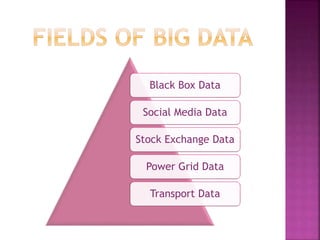
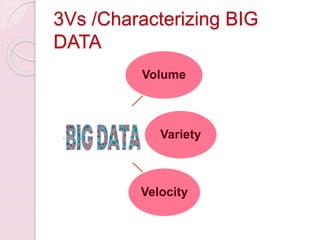
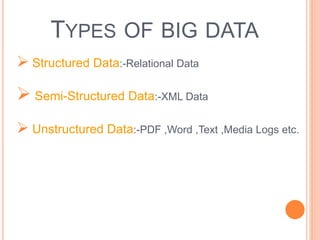
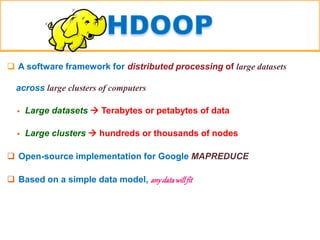
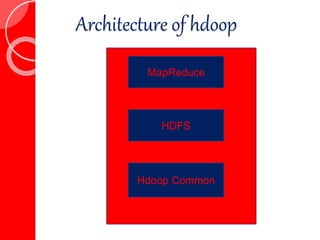
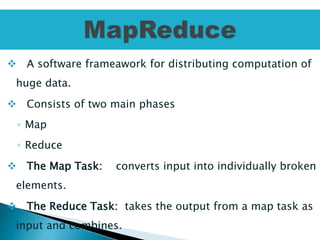
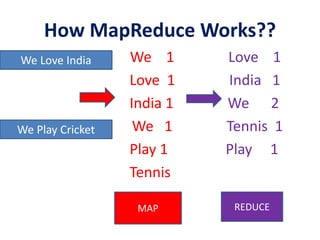
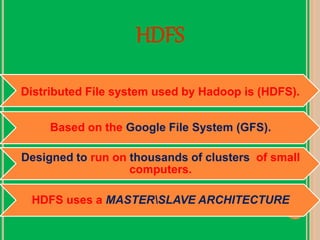
The presentation discusses big data as large and complex datasets that traditional processing methods struggle to handle, emphasizing the challenges in data capture, searching, sharing, analysis, storage, and visualization. It introduces Hadoop, an open-source software framework developed for distributed processing of large datasets, and outlines its architecture, including the MapReduce programming model and the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). The advantages of Hadoop include fault tolerance, automation of data distribution, and the ability to scale dynamically.