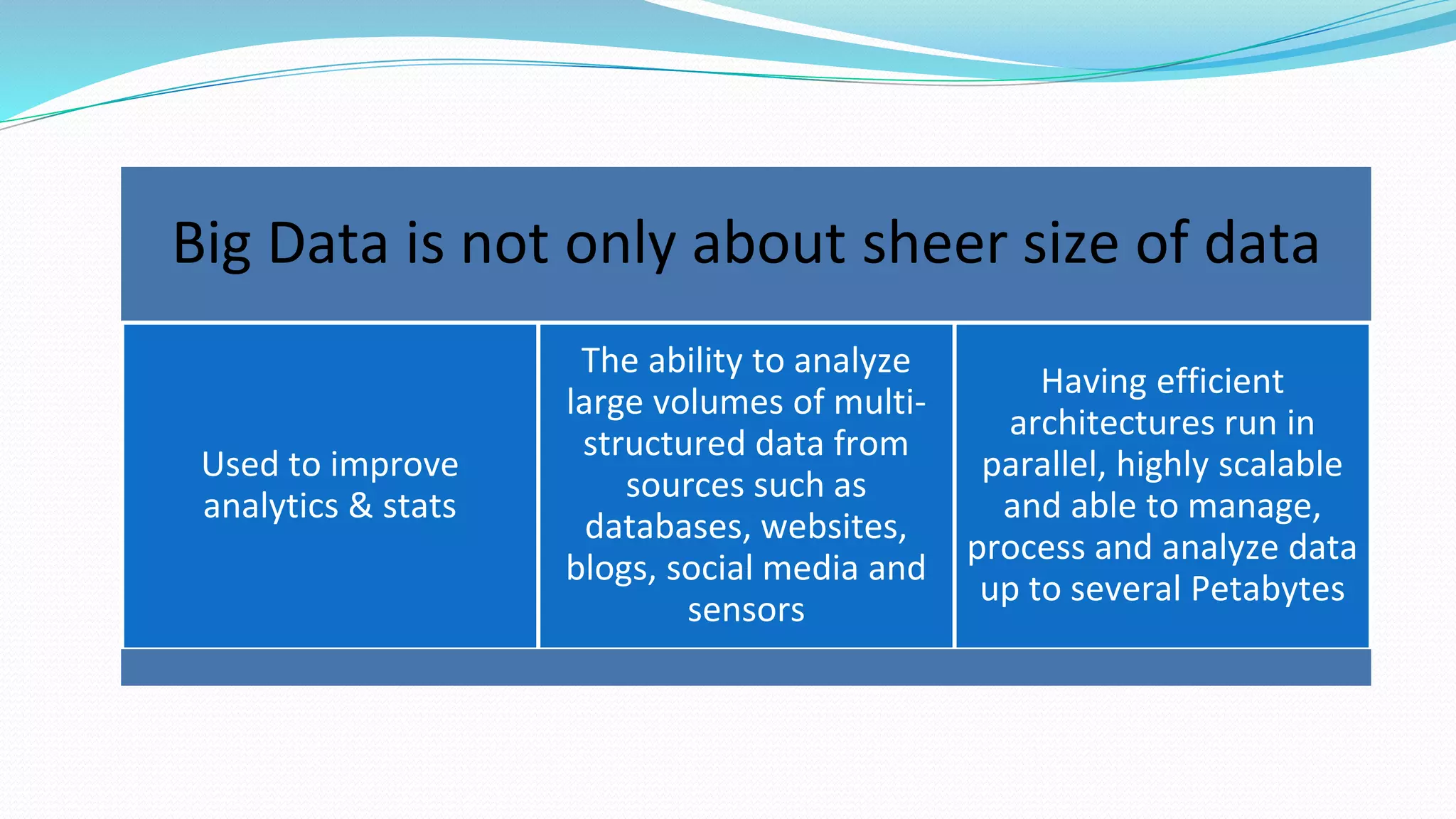
