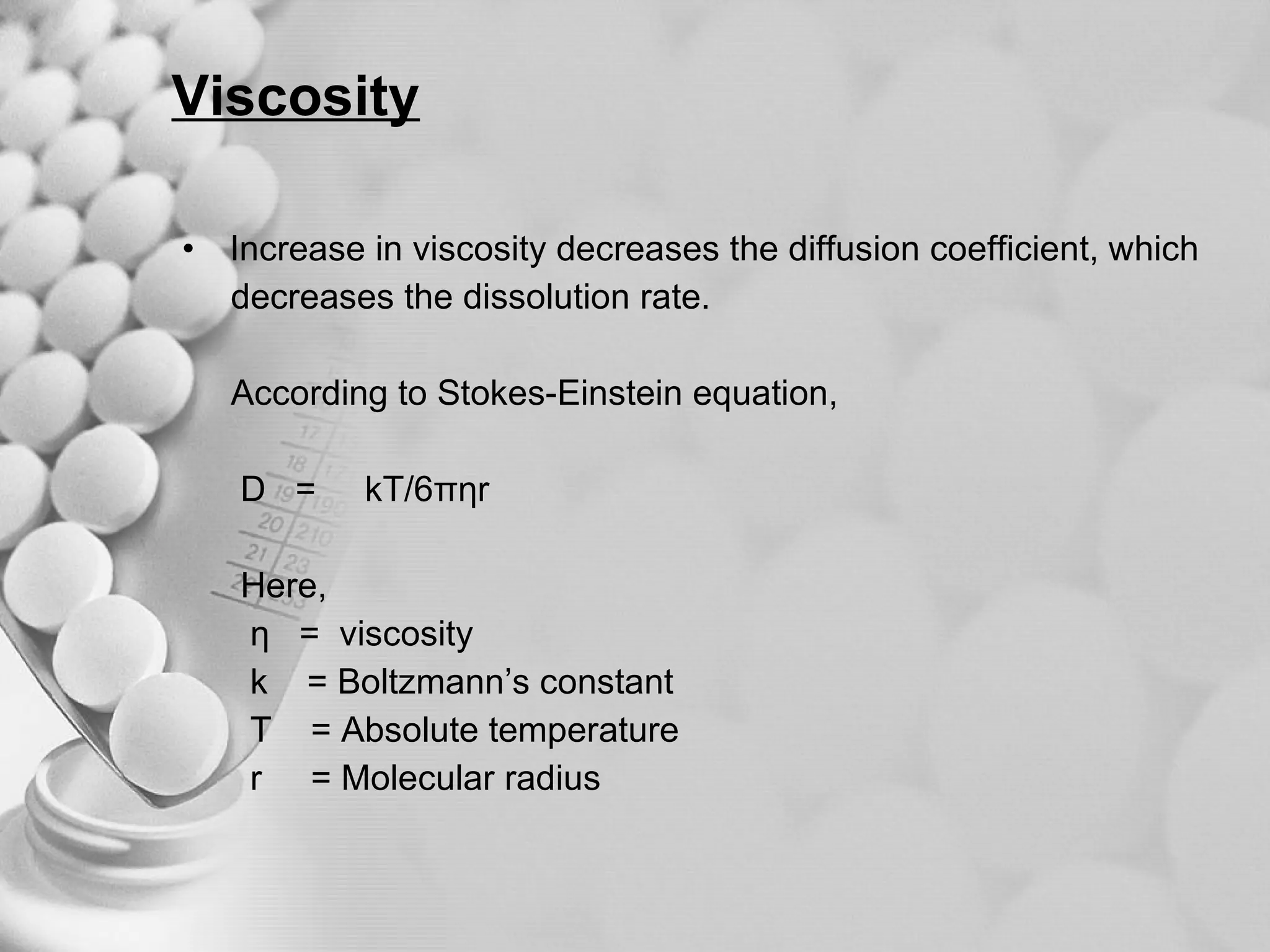
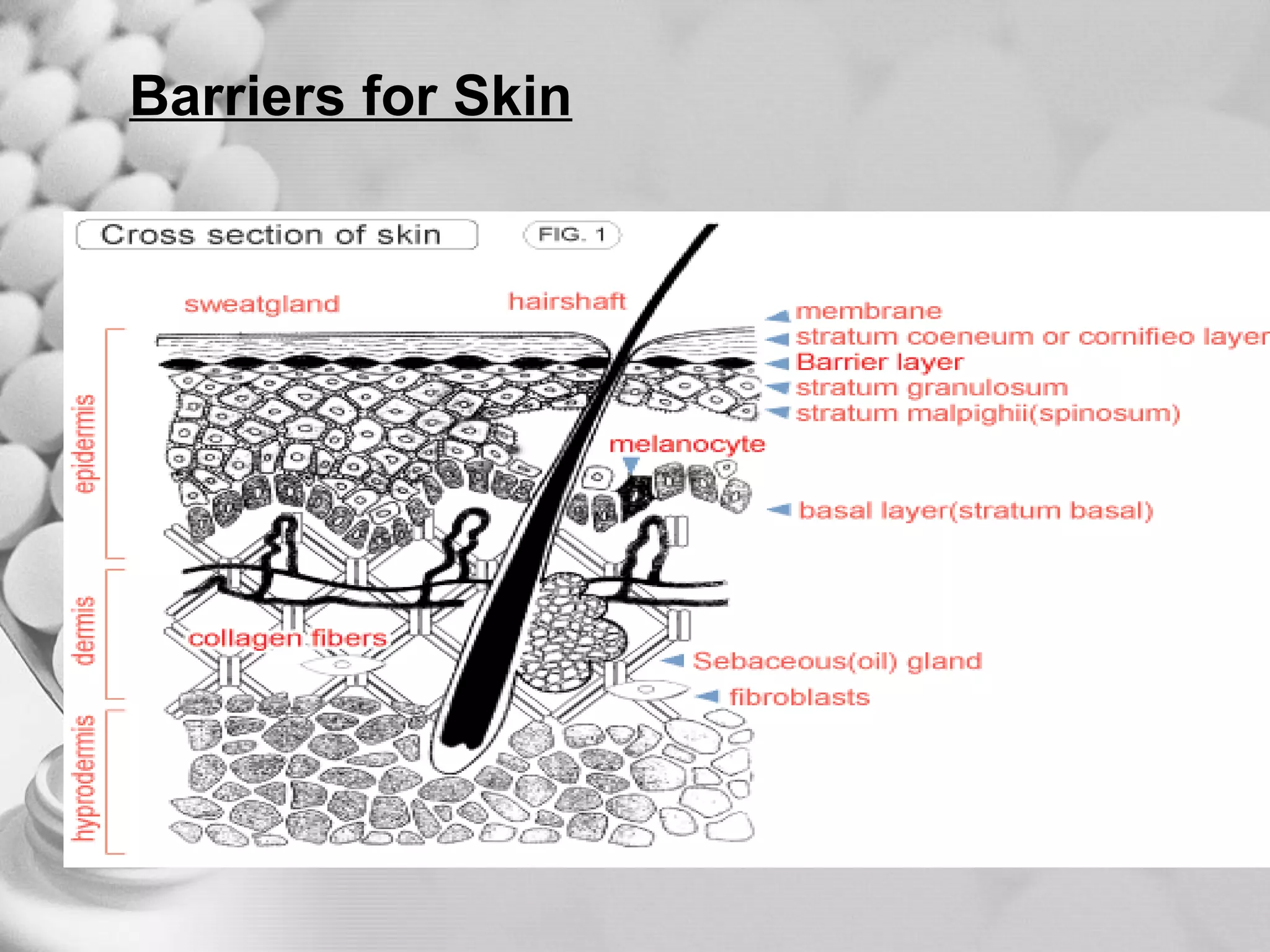
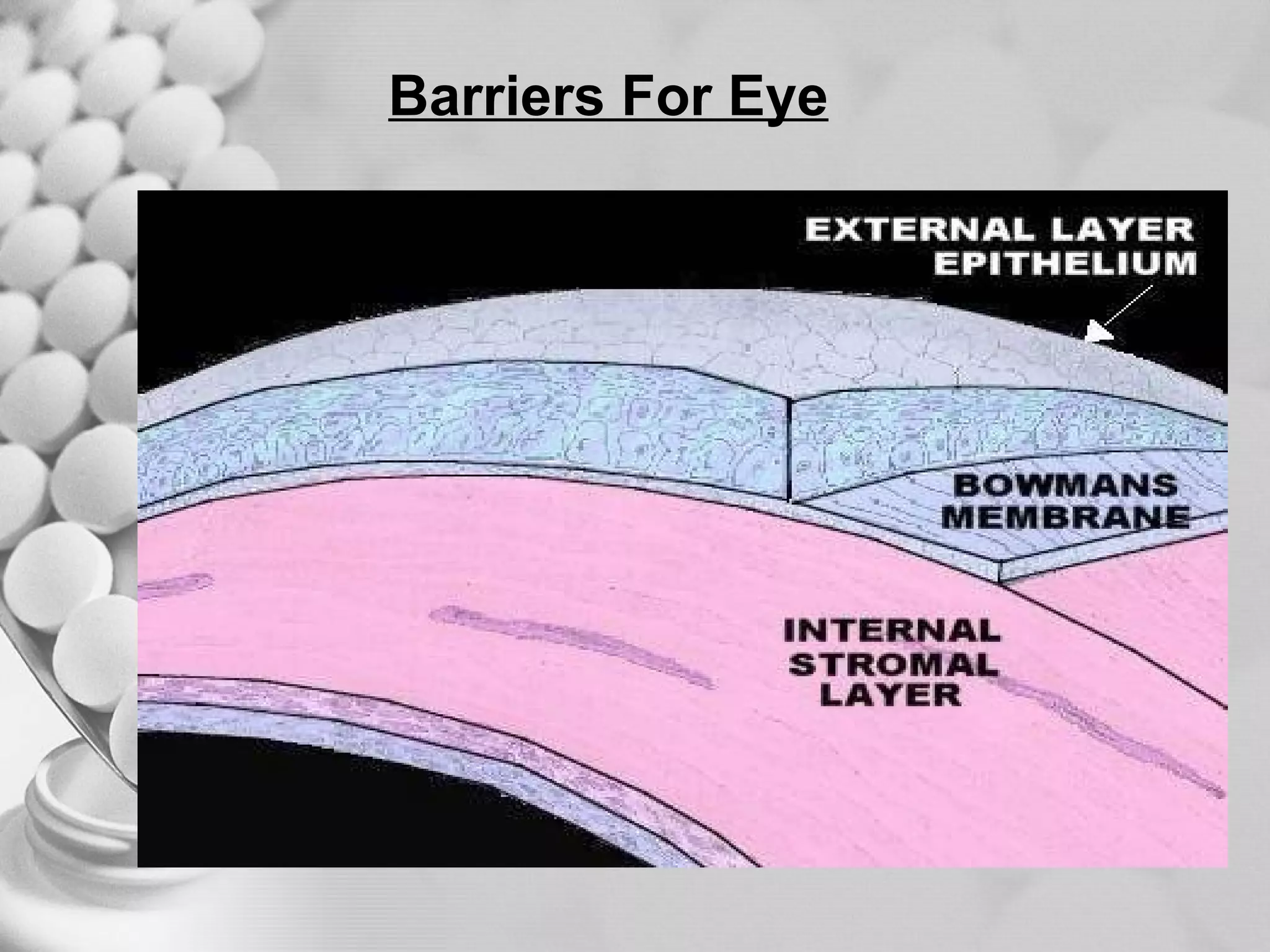
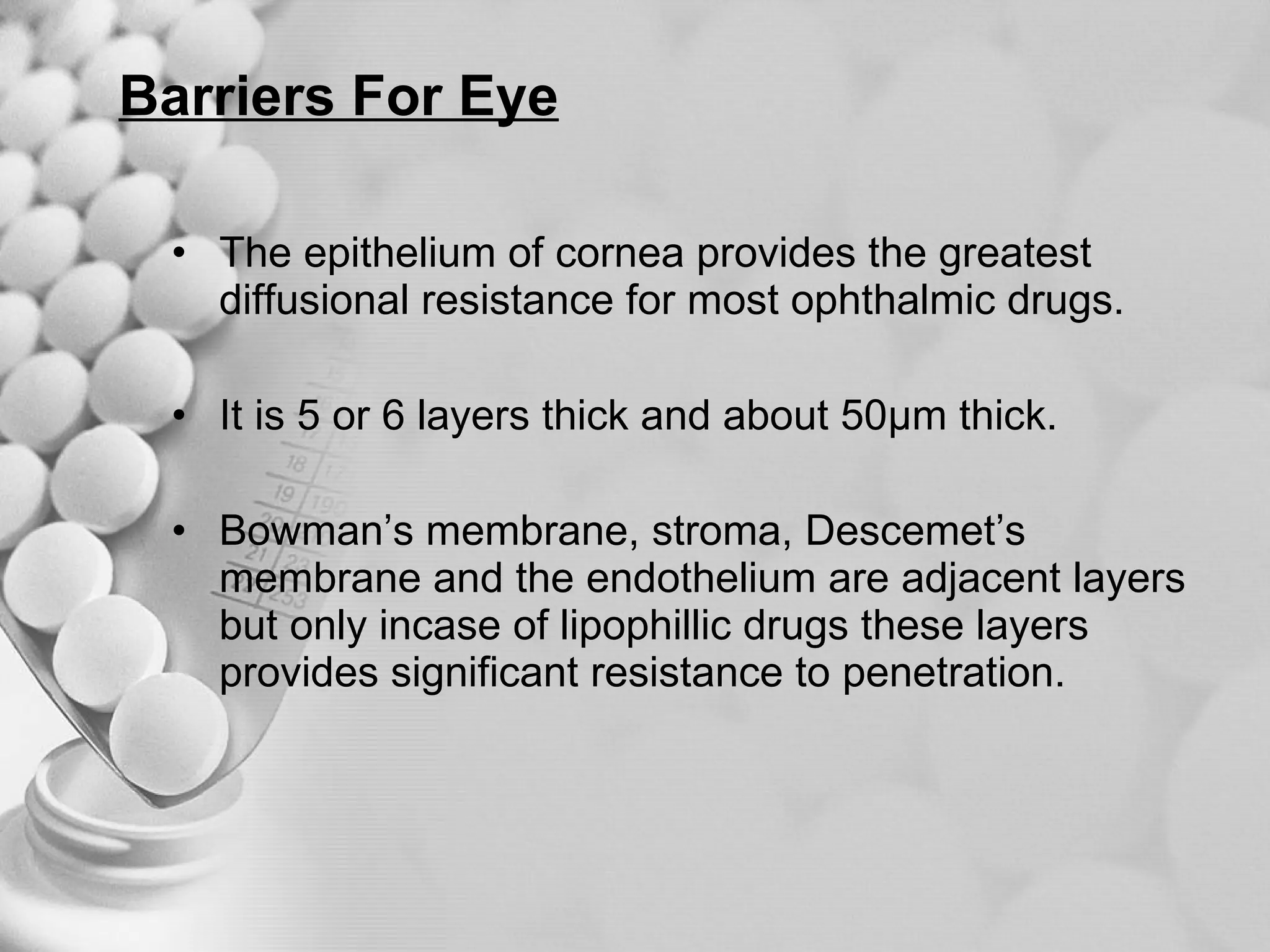
