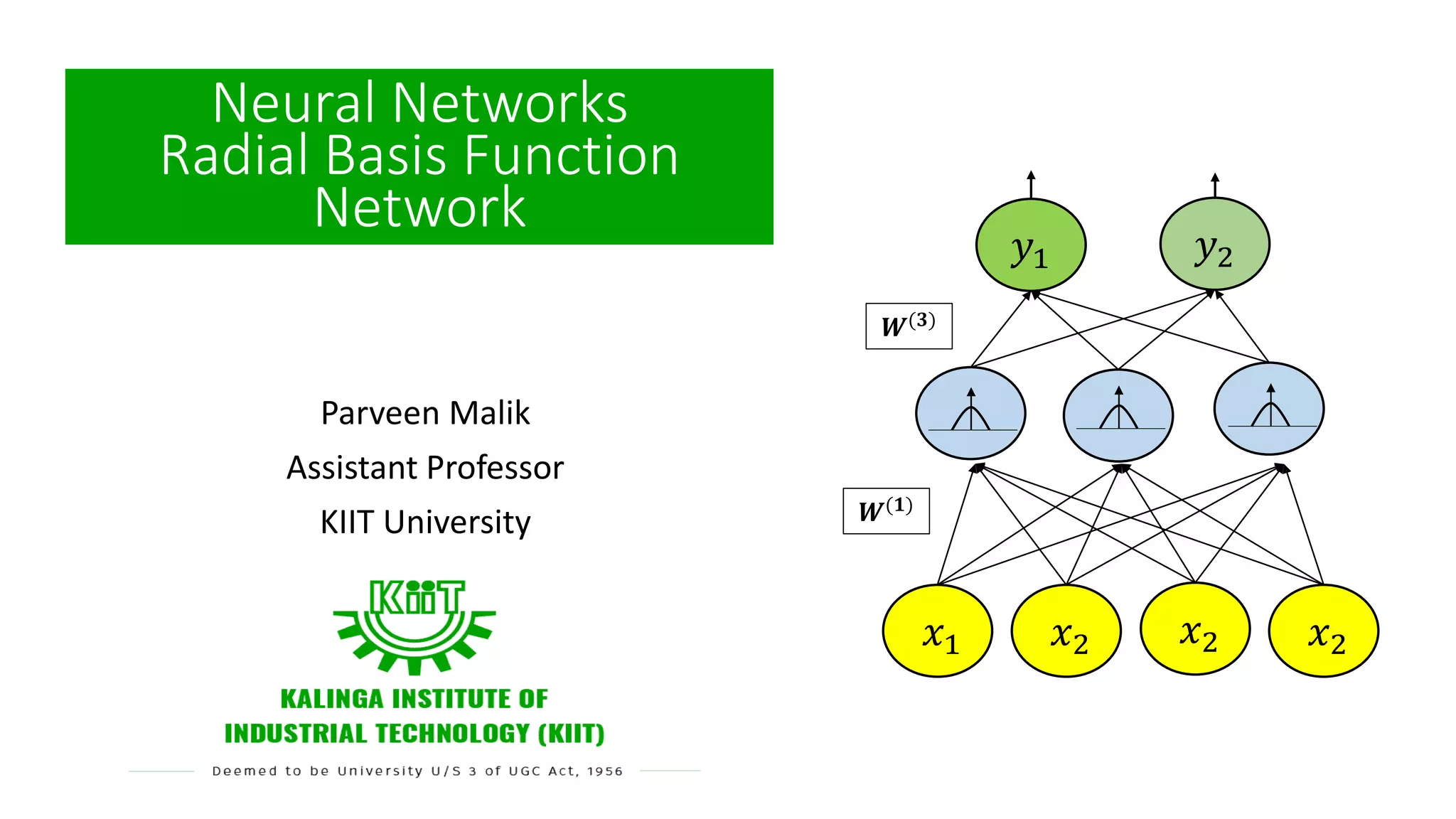
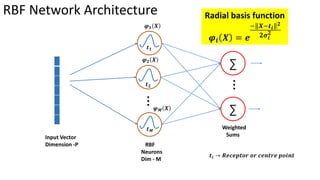
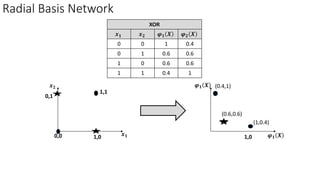
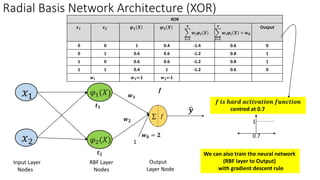
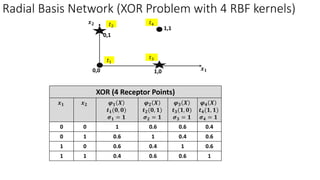
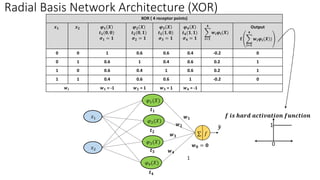
Radial basis function networks can be used to solve nonlinear problems like the XOR problem. They work by mapping input data to a higher dimensional space using radial basis functions with center points, making the data linearly separable. The document discusses using Gaussian radial basis functions with 1, 2 and 4 center points to solve the XOR problem. It shows the calculations of the radial basis functions for different input vectors and how the network with weights can be trained to learn the XOR function.