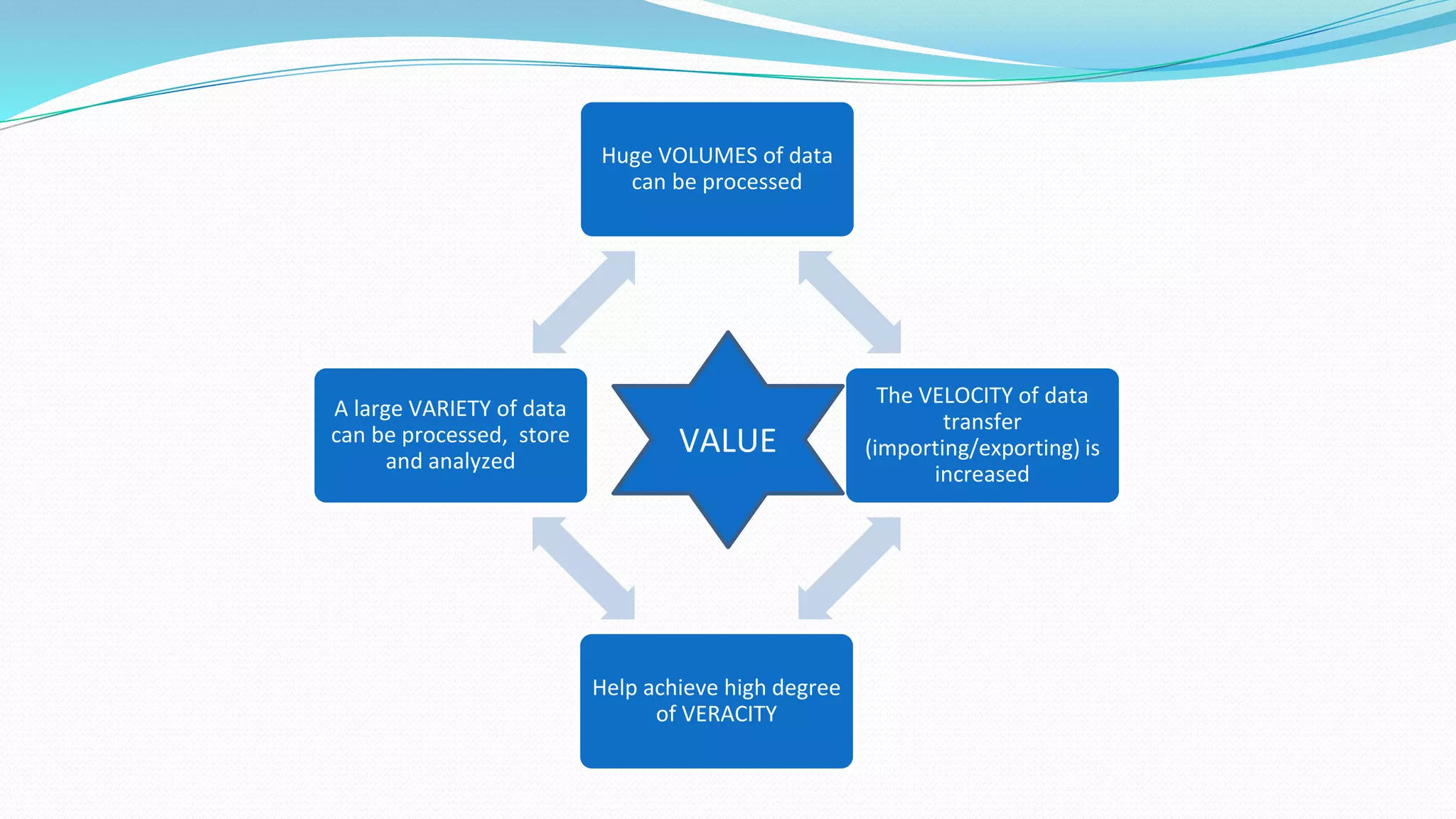