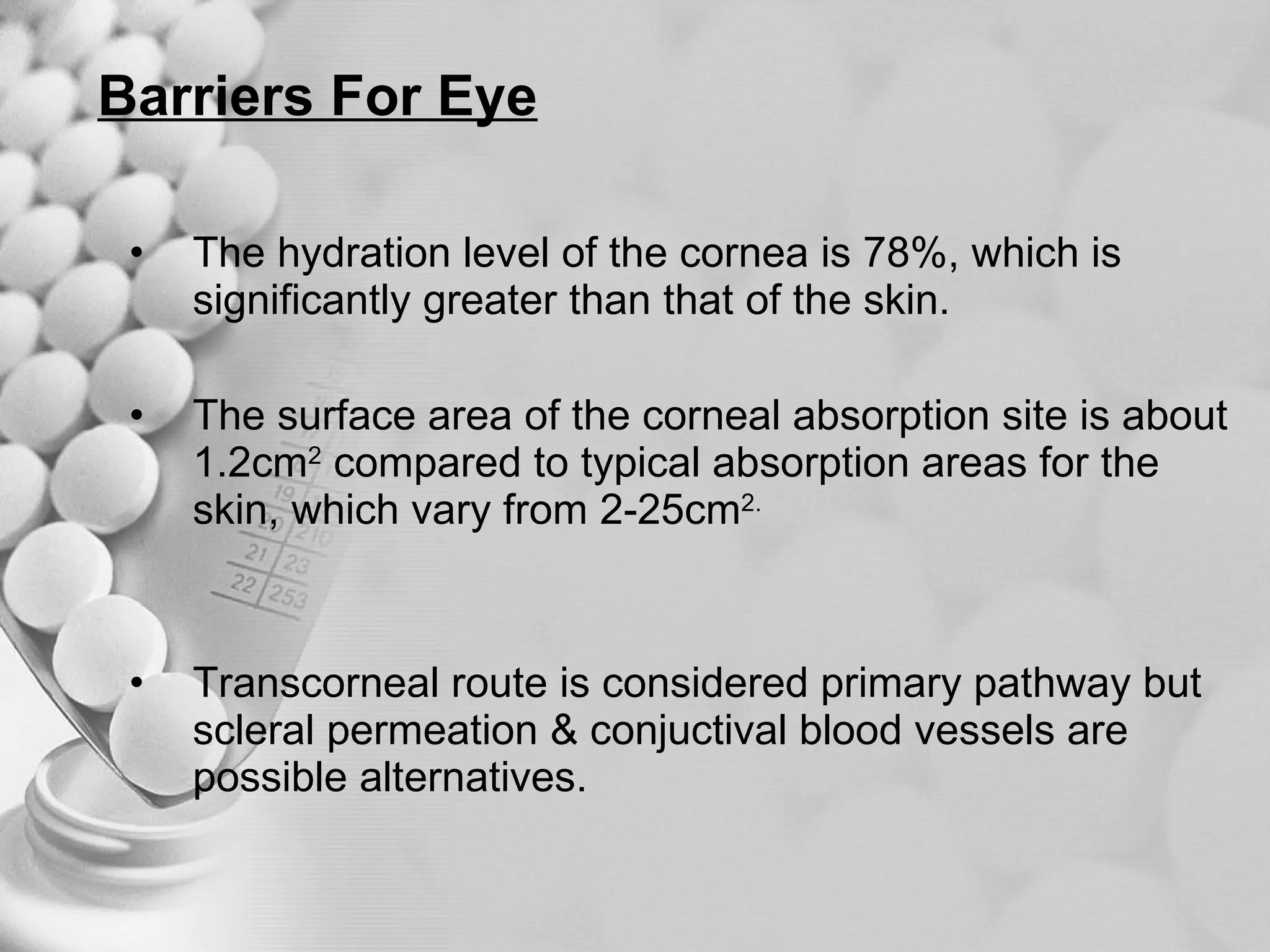
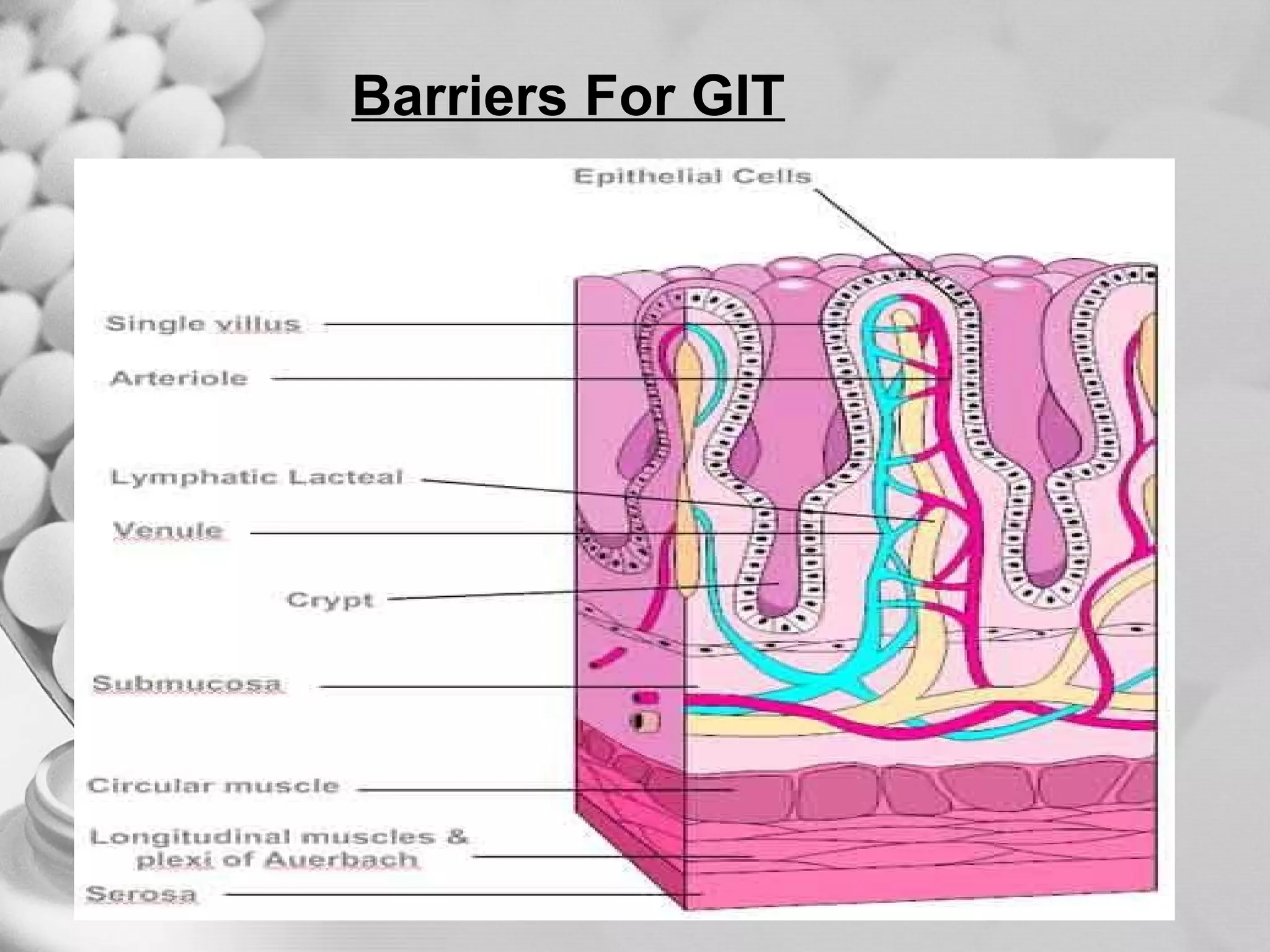
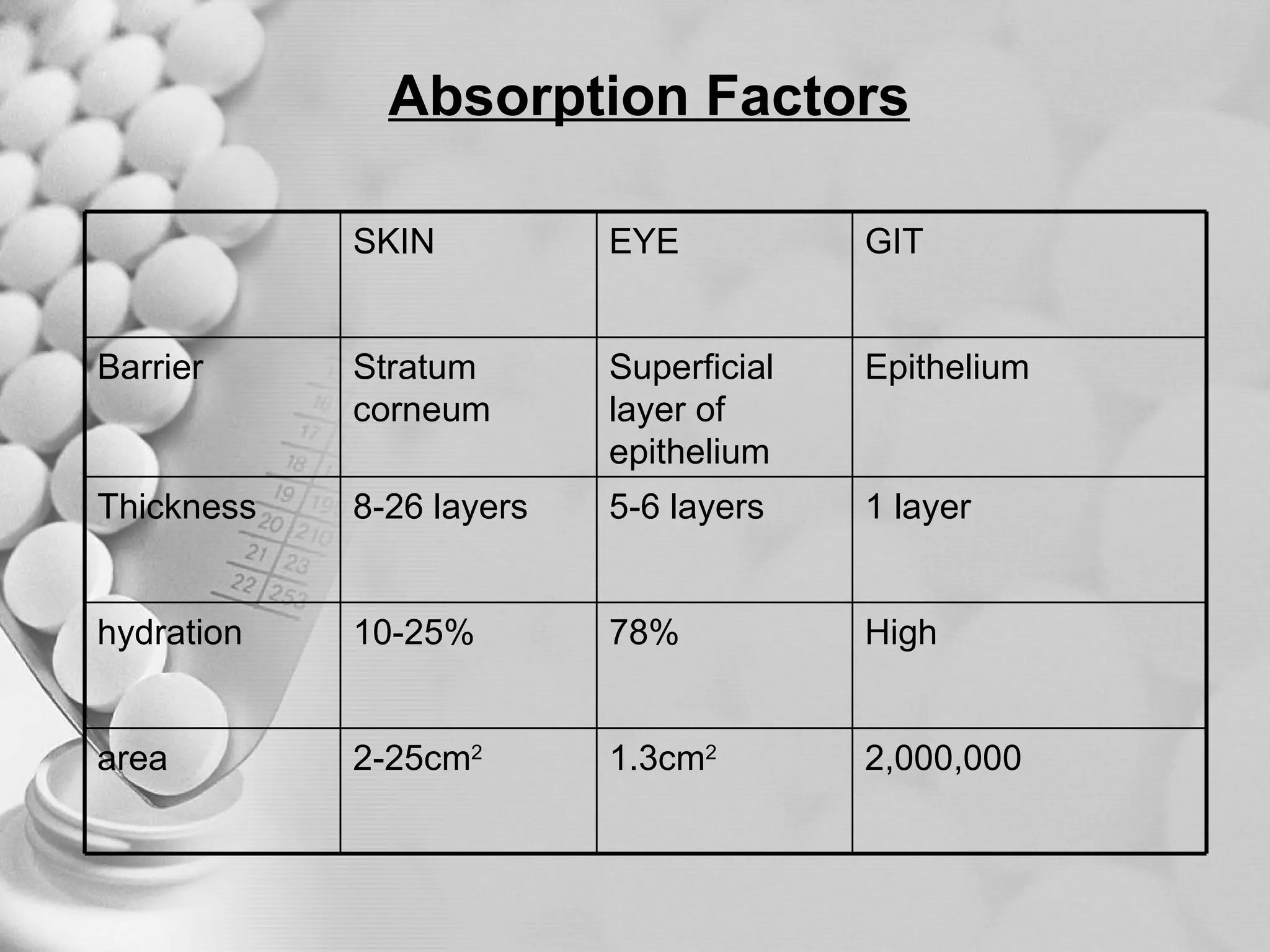
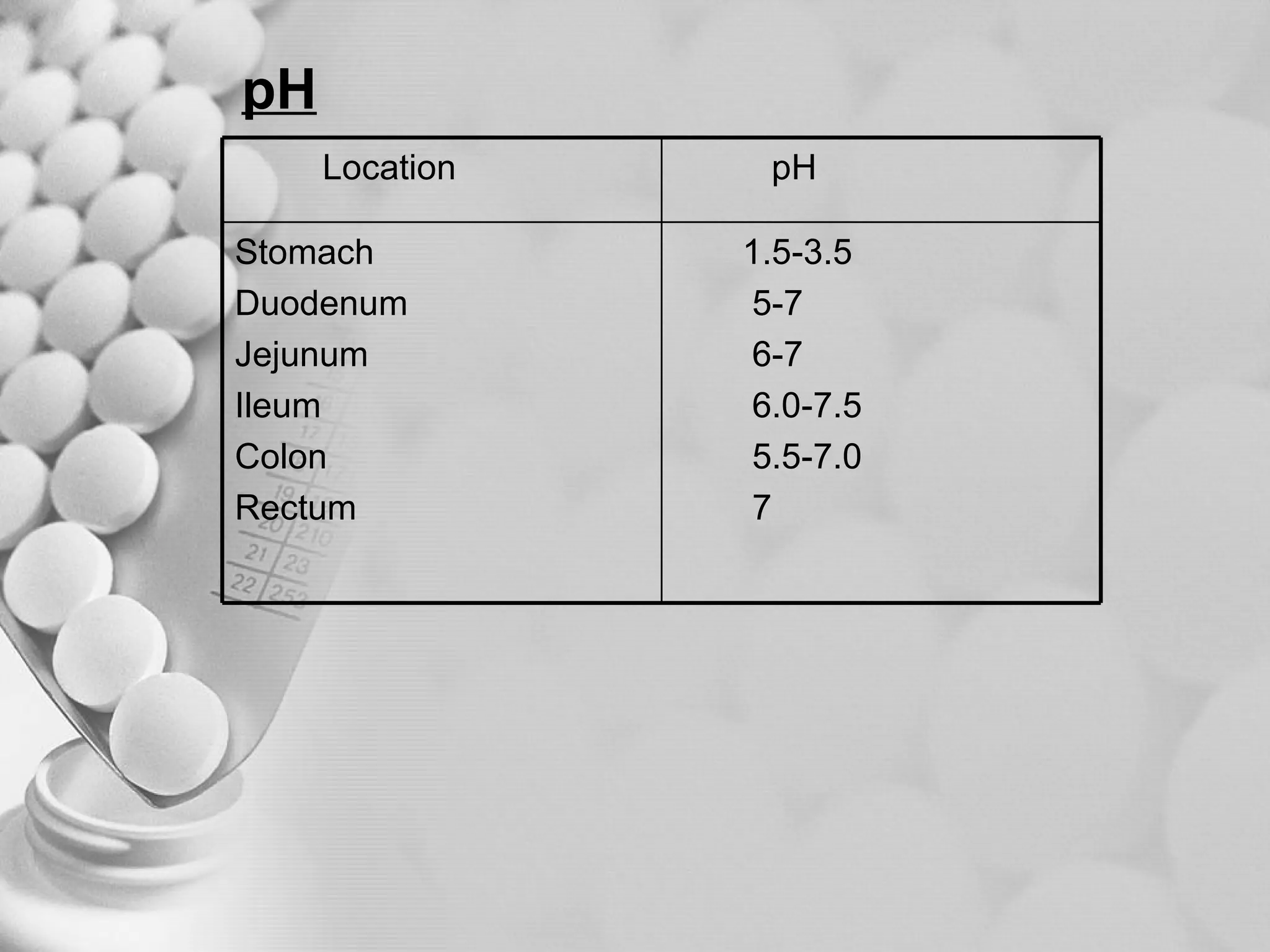
