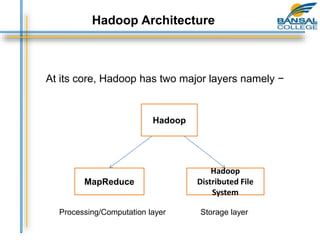
This document provides an overview of the key concepts around big data and Hadoop. It discusses big data sources and challenges, including capturing, storing, searching, sharing, transferring, analyzing and presenting large amounts of data. It then describes how Hadoop provides a cost-effective solution for storage and processing of big data using a distributed architecture. Finally, the document outlines the core components of Hadoop including the Hadoop Distributed File System for storage and MapReduce for distributed processing.