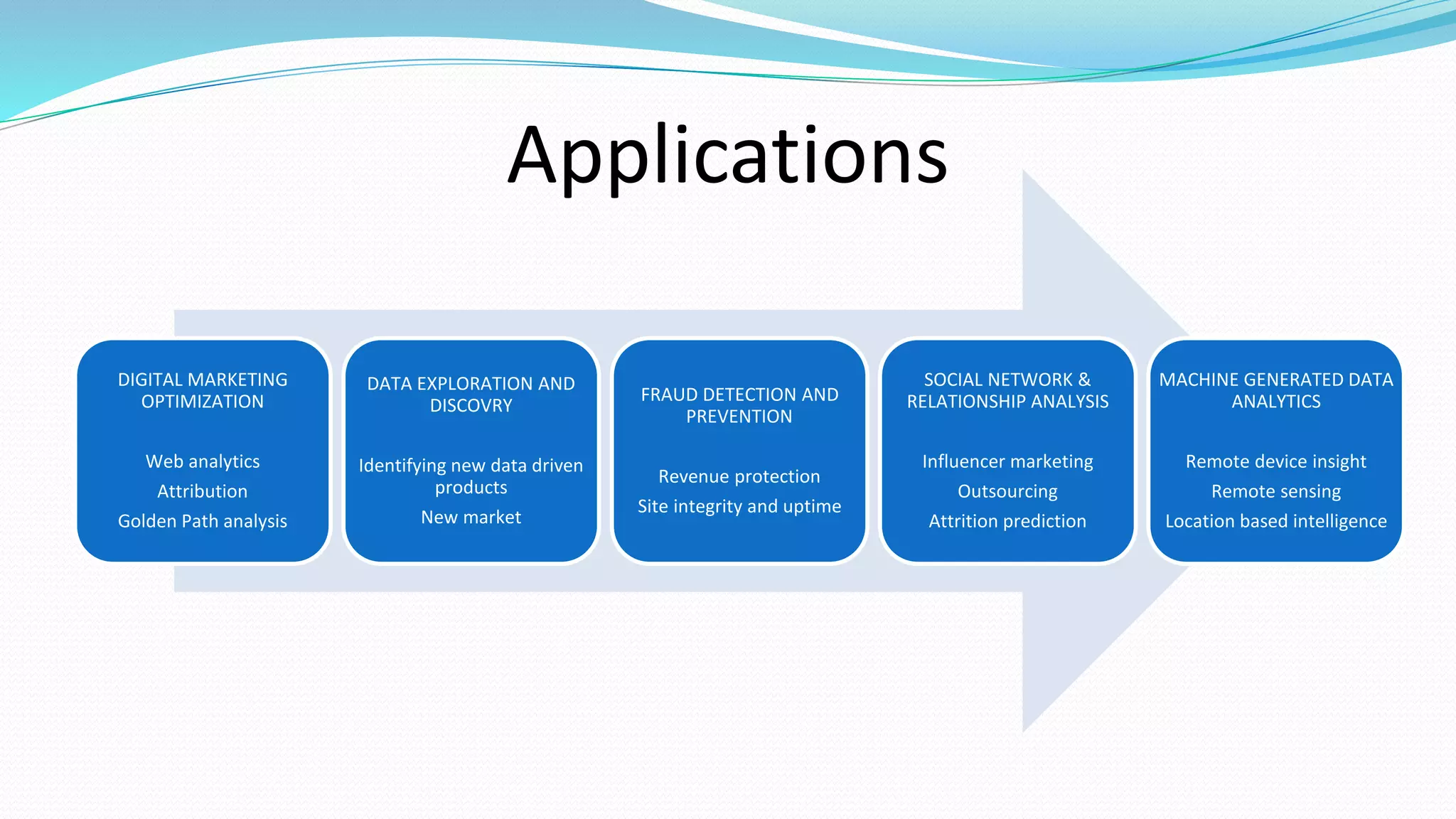