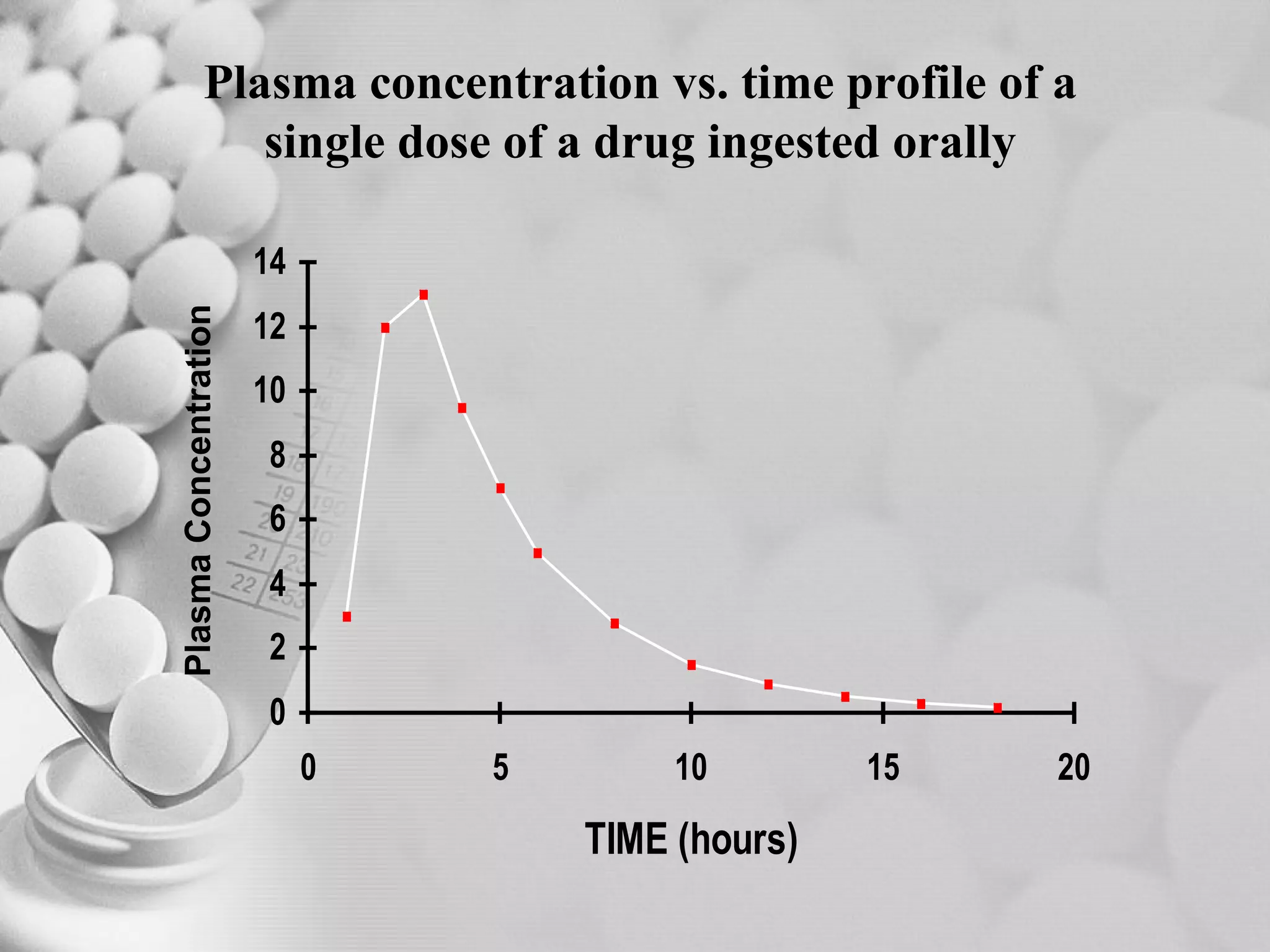
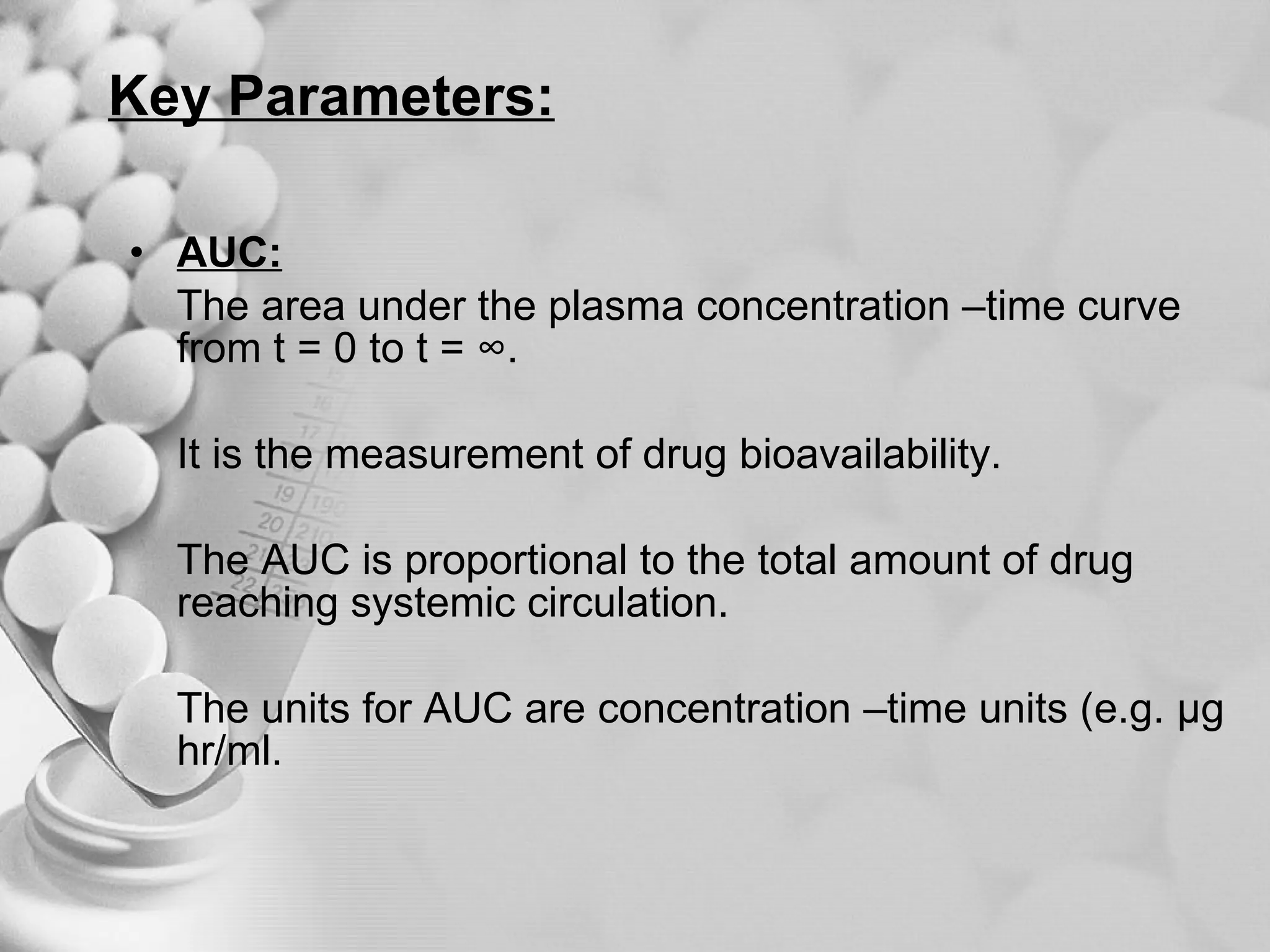
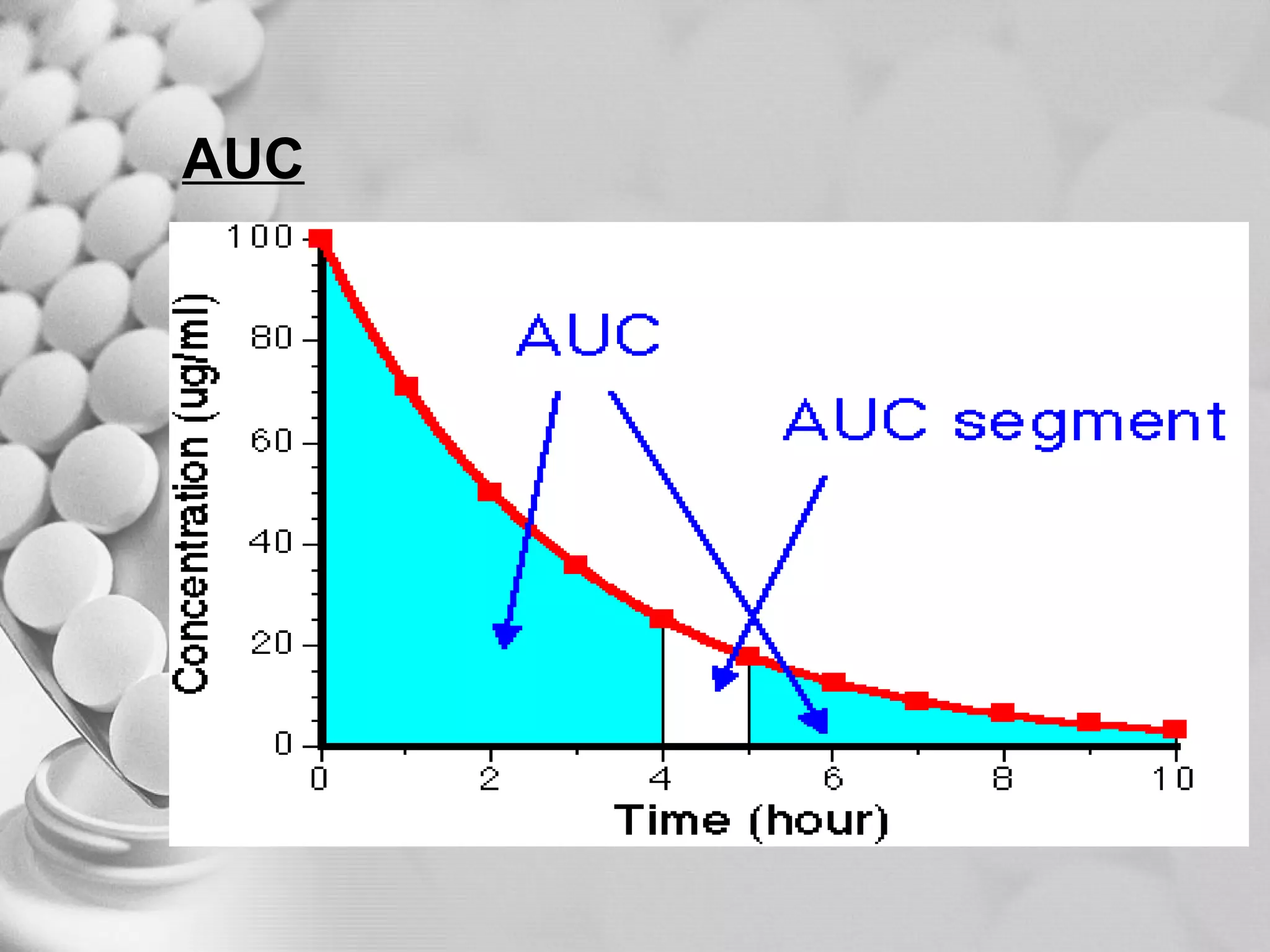
