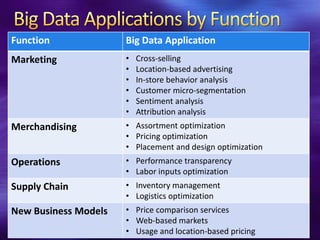
The document explores the significance of big data in business, emphasizing its role in enhancing decision-making and agility through the integration of diverse data sources. It highlights industry use cases and applications where big data creates competitive advantages, such as marketing optimization, supply chain efficiency, and tailored customer experiences. Additionally, it discusses the evolving technologies and practices for handling large, complex datasets, illustrating how organizations can derive actionable insights to drive business success.