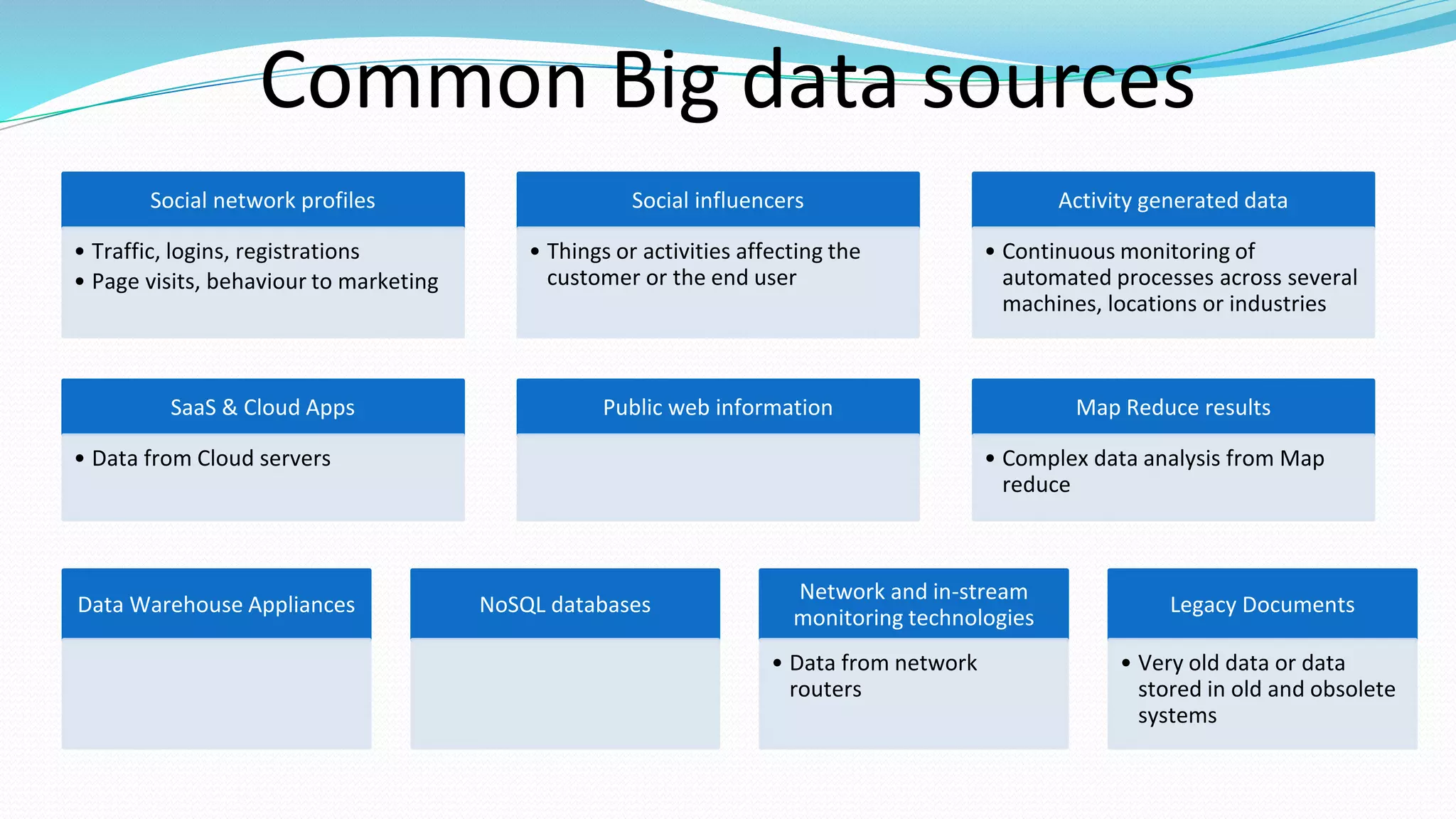