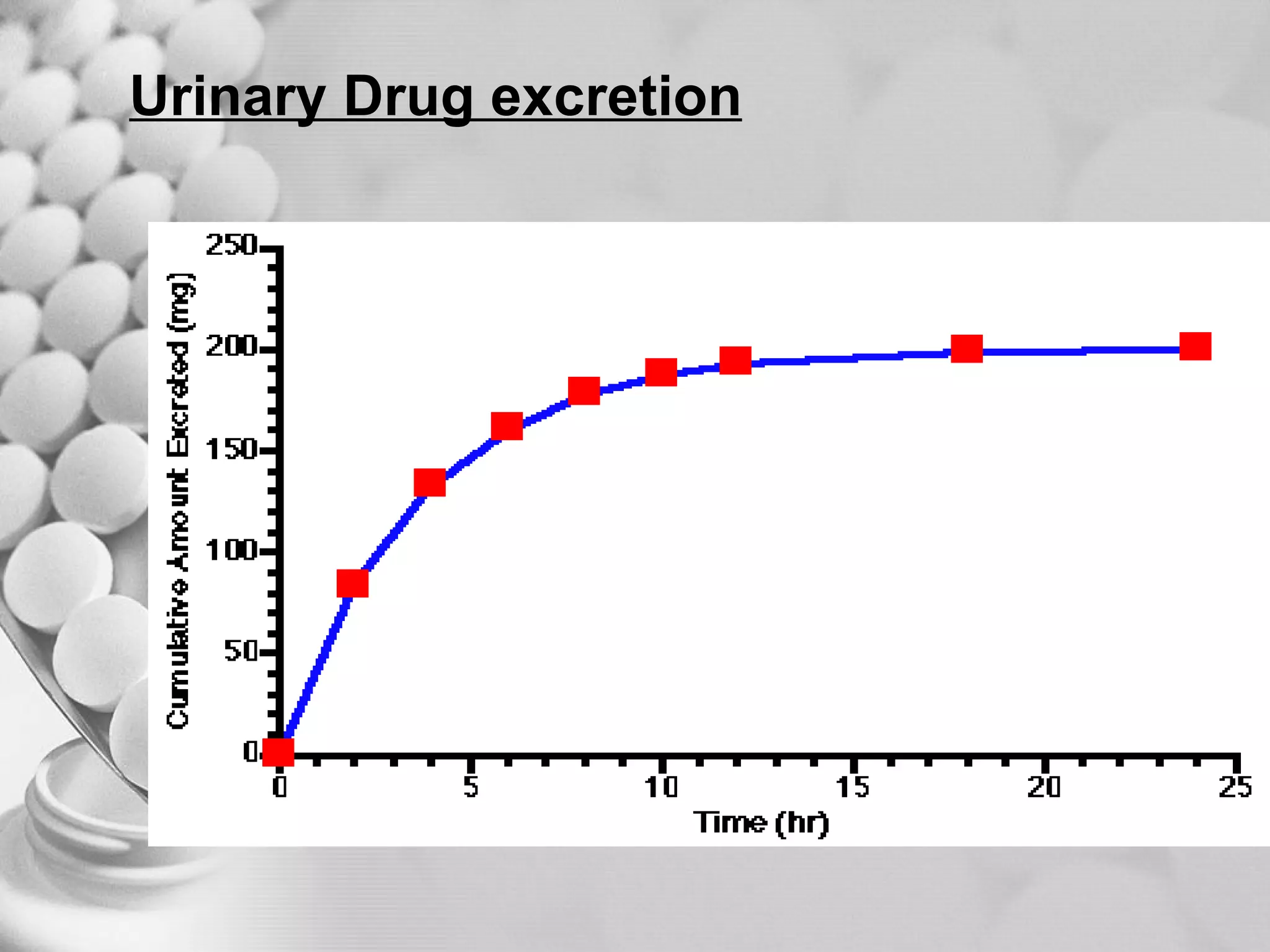
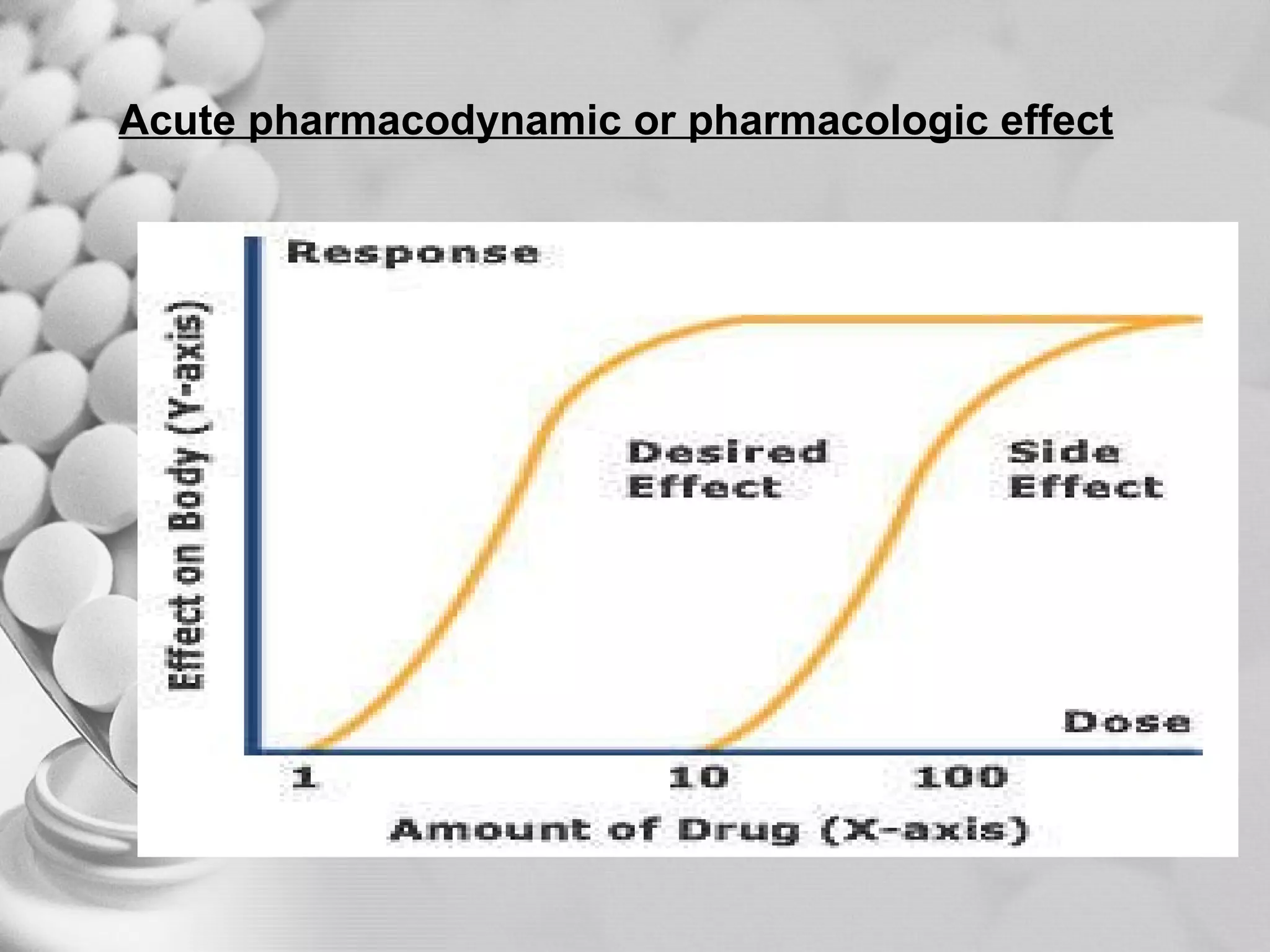
The document discusses bioavailability of disperse dosage forms. It defines relative bioavailability as the systemic availability of a drug from a dosage form compared to a reference standard given by the same route of administration. Absolute bioavailability is the fraction of drug systemically absorbed from the dosage form. It also discusses factors affecting drug release and absorption from disperse systems like particle size, viscosity, and barriers to absorption for different routes of administration like skin, eye, gastrointestinal tract, and lungs.
