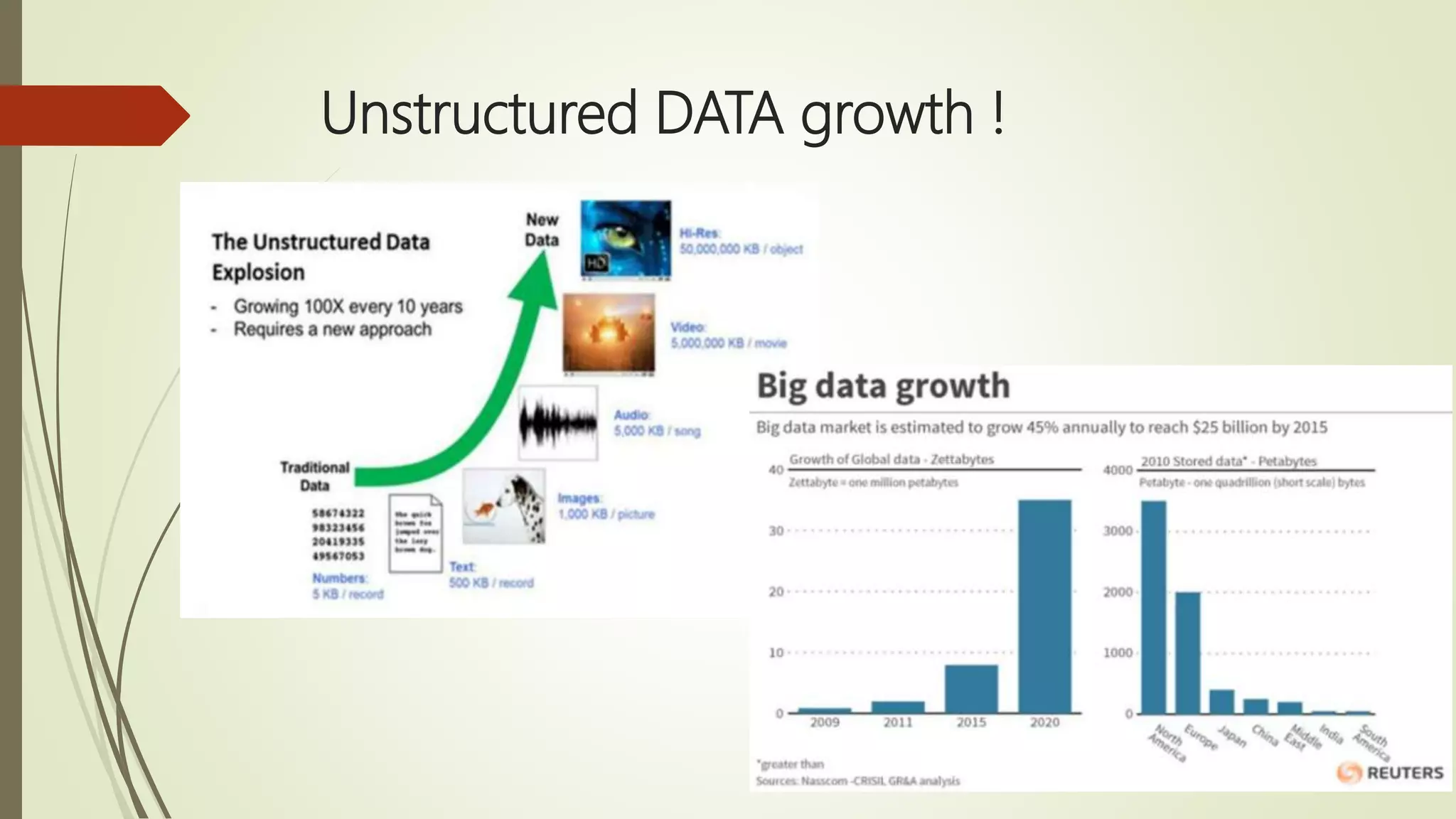
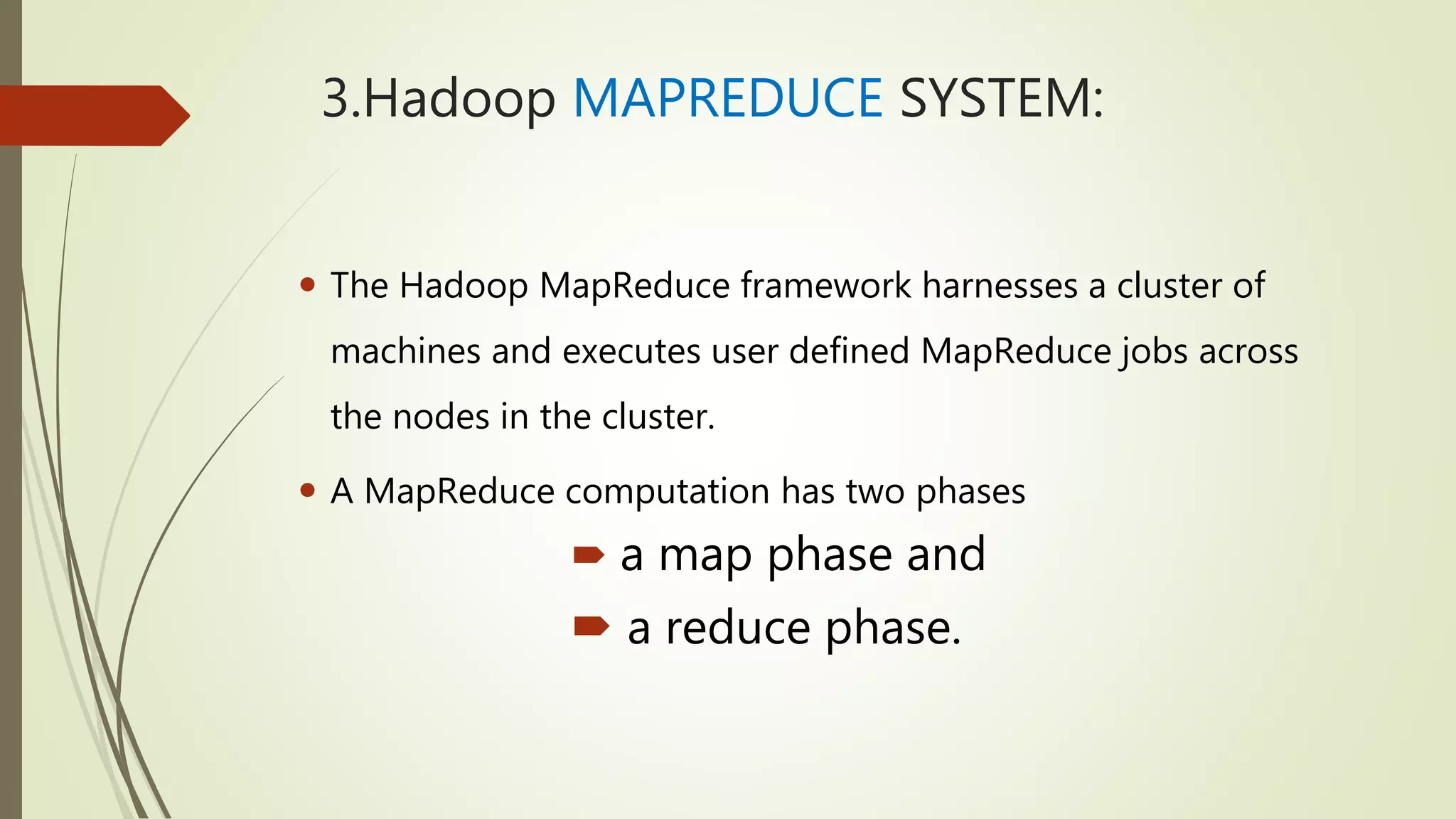
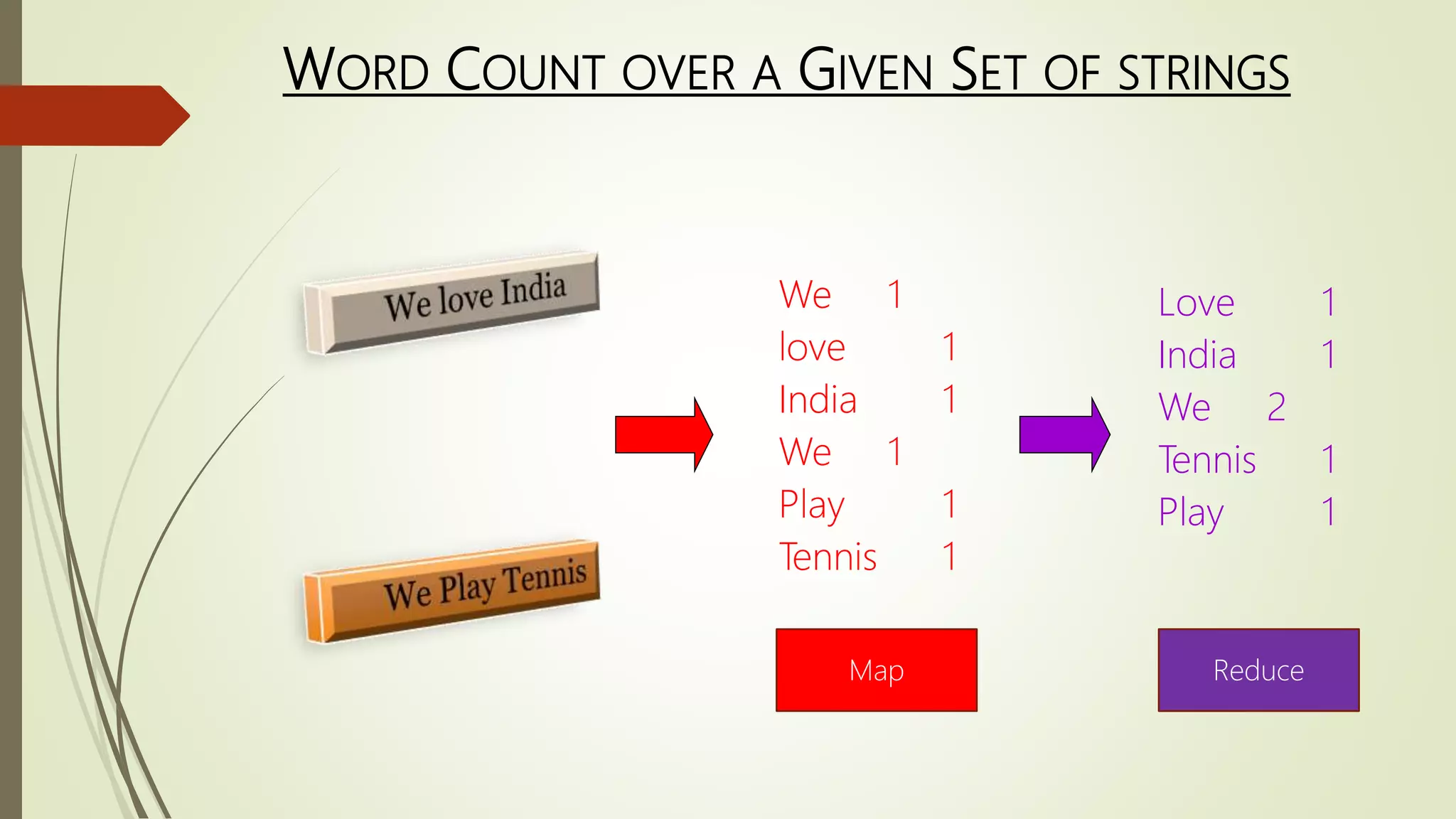