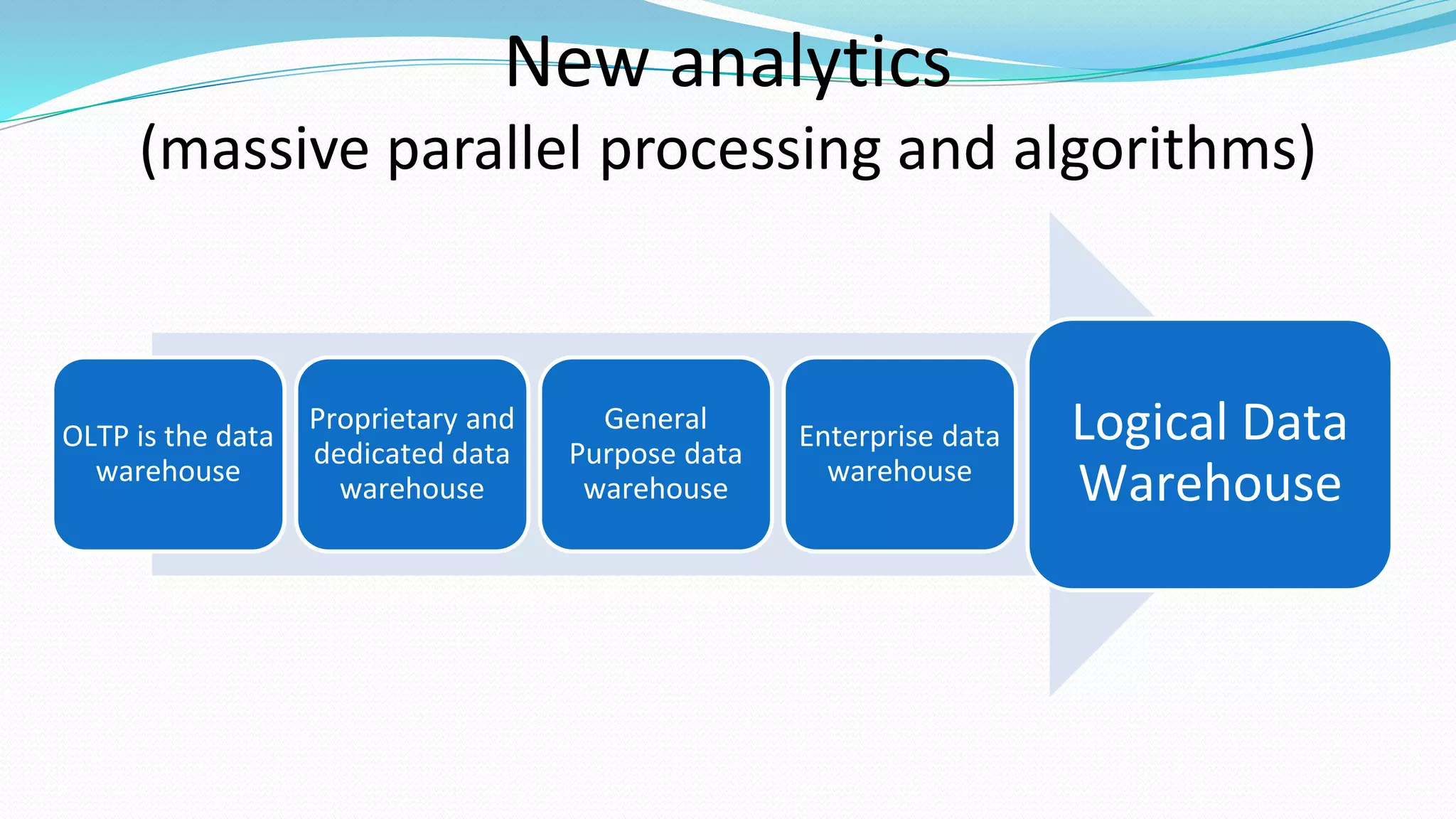
