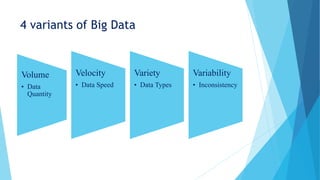
This presentation introduces big data and data mining. Big data refers to extremely large data sets that cannot be processed by traditional software. Data mining is the process of discovering patterns in large data sets using machine learning, statistics, and database systems. The presentation discusses key facts about the growth of data, examples of big data sources like Facebook and Google, challenges of big data like hardware limitations, and solutions like parallel computing. Common big data mining tools are also introduced, including Hadoop, Apache S4, and Storm. Applications of big data and data mining are highlighted in various domains like healthcare, public sector, and biology.