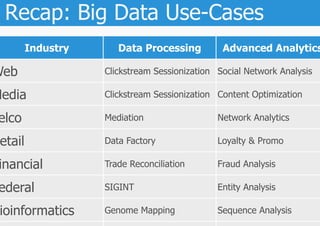
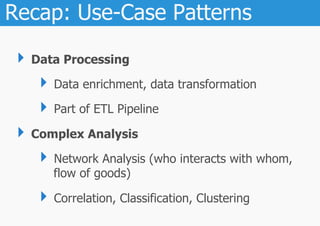
The document discusses the importance of big data use-cases across various industries and emphasizes the need for businesses to leverage data for solving immediate problems and driving innovation. It outlines the maturity levels of big data applications, from improving existing models to creating new, data-driven business models. Additionally, it highlights the challenges of using external data sources and legal considerations regarding data privacy in Europe.