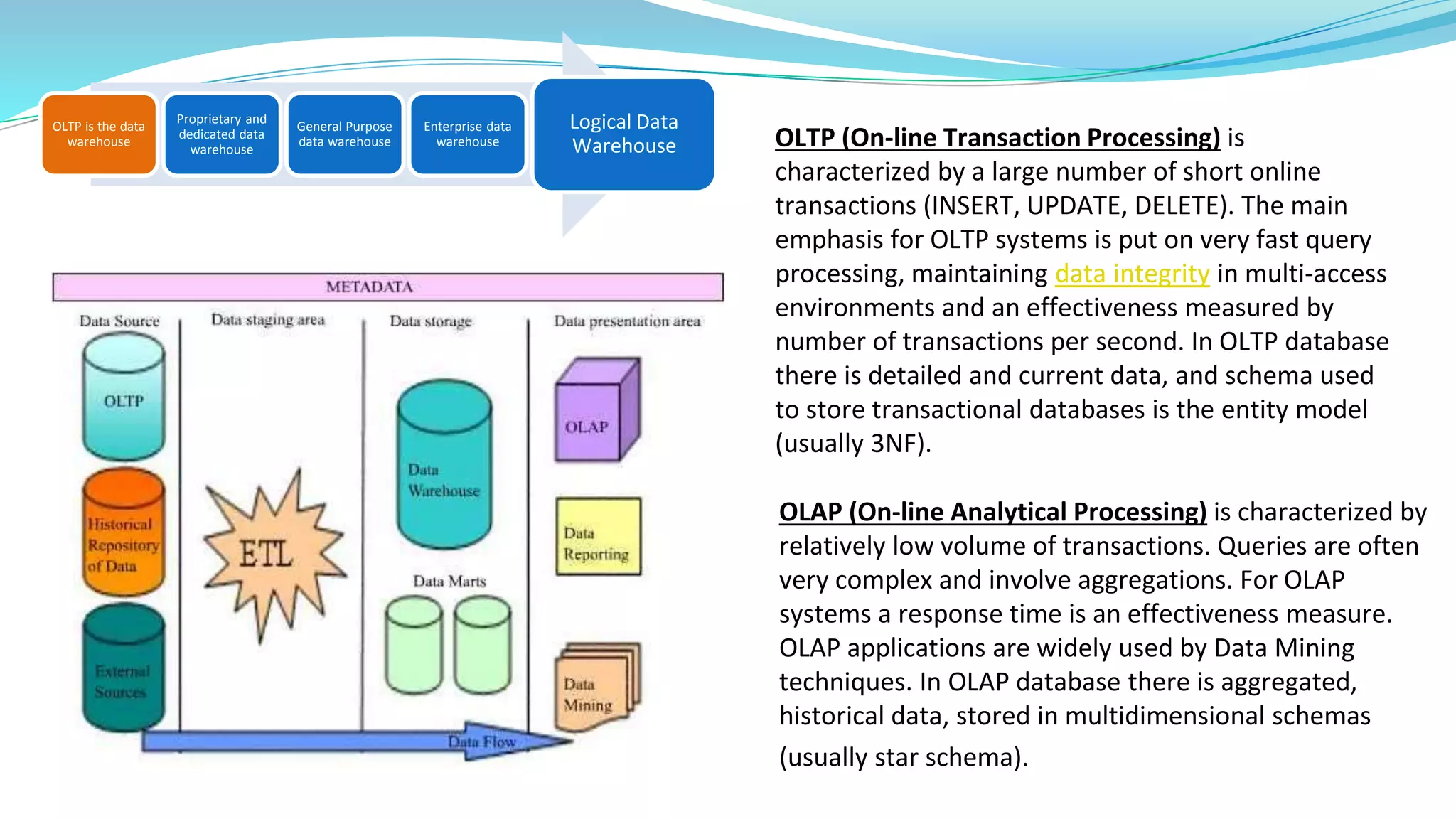
