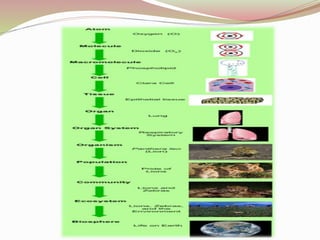
Biology is the study of living organisms and their interactions. The document outlines the definition of biology, its major divisions (botany, zoology, microbiology), and branches such as anatomy, physiology, genetics, and molecular biology. It also discusses how biology relates to other sciences like physics, chemistry, mathematics, and discusses levels of biological organization from atoms to ecosystems. Finally, it notes how the Quran instructs humans to study and reveal knowledge about the origins and characteristics of life.