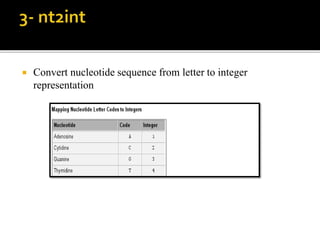
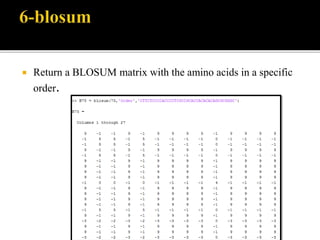
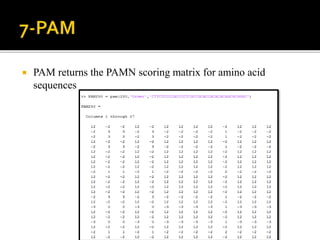
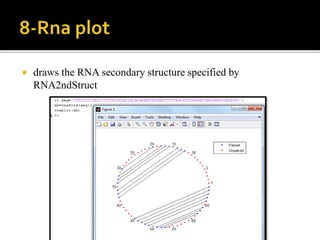
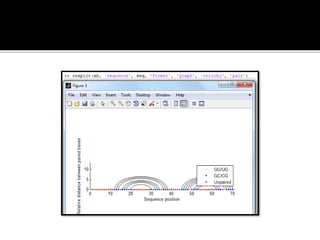
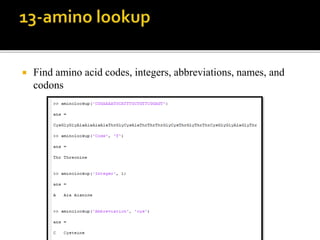
MATLAB is a programming environment used for numerical computation, data analysis, and visualization. It can be used to analyze data, develop algorithms, create models and applications. The document also provides information about the BCL2 gene, including its function as a transcriptional regulator. It describes several MATLAB functions including converting between DNA/RNA and integer representations, finding complements, and analyzing sequences through alignment and counting bases/words.


![ BCL2 B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 [Homo sapiens (human)]
Function
Transcriptional regulator that acts as an activator. Promotes beta-
catenin transcriptional activity
Fasta format
>gi|568815580:c63319778-63123346 Homo sapiens chromosome
18, GRCh38 Primary
AssemblyCTTCTCCCCACCCCTCGCCGCACCACACACAGCG
CGGGCTTCTAGCGCTCGGCACCGGCGGGCCAGGCGCGTCC
TGCCTTCATTTATCCAGCAGCTTTTCGGAAAATGCATTTGC
TGTTCGGAGTTTAATCAGAAGAGGATTCCTGCCTCCGTCC
CCGGCTCCTTCATCGTCCCCTCTCCCCTGTCTCTCTCCTGG
GGAGGCGTGAAGCG](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bioinfo-150517111307-lva1-app6891/85/Bio-info-3-320.jpg)