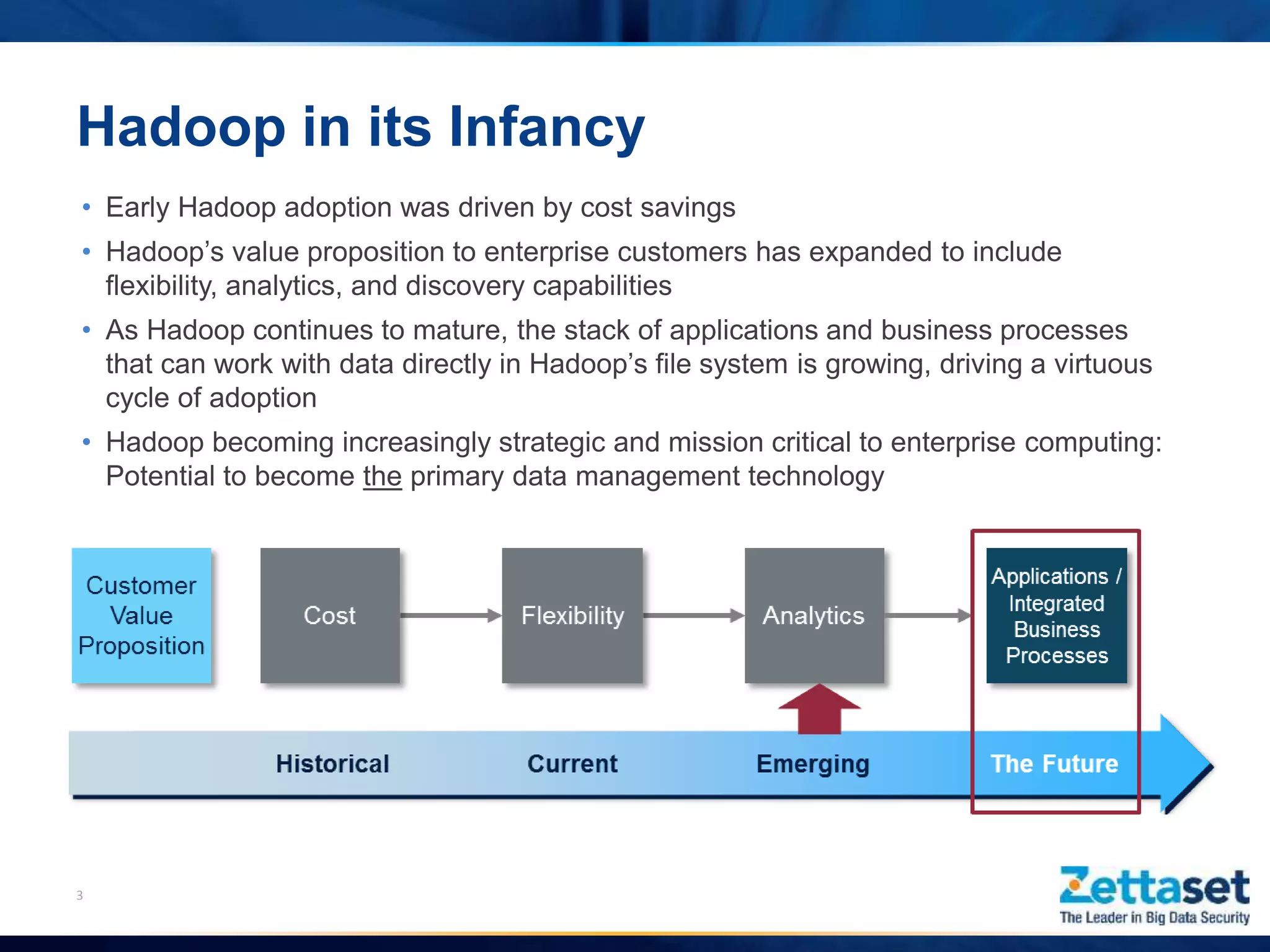
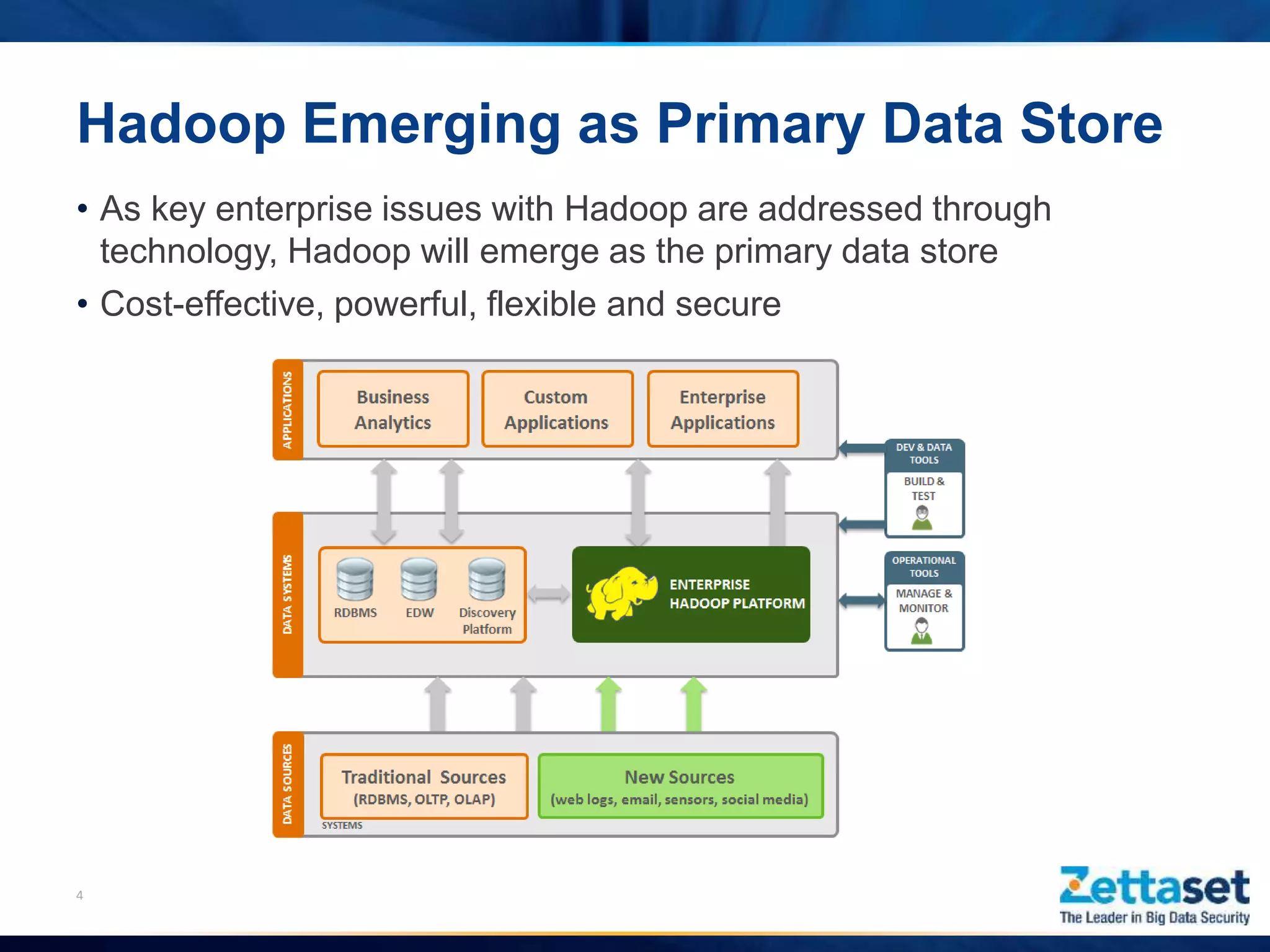
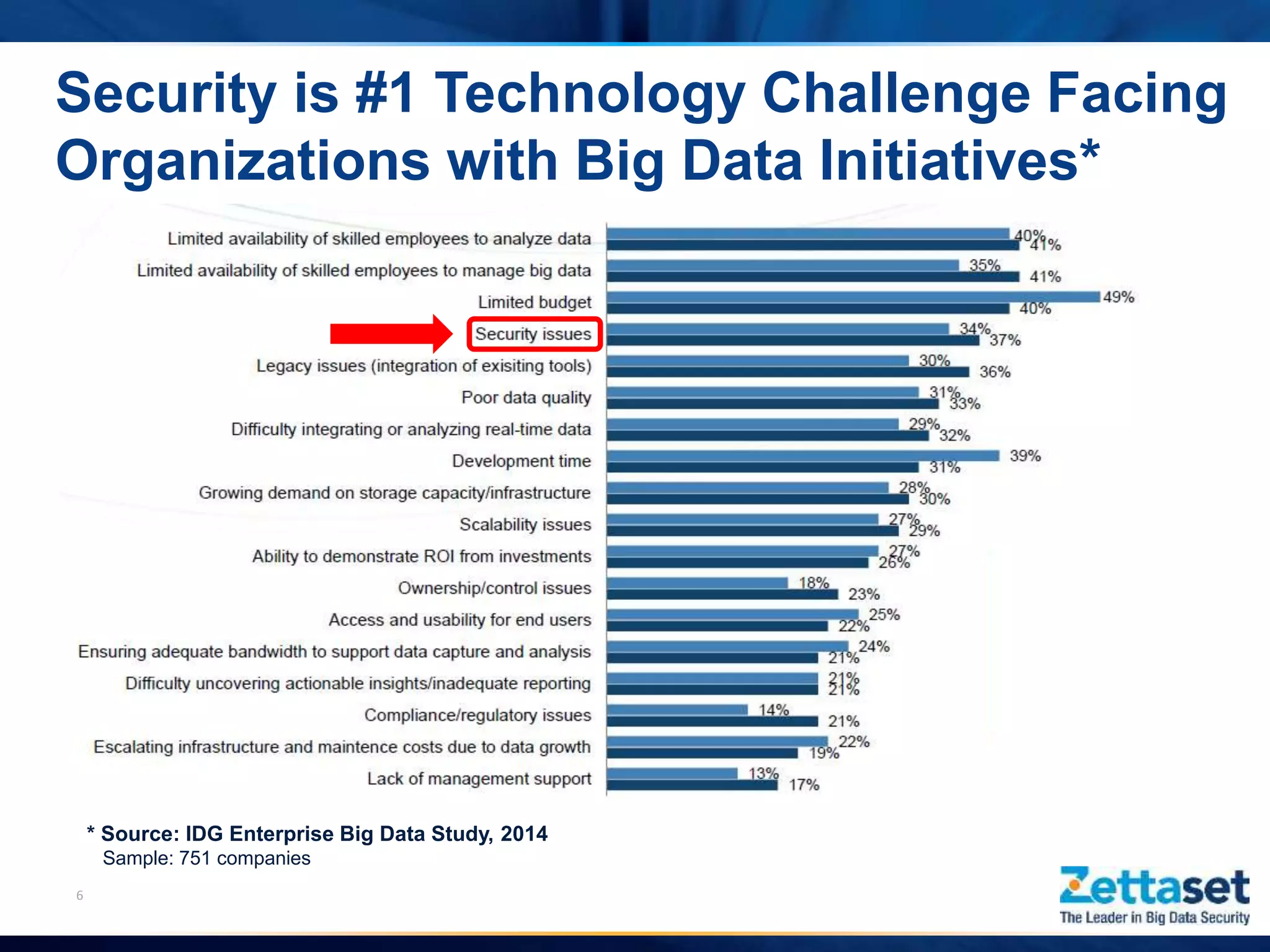
