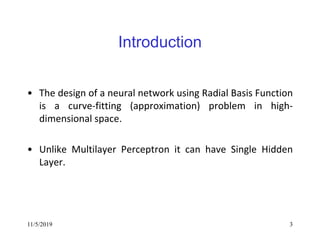
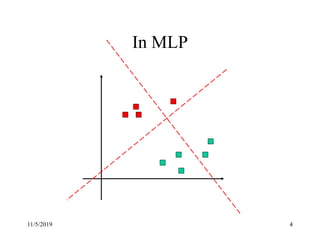
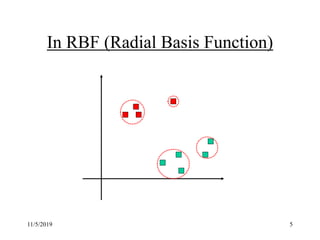
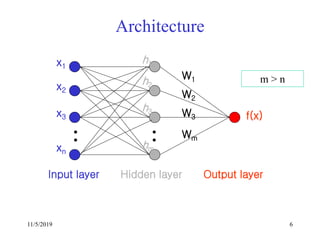
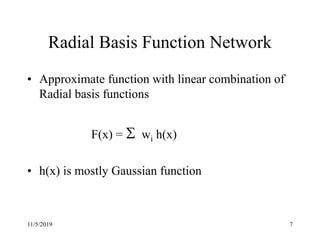
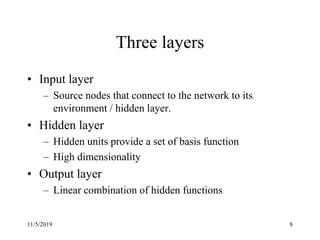
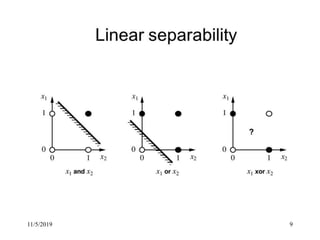
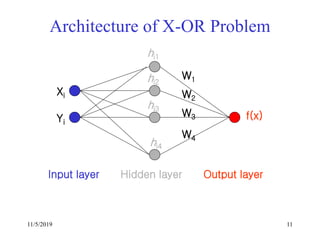
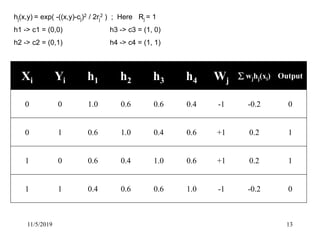
This document discusses radial basis functions and splines for neural network modeling. It presents the architecture of a radial basis function network, which uses radial basis functions as activations in a single hidden layer. The network approximates functions as a linear combination of radial basis functions centered at different locations. The document then shows how to classify the output of an XOR gate using such a network with 4 radial basis functions in the hidden layer and computes the weights between the hidden and output layers to perform the classification.




![11/5/2019 14
Computation of Weight (Wj)
f(x) = wjhj(x)
(i) Now, Calculate the Error
e = wjhj(x) – f(x)
(ii) If Error is present
Use Gradient function
wj = [hj
T hj]-1 hj f(x)
(iii) If input € wj
then f(x) = 1
else
f(x) = 0
h1 h2 h3 h4
1.0 0.6 0.6 0.4
0.6 1.0 0.4 0.6
0.6 0.4 1.0 0.6
0.4 0.6 0.6 1.0
The Value of hj](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bikashphdcse201904-191105082437/85/Radial-Basis-Function-and-Splines-14-320.jpg)

