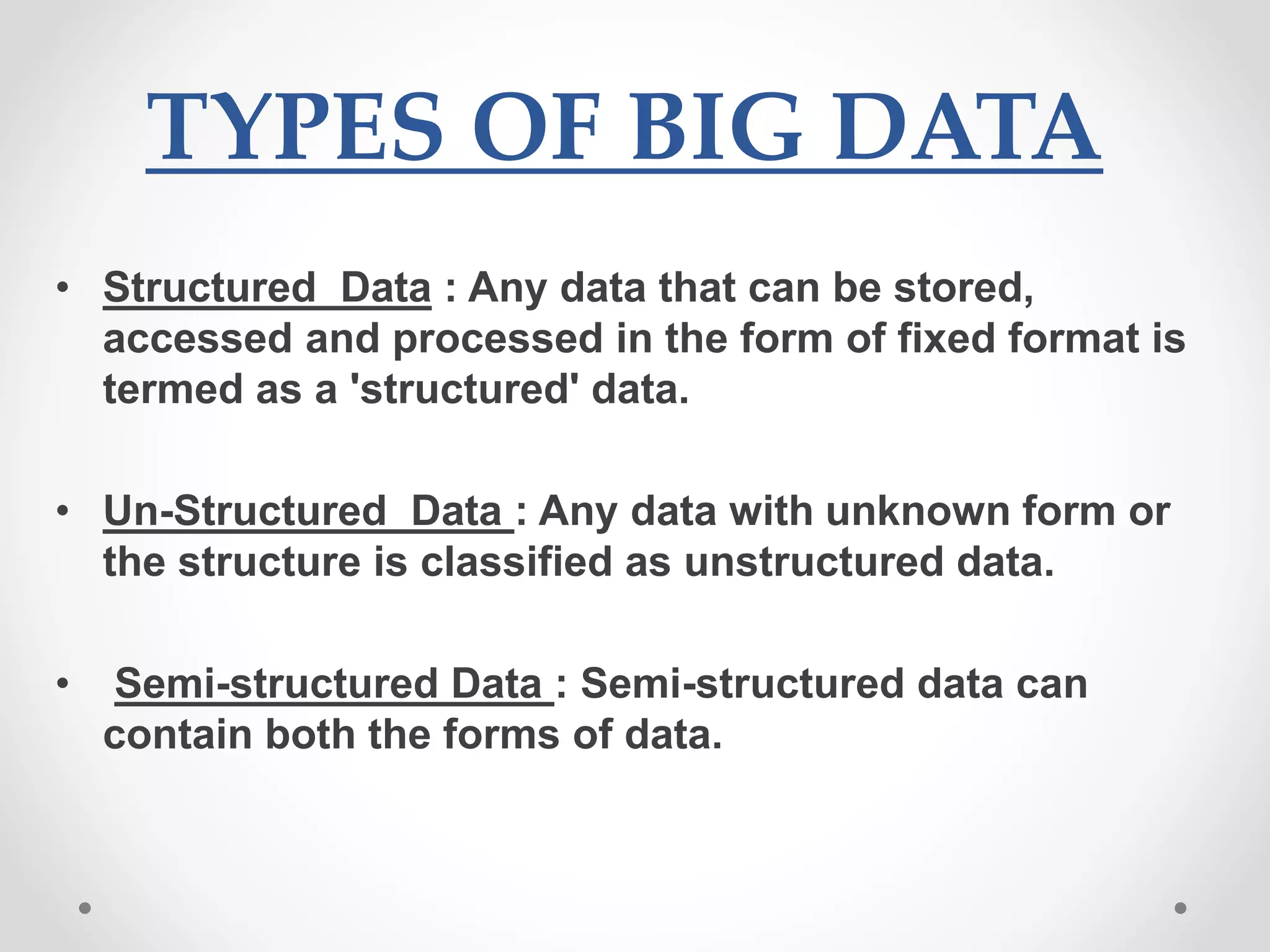
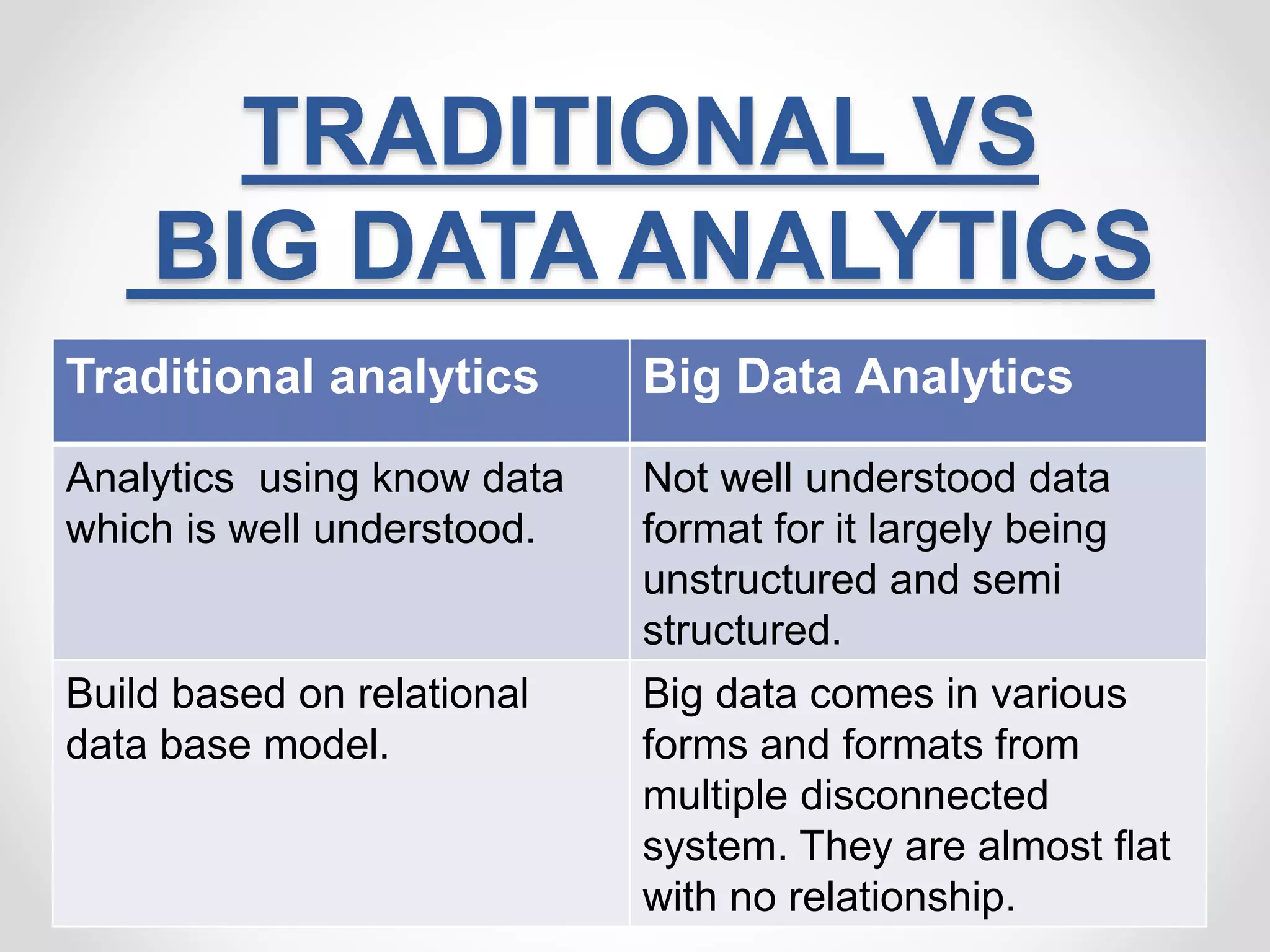
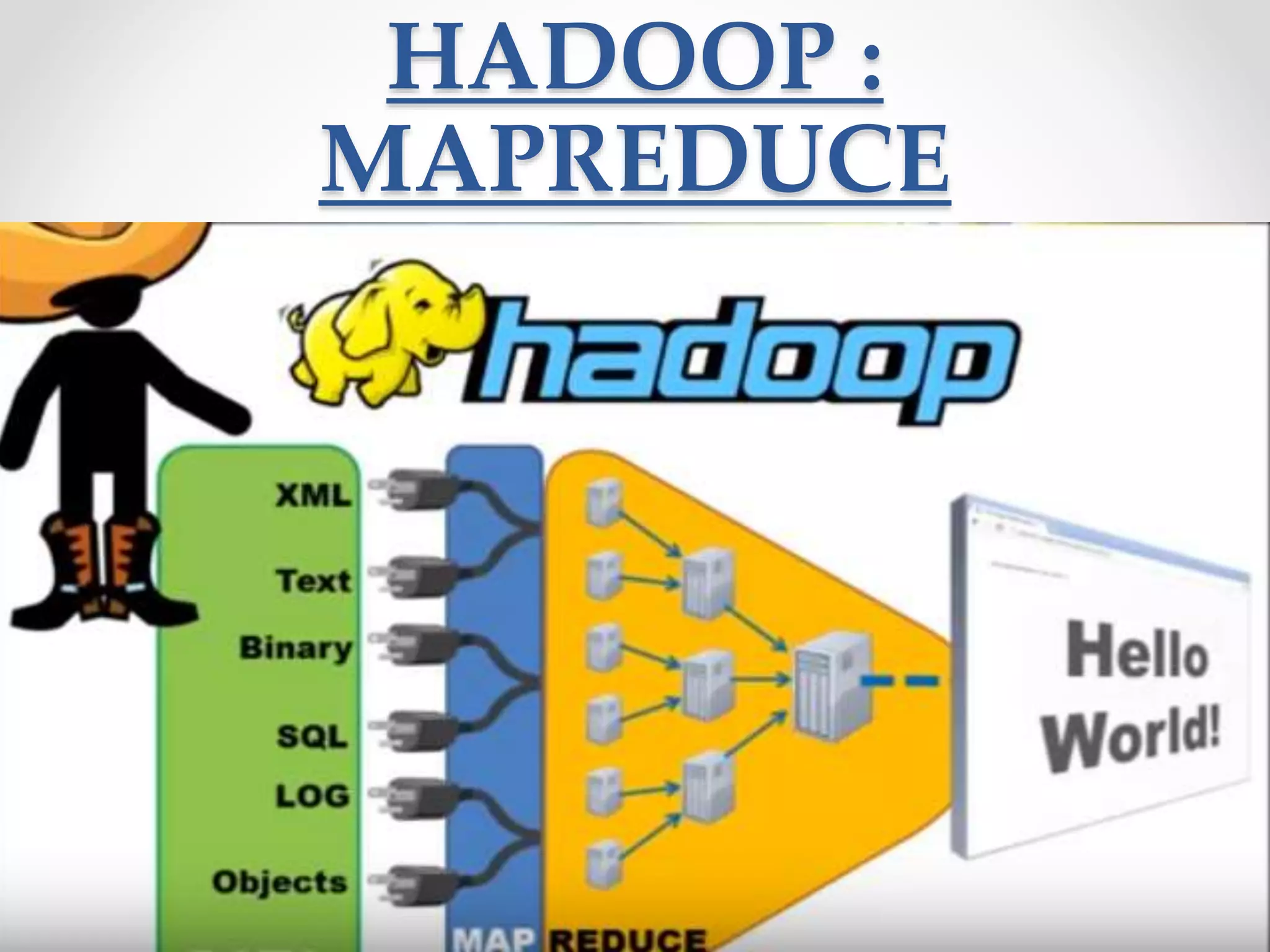
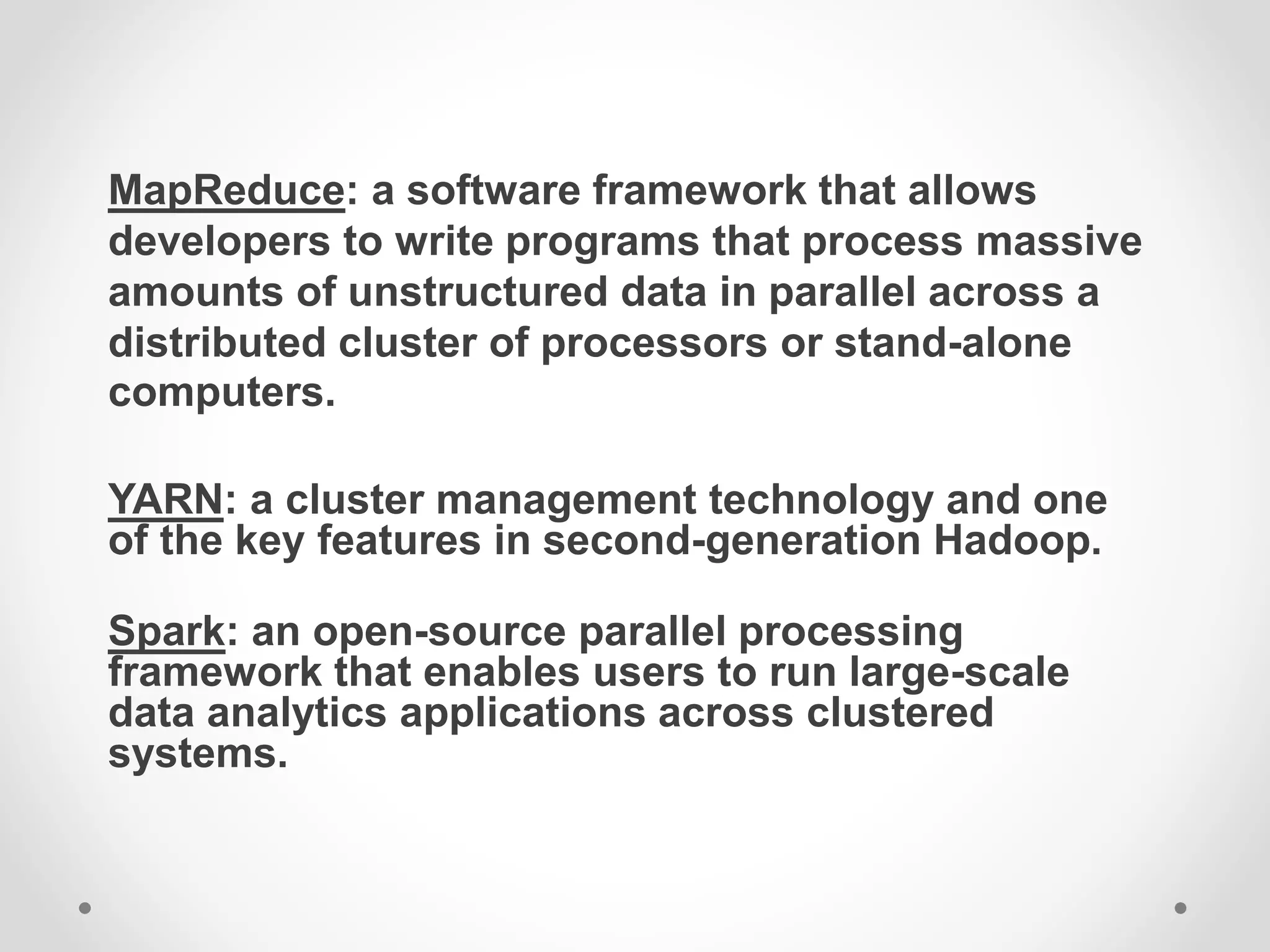
This document provides an overview of big data and big data analytics. It defines big data as large, complex datasets that grow quickly in volume and variety. Big data analytics involves examining these large datasets to find patterns and useful information. The challenges of big data include increased storage needs and handling diverse data formats. Hadoop is a framework that allows distributed processing of big data across clusters of computers. Common big data analytics tools include MapReduce, Spark, HBase and Hive. The benefits of big data analytics include improved decision making, customer service and efficiency.




![DATA VS BIG DATA
Big data is just data with:
• More volume
• Faster data generation (velocity)
• Multiple data format (variety)
World's data volume to grow 40%
per year & 50 times by 2020 [1]
Data coming from various human
& machine activity](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataanalytics-180614075942/75/Big-data-analytics-5-2048.jpg)