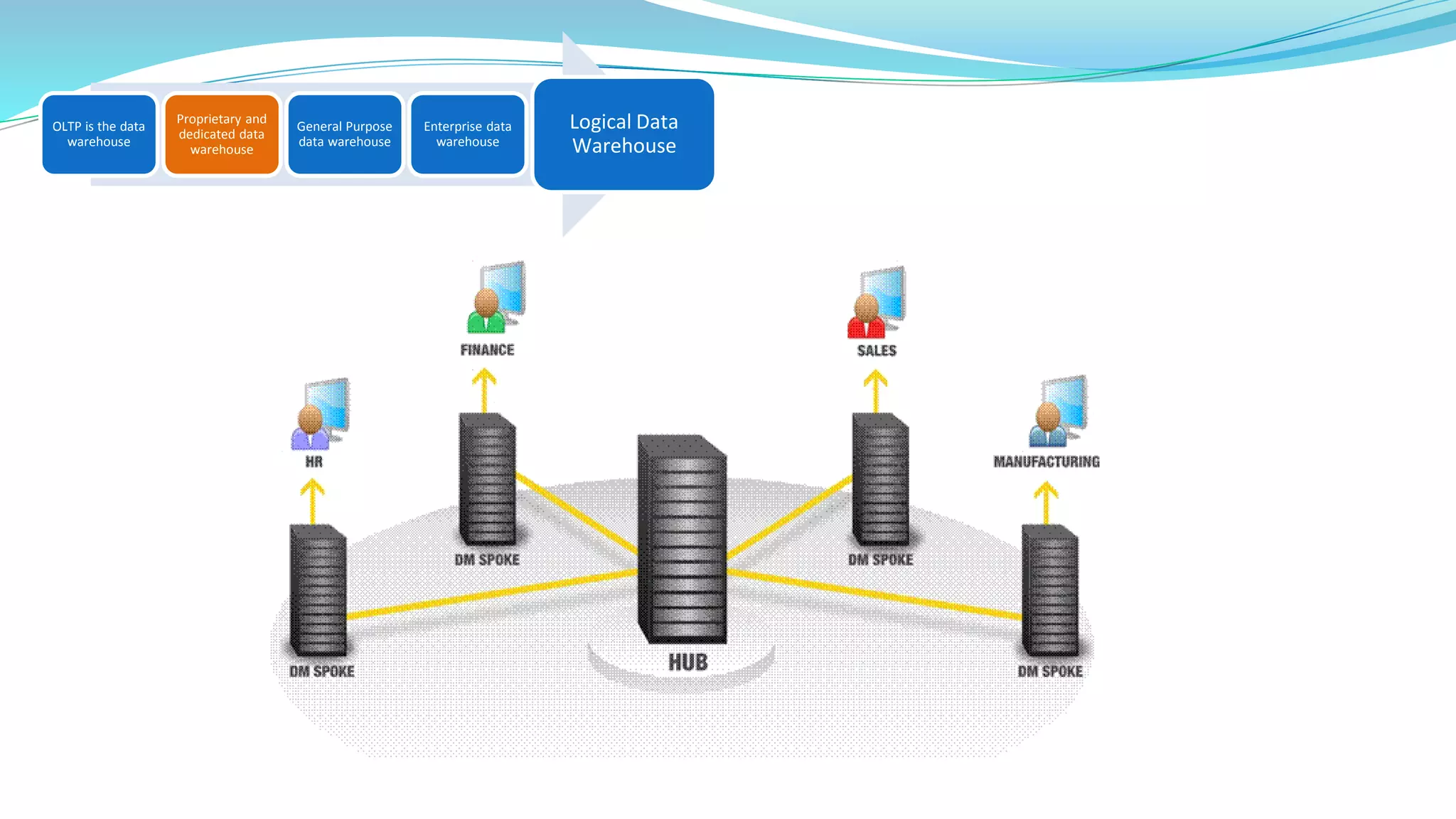
