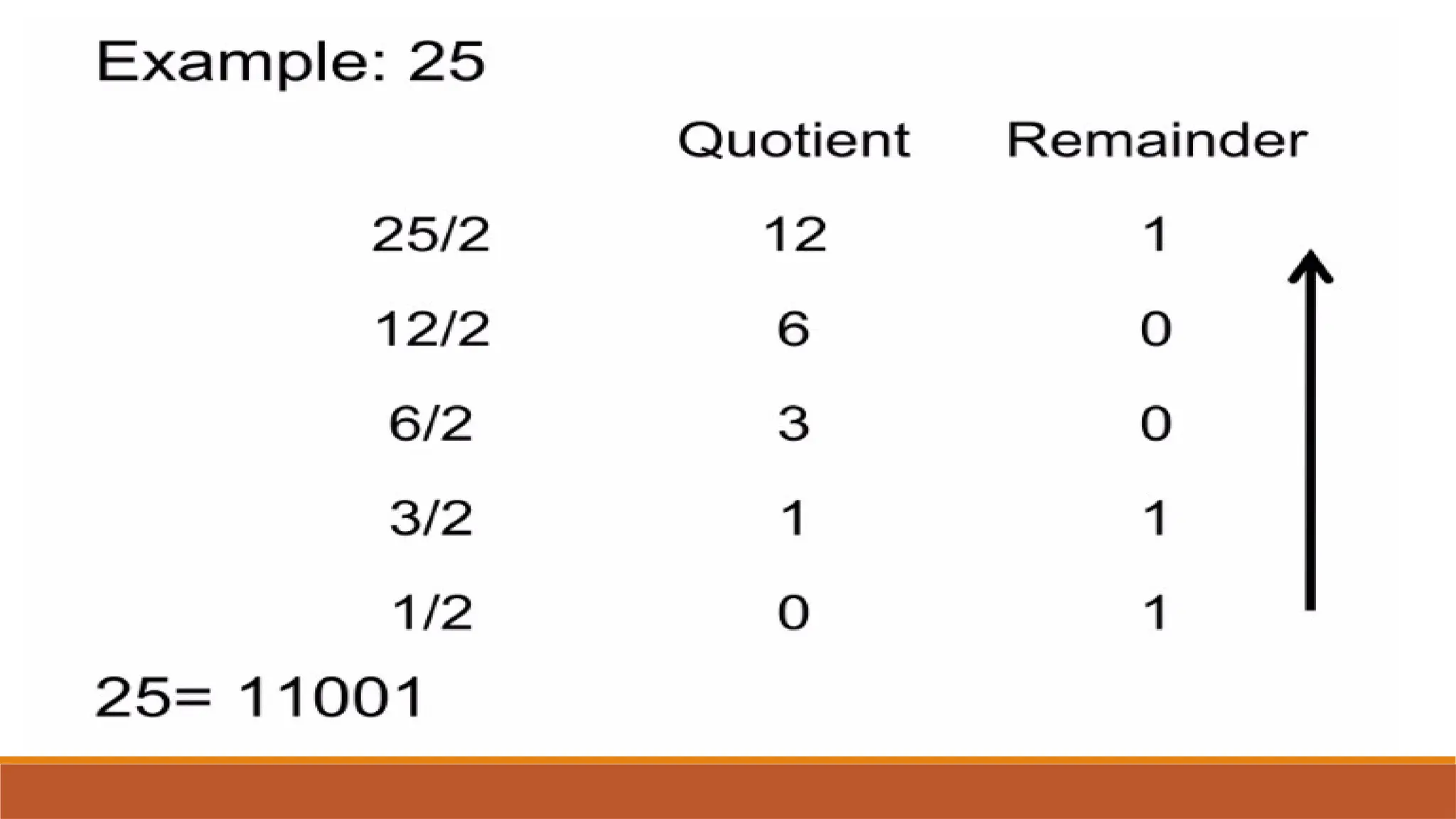
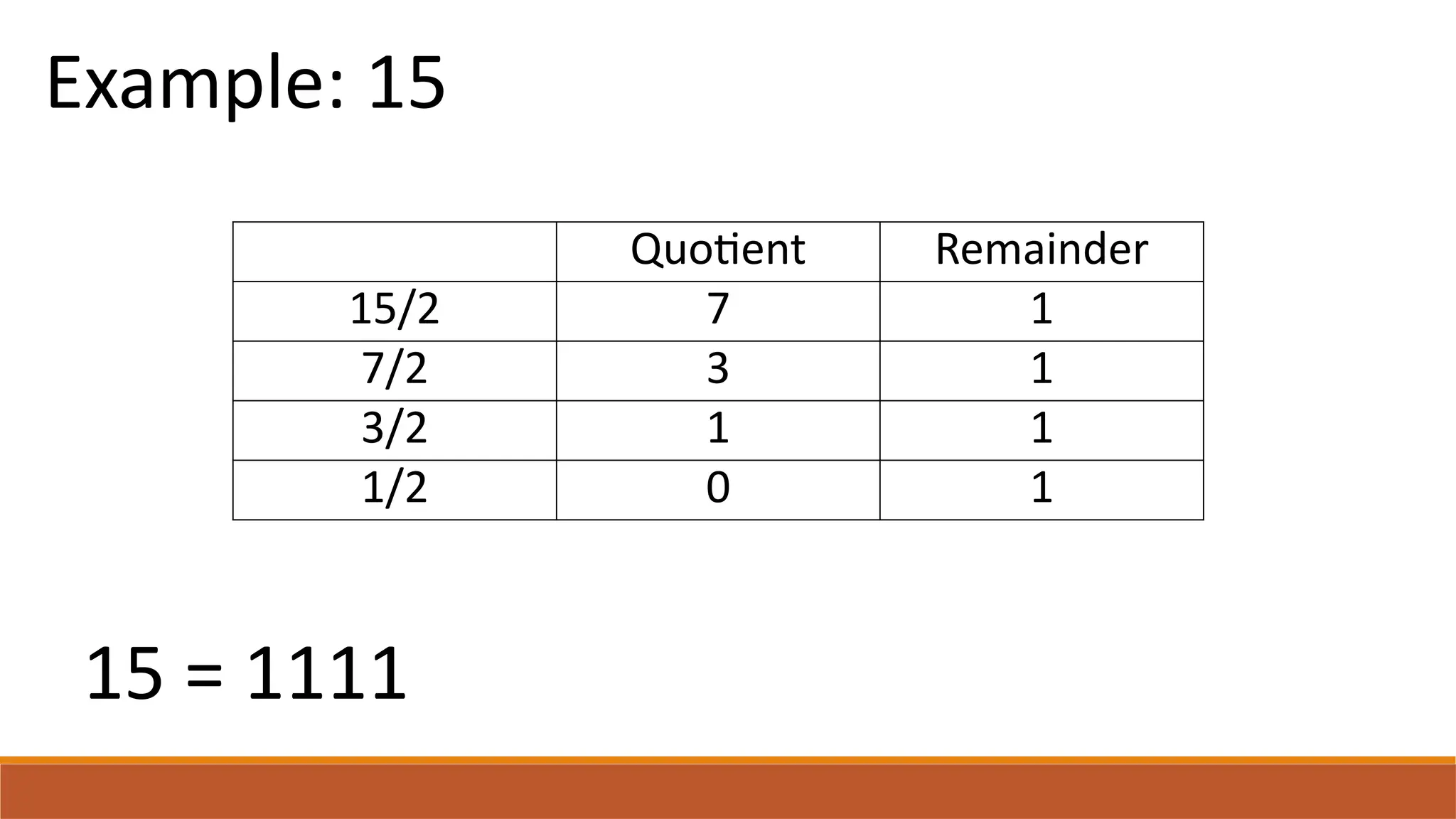
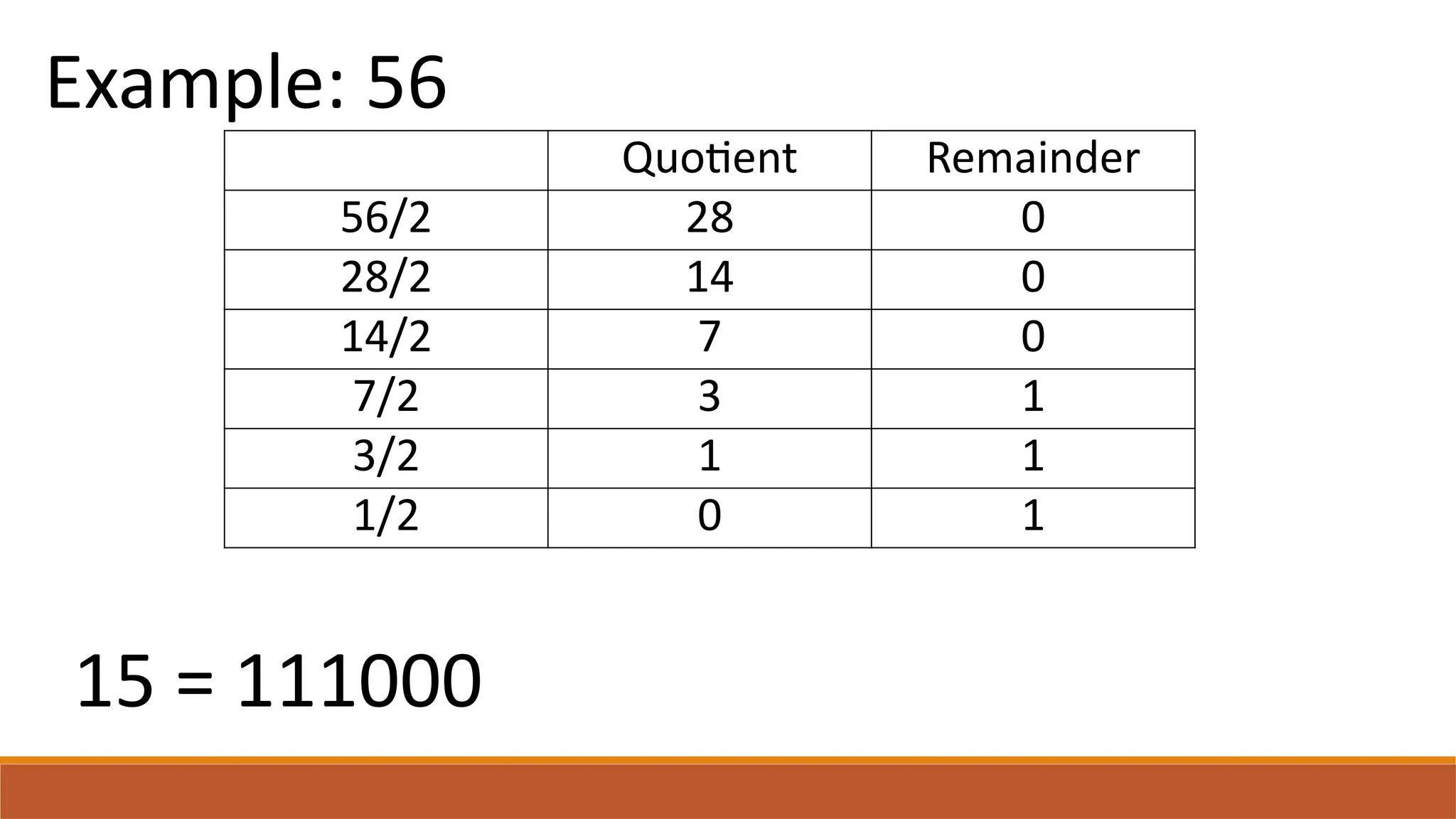