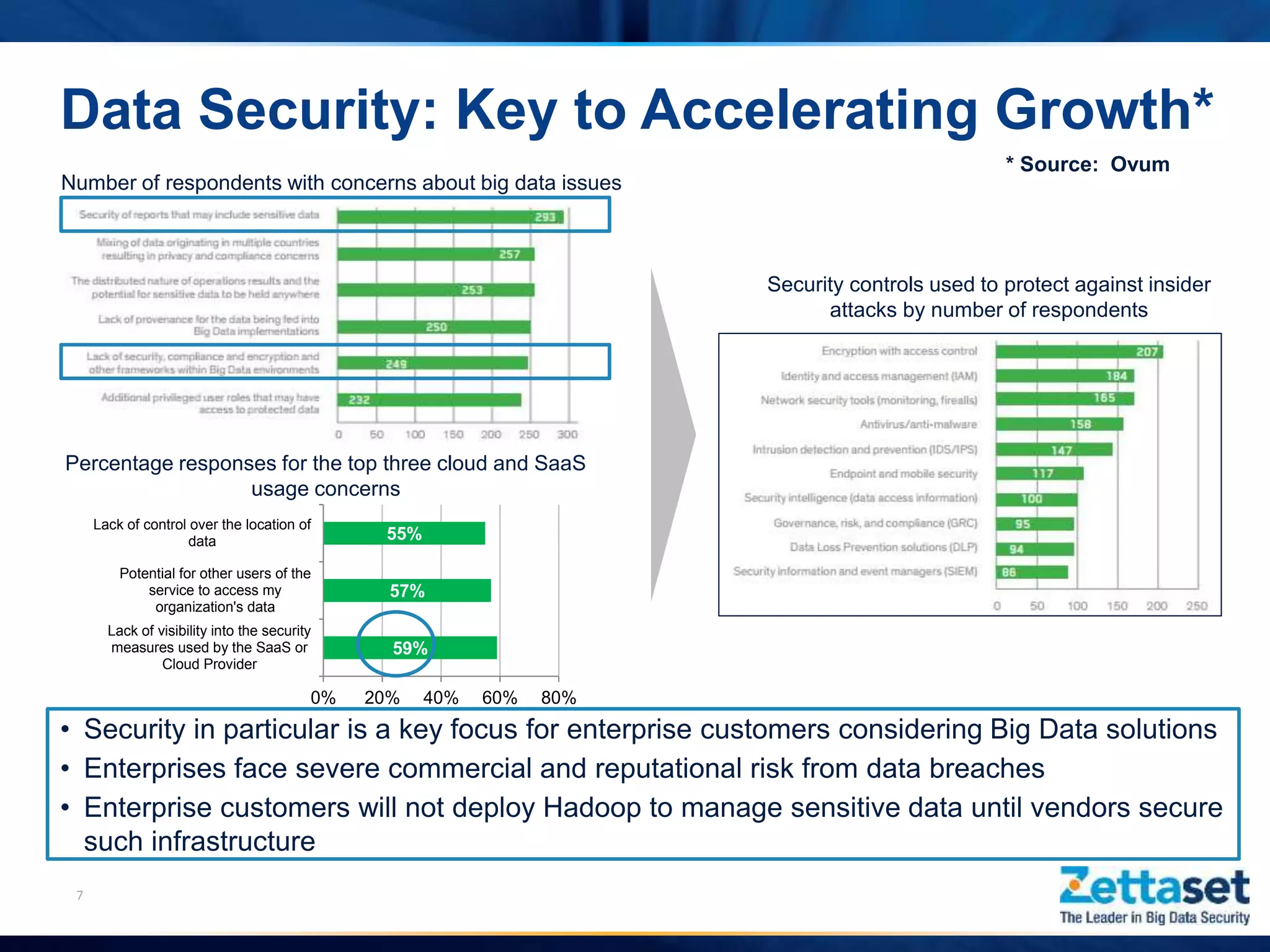
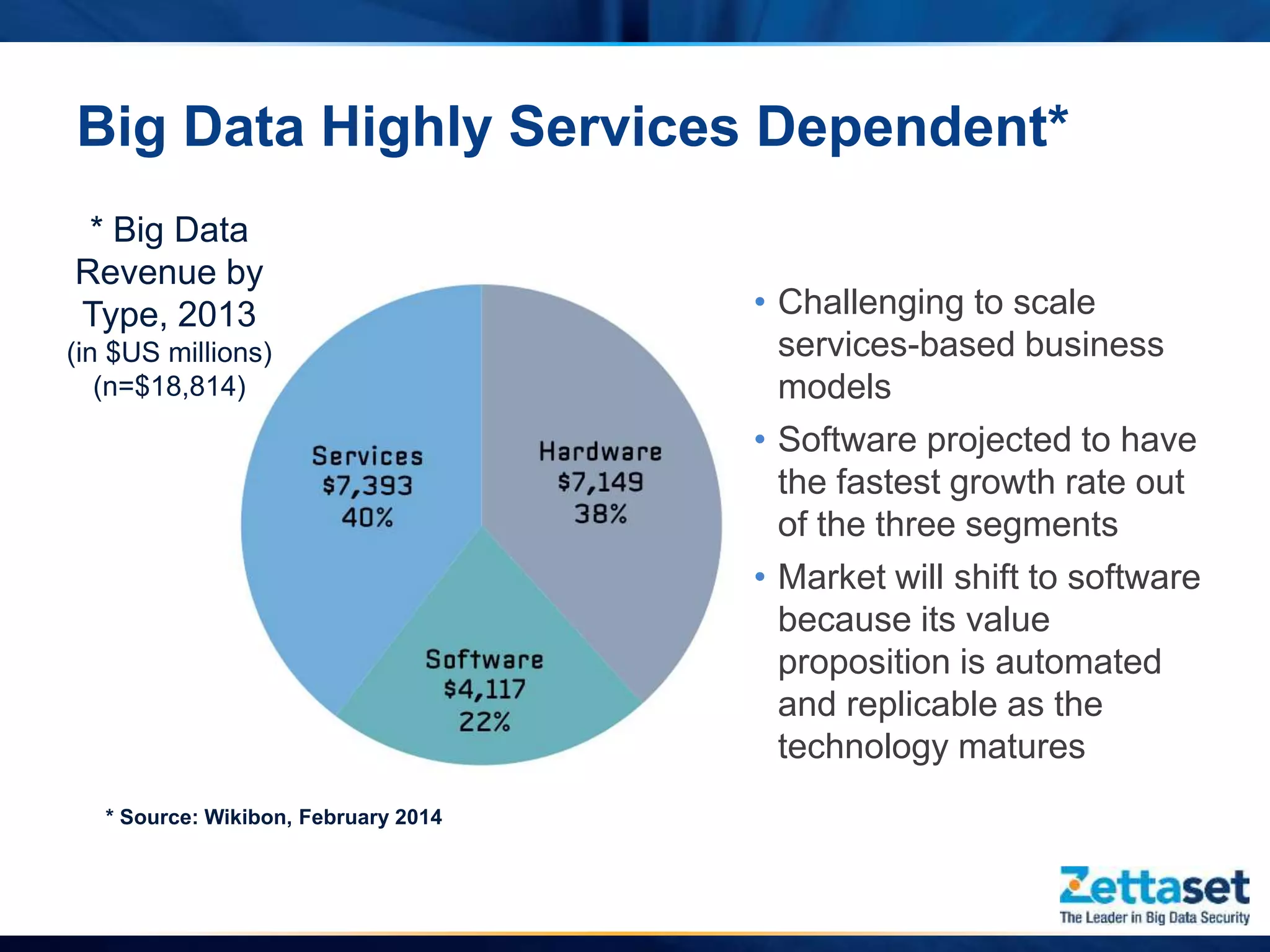
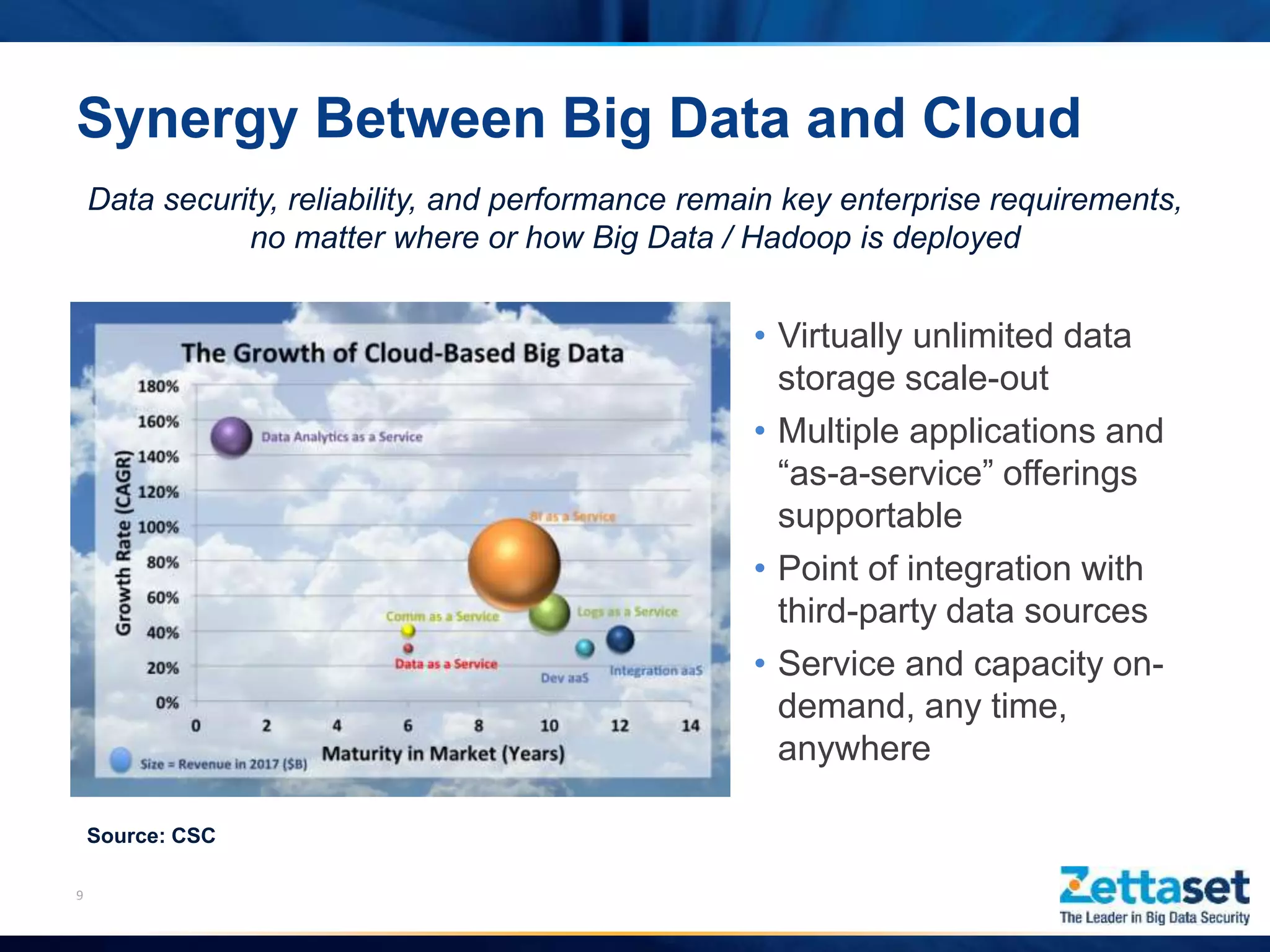
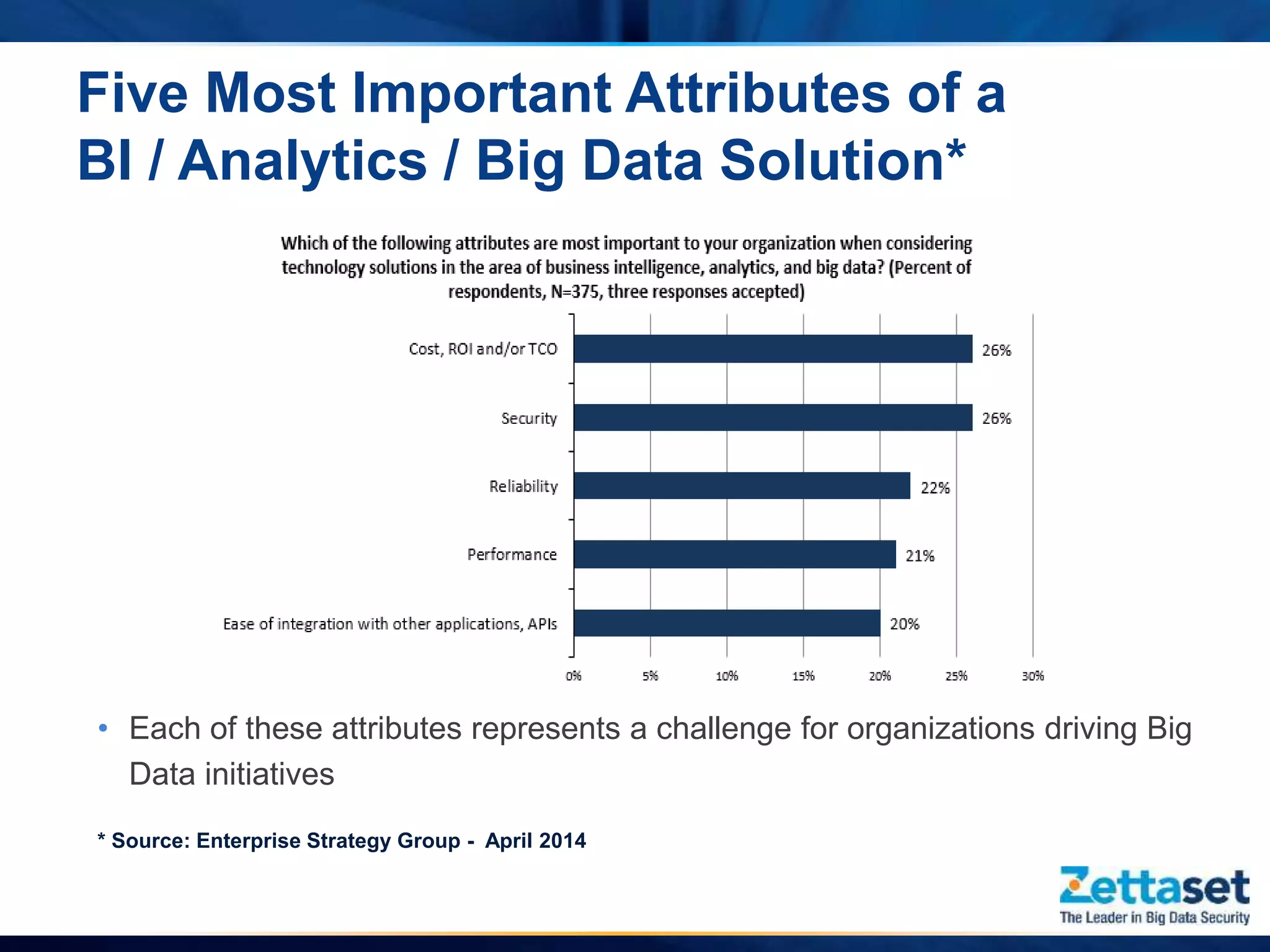