![Bioavailability Of Disperse Dosage Forms By Mohammad Sohail Mphil pharmaceutics Islamia university Bahawalpur [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityofdispersedosageform-100602022239-phpapp02/75/Bioavailability-Of-Disperse-Dosage-Form-1-2048.jpg)


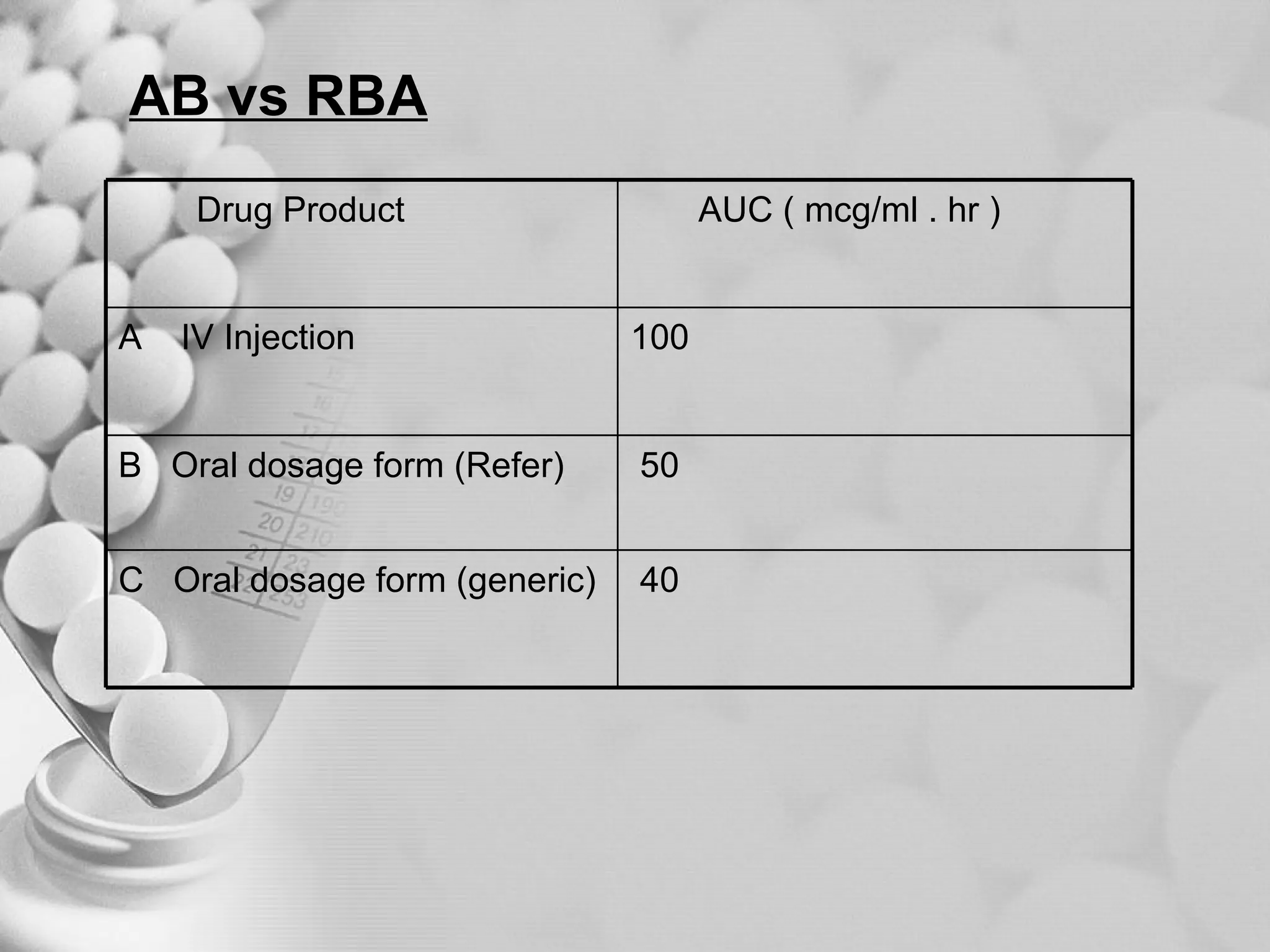
![RBA The determination of RBA is important in generic drug studies ( e.g. Bioequivalence studies ). Bioequivalence is the relative bioavailability study. [ AUC ] Oral test / Dose oral test RBA = _______________________ [ AUC ] oral reference / Dose oral Ref](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityofdispersedosageform-100602022239-phpapp02/75/Bioavailability-Of-Disperse-Dosage-Form-4-2048.jpg)

![Absolute Bioavailability An ‘F’ value of 0.80 0r 80% indicated that only 80% of the drug was systemically available from the oral dosage form. [ AUC ] Oral / Dose oral F = ______________________ [ AUC ] IV / Dose IV](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioavailabilityofdispersedosageform-100602022239-phpapp02/75/Bioavailability-Of-Disperse-Dosage-Form-6-2048.jpg)