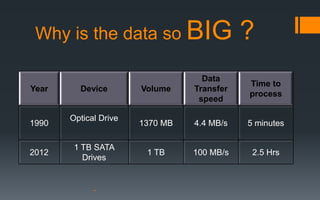
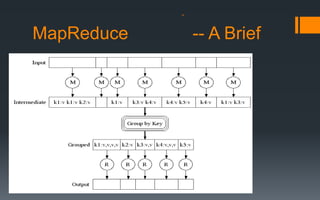
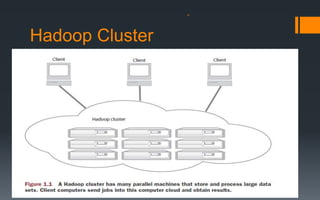
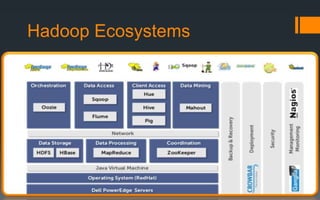
This document provides an overview of Hadoop, a tool for processing large datasets across clusters of computers. It discusses why big data has become so large, including exponential growth in data from the internet and machines. It describes how Hadoop uses HDFS for reliable storage across nodes and MapReduce for parallel processing. The document traces the history of Hadoop from its origins in Google's file system GFS and MapReduce framework. It provides brief explanations of how HDFS and MapReduce work at a high level.