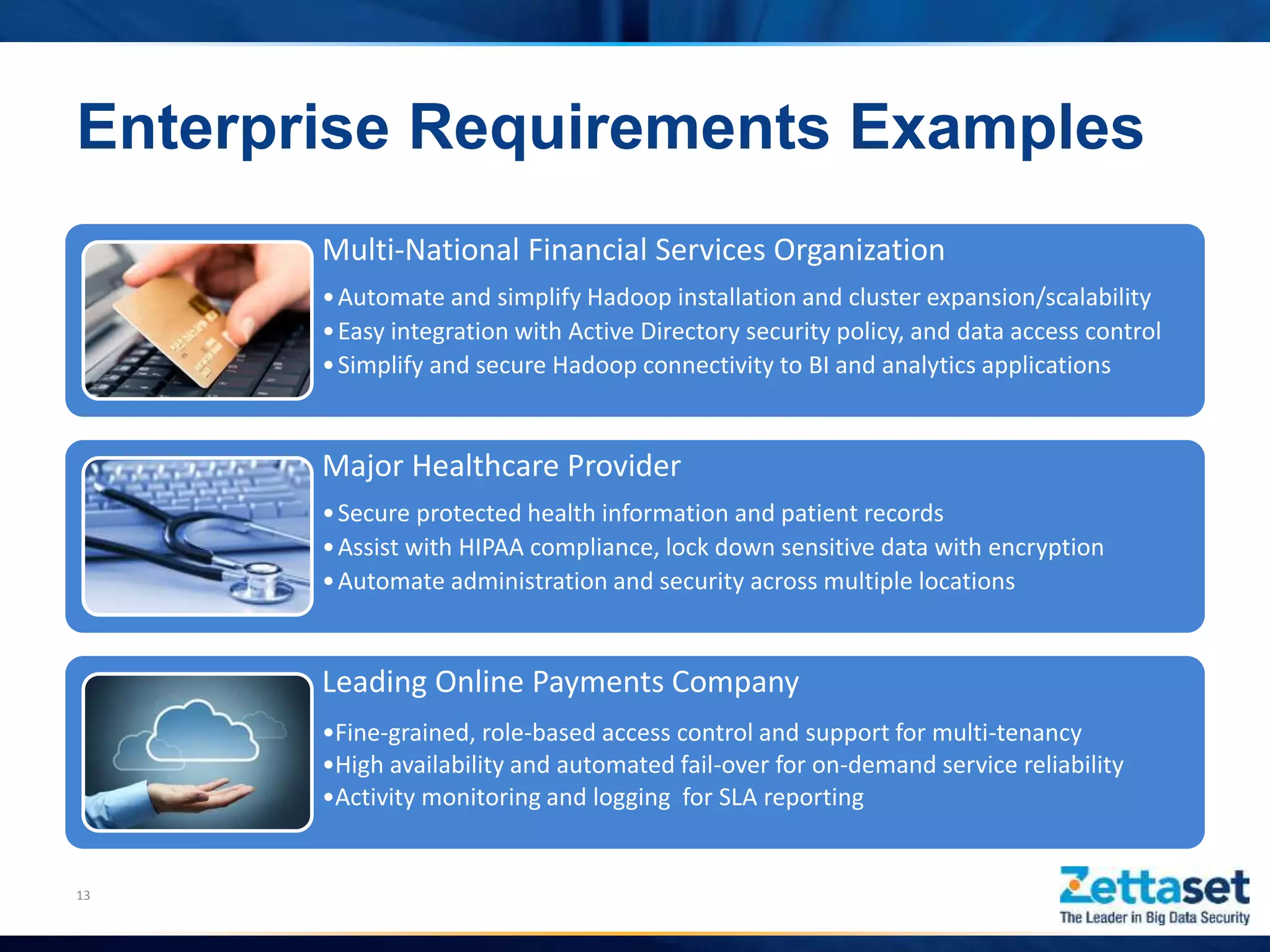
This document summarizes a presentation given by Jim Vogt, President and CEO of Zettaset, on making Hadoop work in business units. It outlines how customer focus is shifting to higher layers of the big data stack like analytics and applications. While Hadoop's value proposition has expanded, enterprises face issues with security, reliability, integration and reliance on professional services. The document discusses use cases in financial services, healthcare and retail payments and how meeting requirements like data security, availability and multi-tenancy is key to Hadoop adoption. It concludes that focus needs to be on business applications over database mechanics with comprehensive security and simplified integration into existing systems and processes.