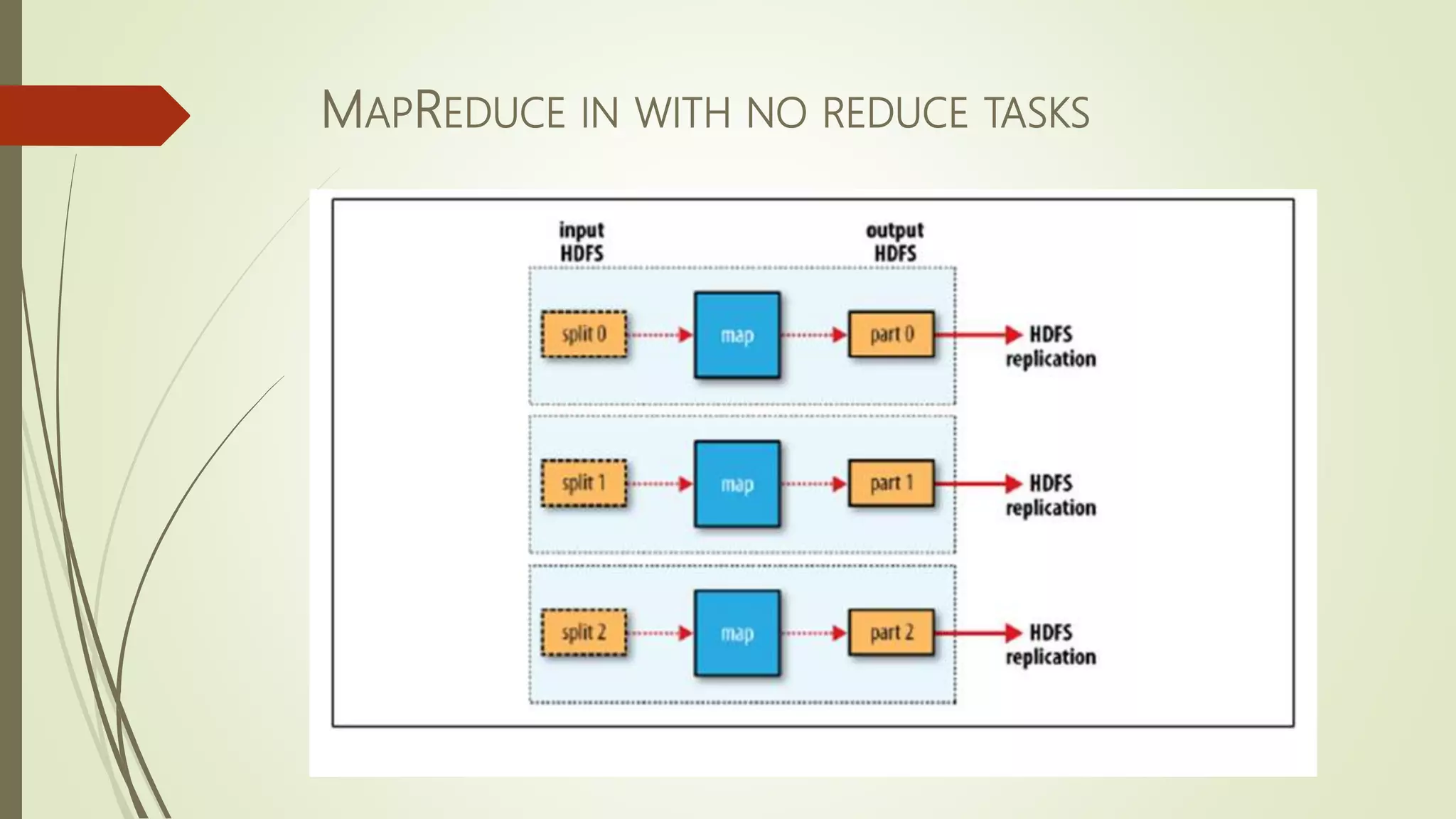
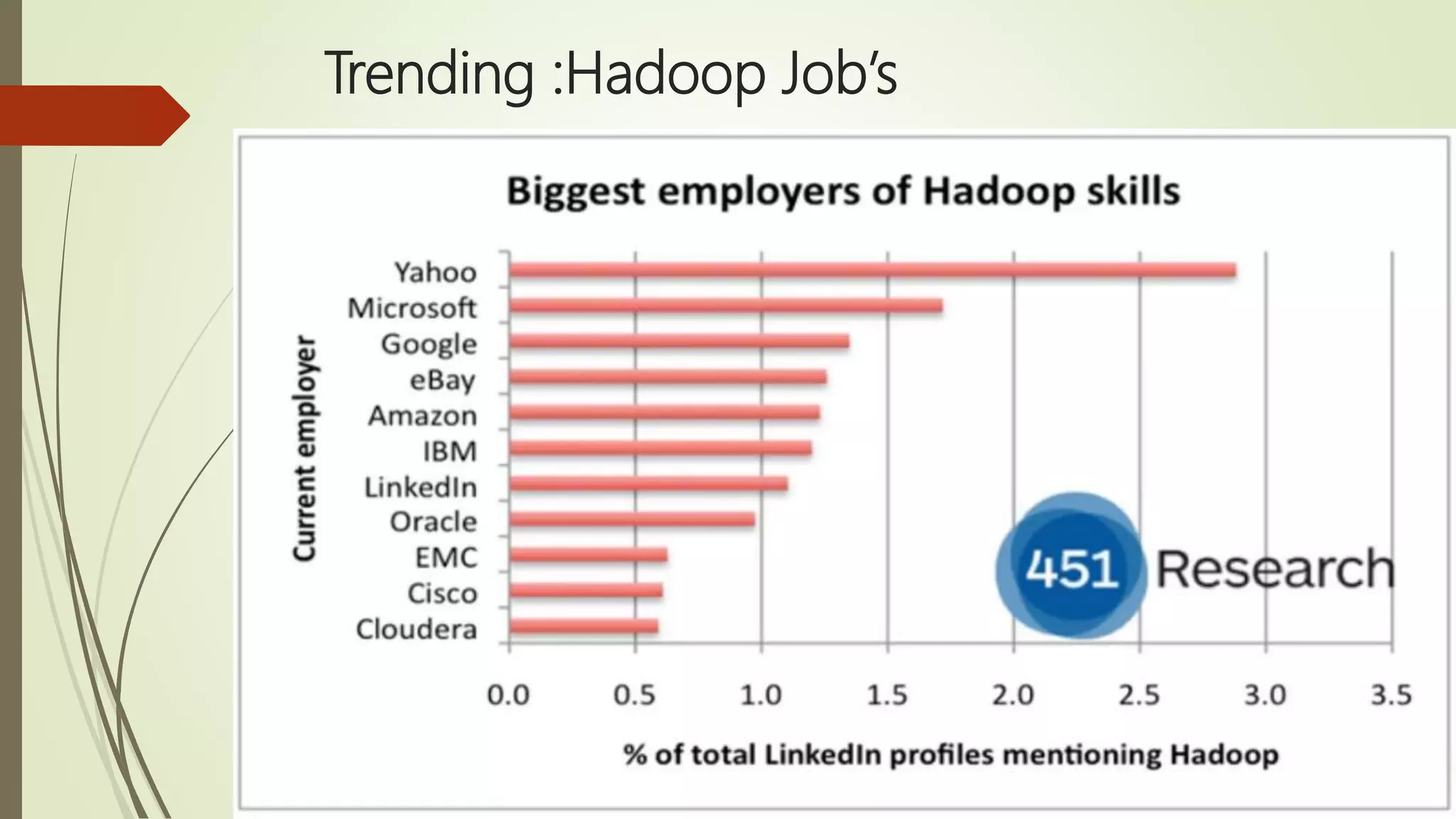