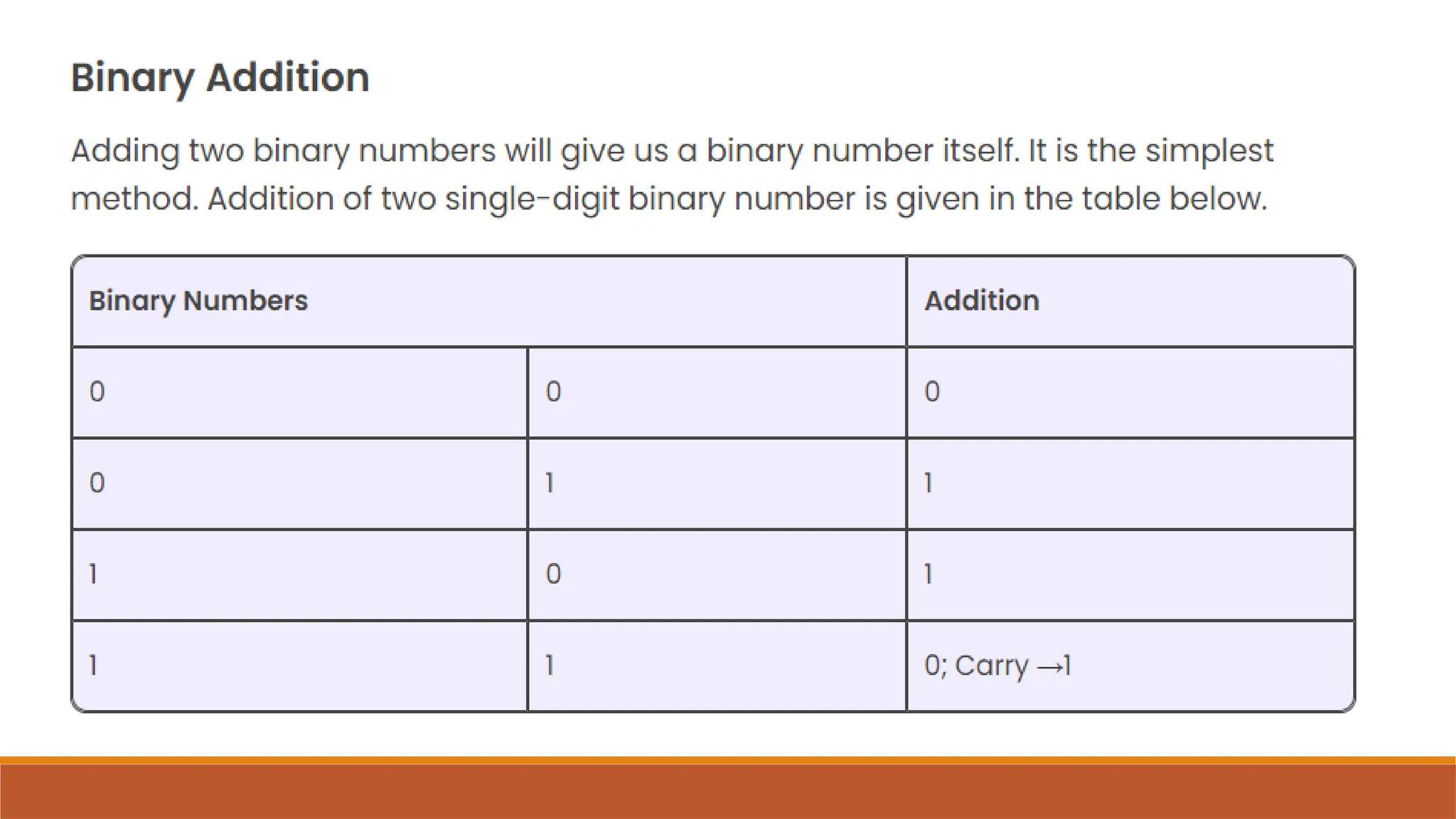
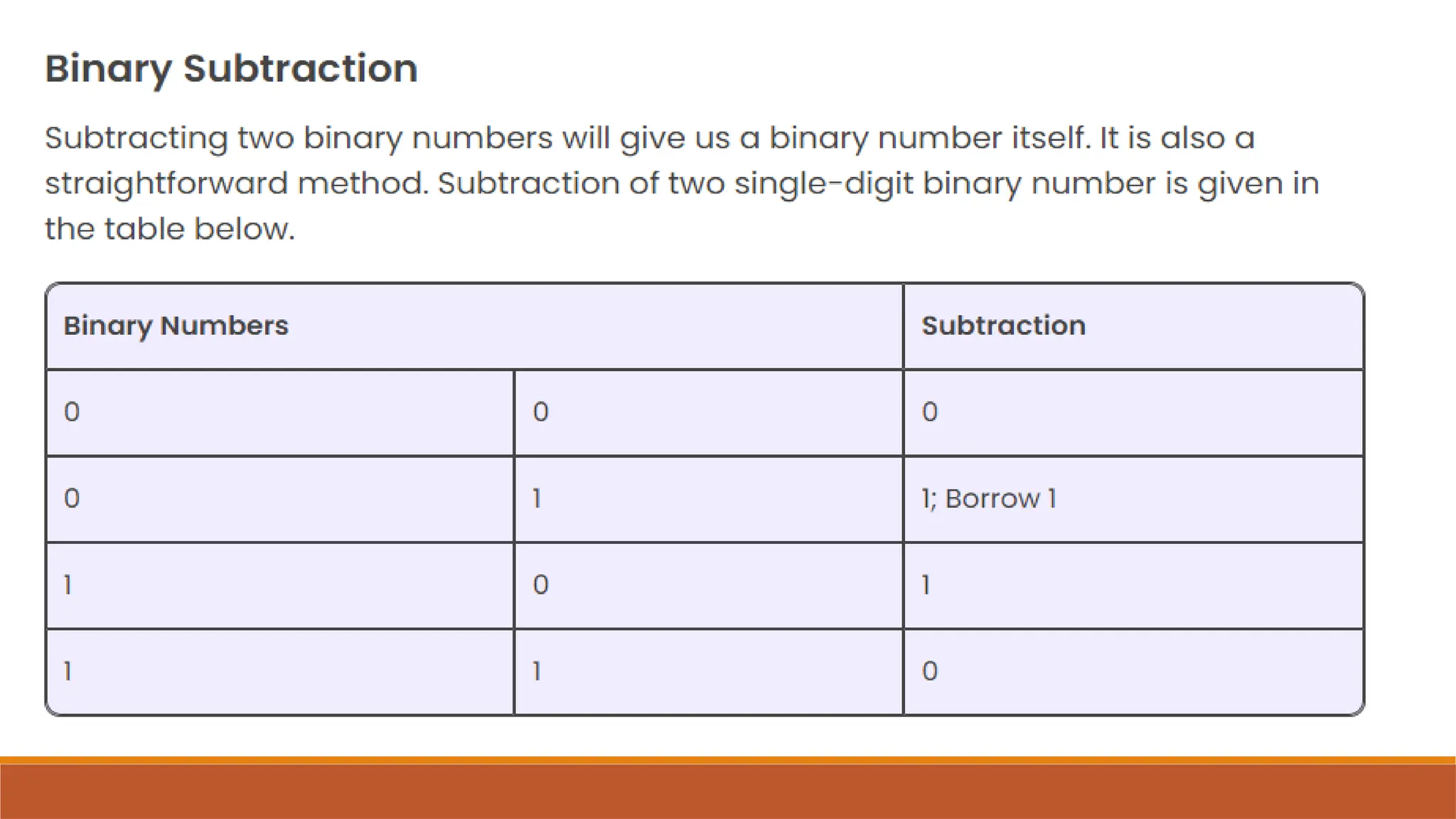
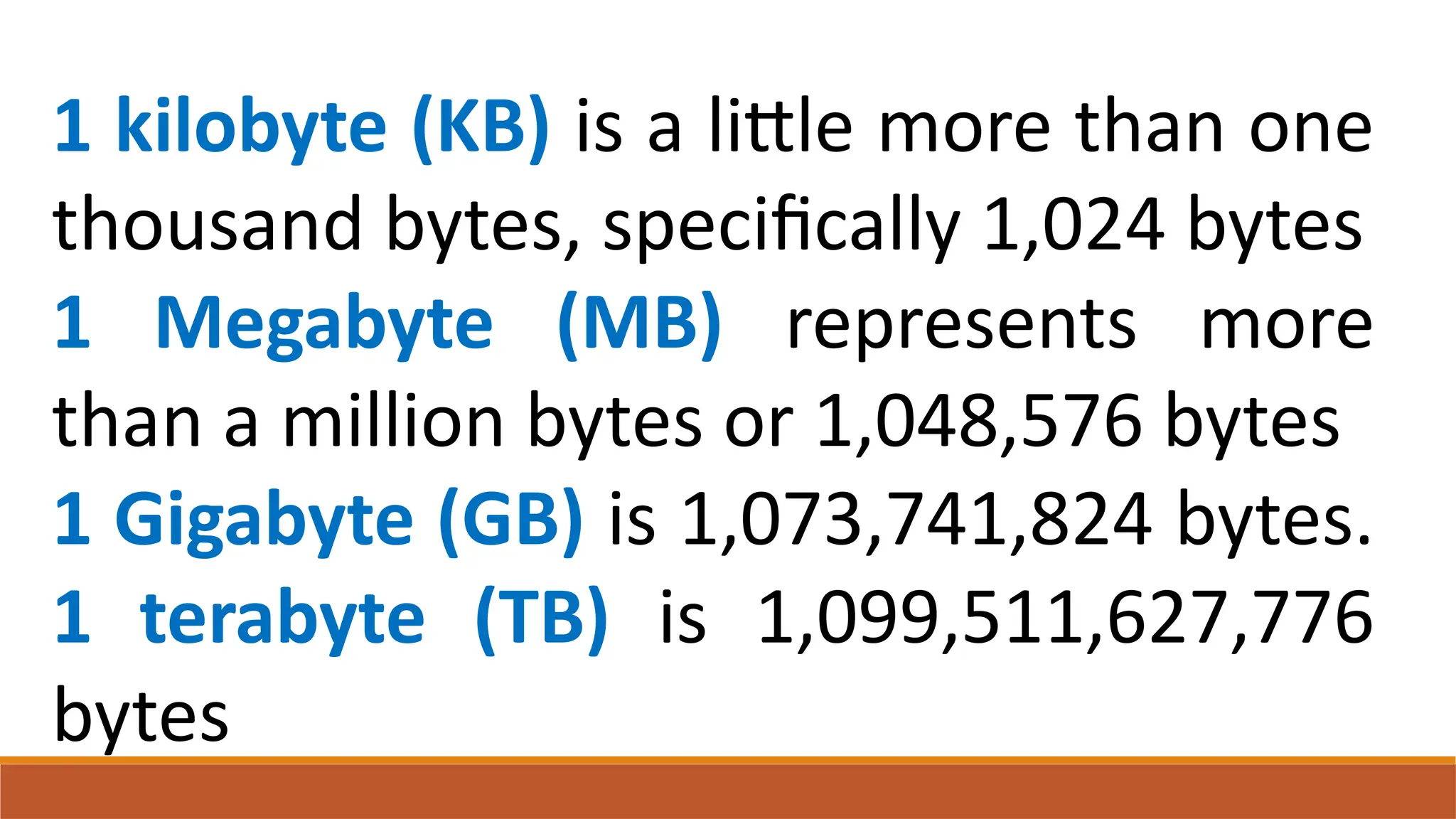
The document explains digital circuits and the representation of information using binary codes, specifically ASCII for characters. It details the concept of bytes and data storage measurements such as kilobytes and gigabytes, outlining the relationship between file size and storage capacity. Additionally, it includes practical examples and directions for converting decimal numbers to binary and solving storage capacity problems.