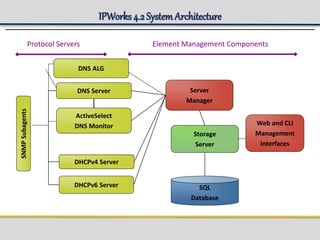
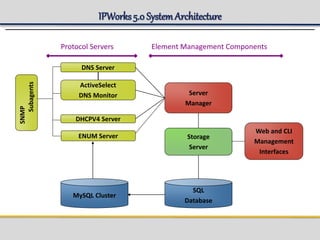
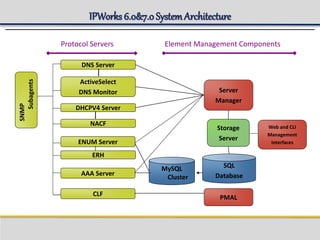
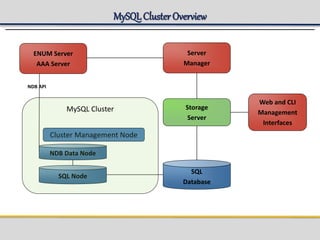
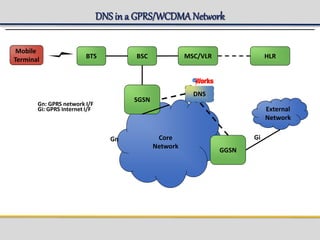
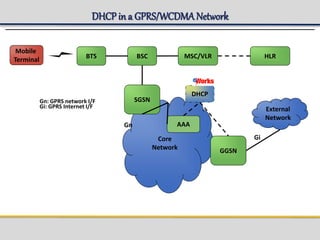
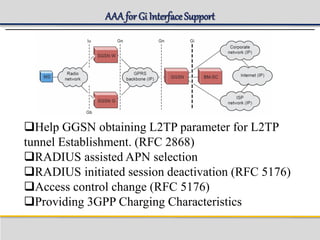
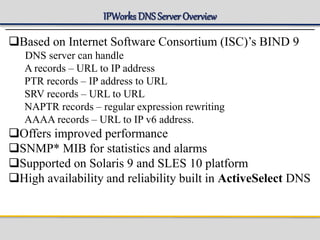
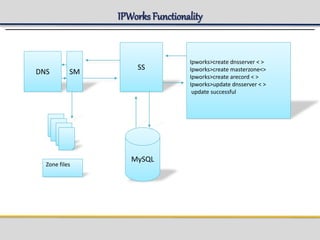
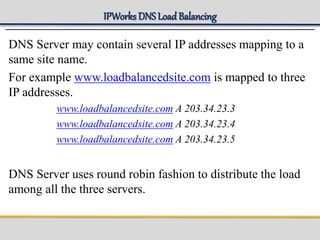
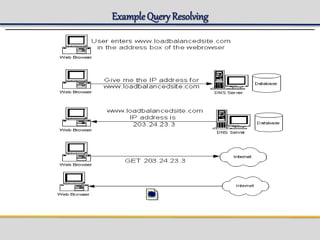
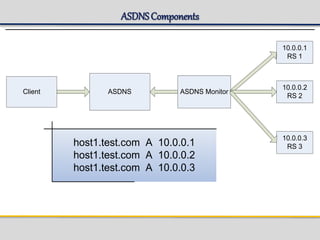
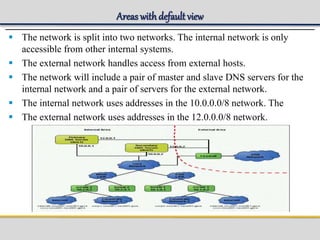
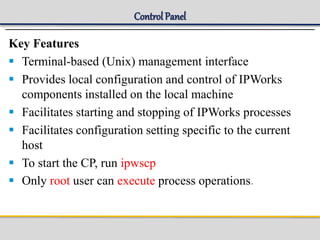
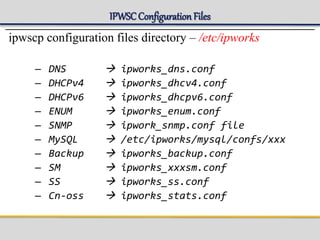
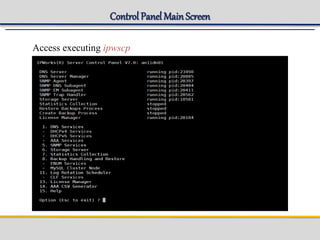
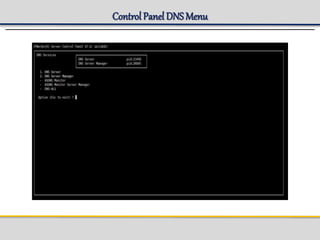
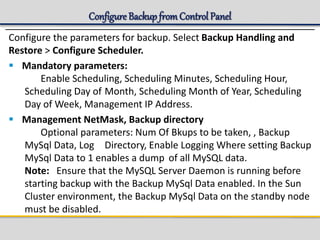
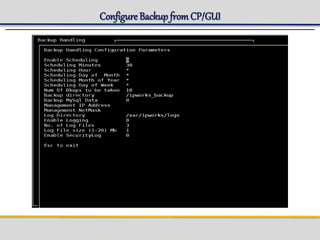
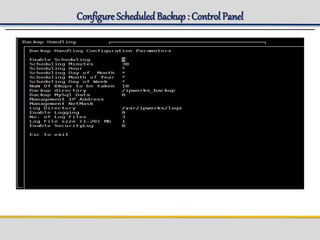
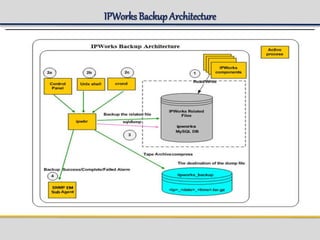
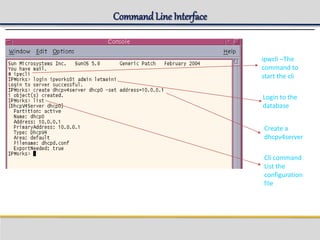
IPWorks is a software platform that provides DNS, DHCP, AAA and other services for IPv4 networks, including an element management system for configuration and monitoring; it includes protocol servers like DNS, DHCP and AAA servers as well as element management components; the document discusses the architecture and components of IPWorks, including features of the DNS, DHCP and AAA servers, and how IPWorks is used in GPRS/WCDMA networks.