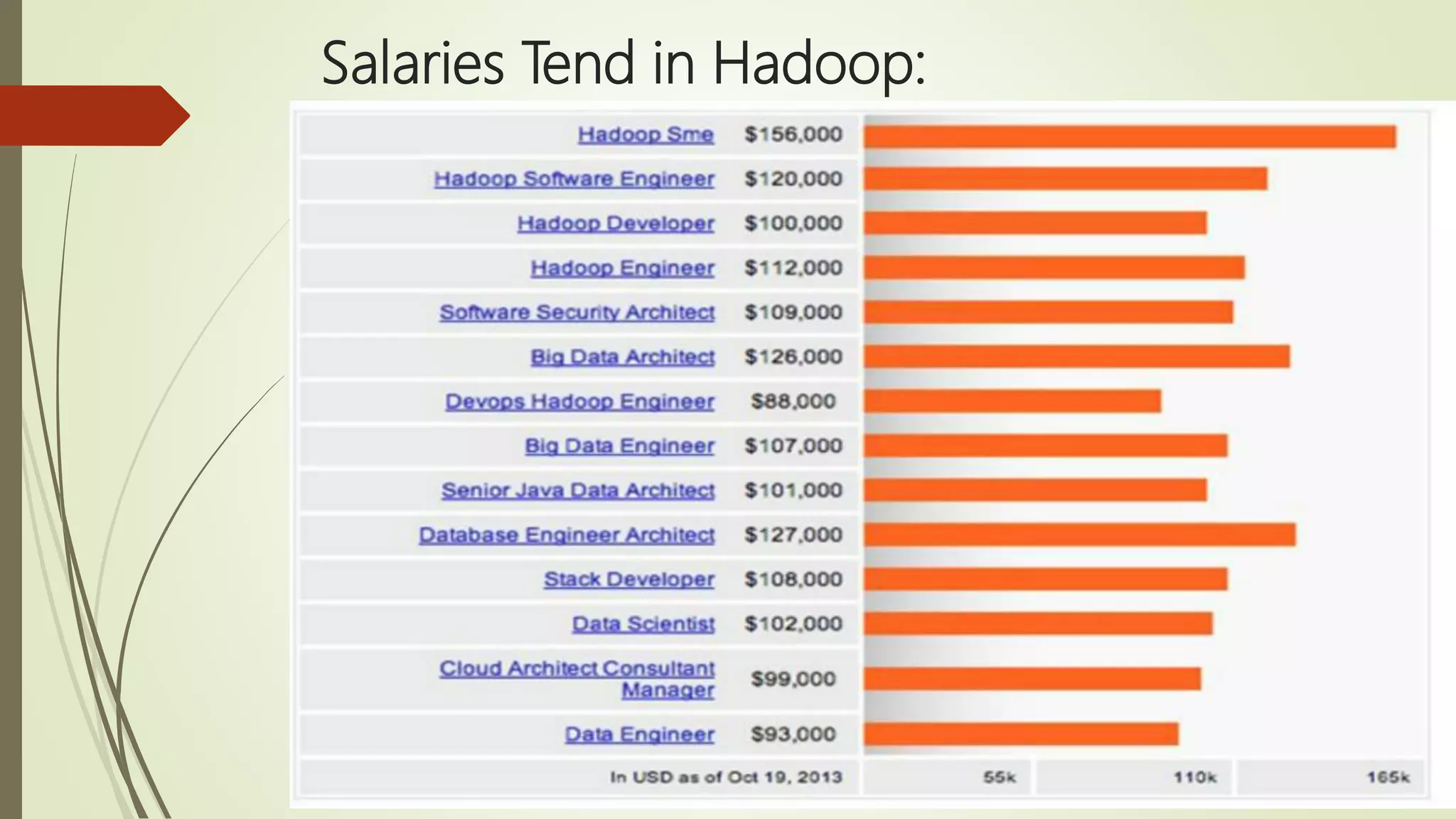
The document discusses big data, its challenges in processing large datasets, and introduces Hadoop as a solution developed for distributed data processing. It describes Hadoop's architecture, including HDFS and MapReduce components, and highlights its prominent users in the industry. The conclusion emphasizes Hadoop's capability to efficiently handle data and computations, making it a valuable tool for modern IT challenges.