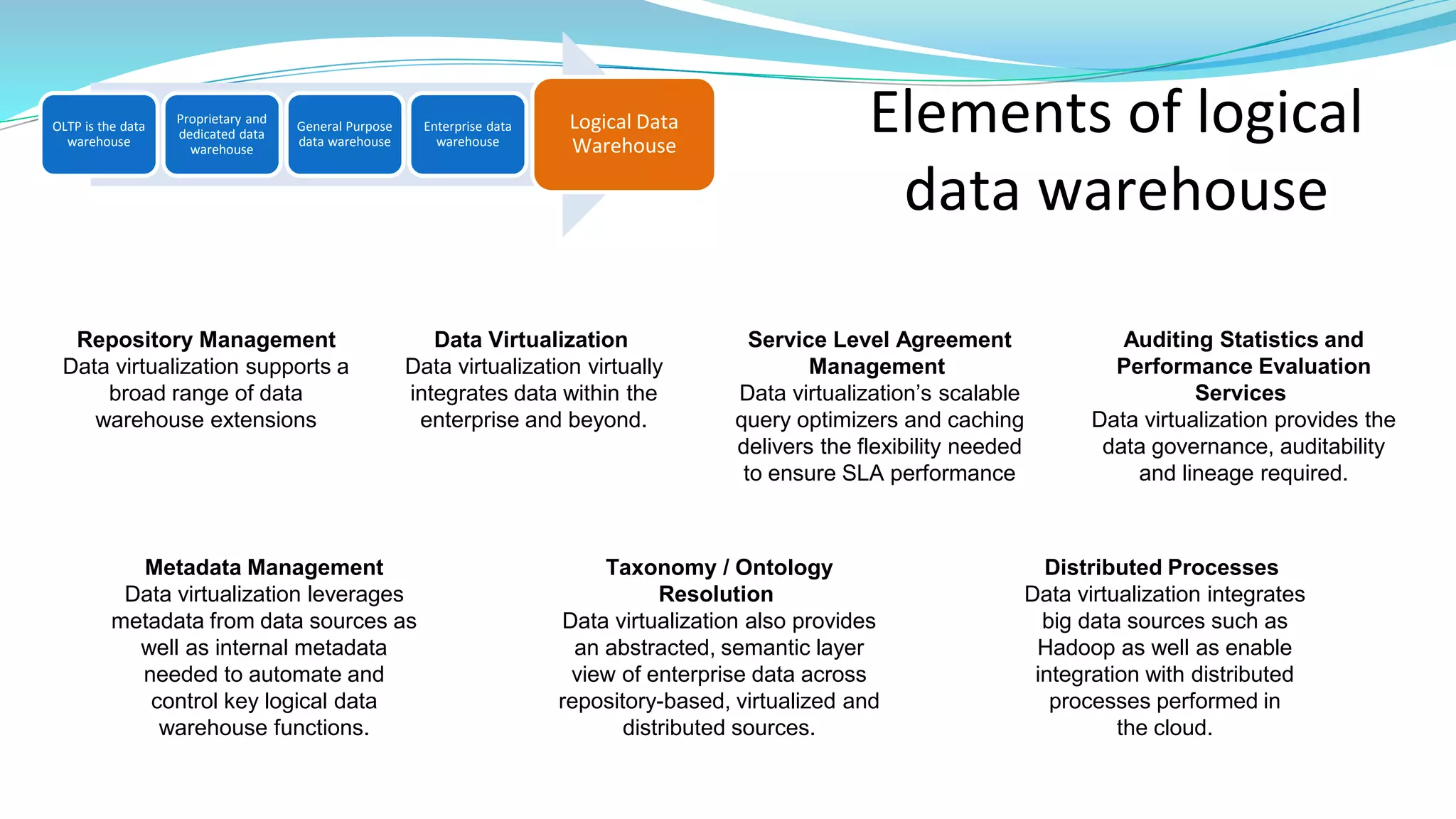
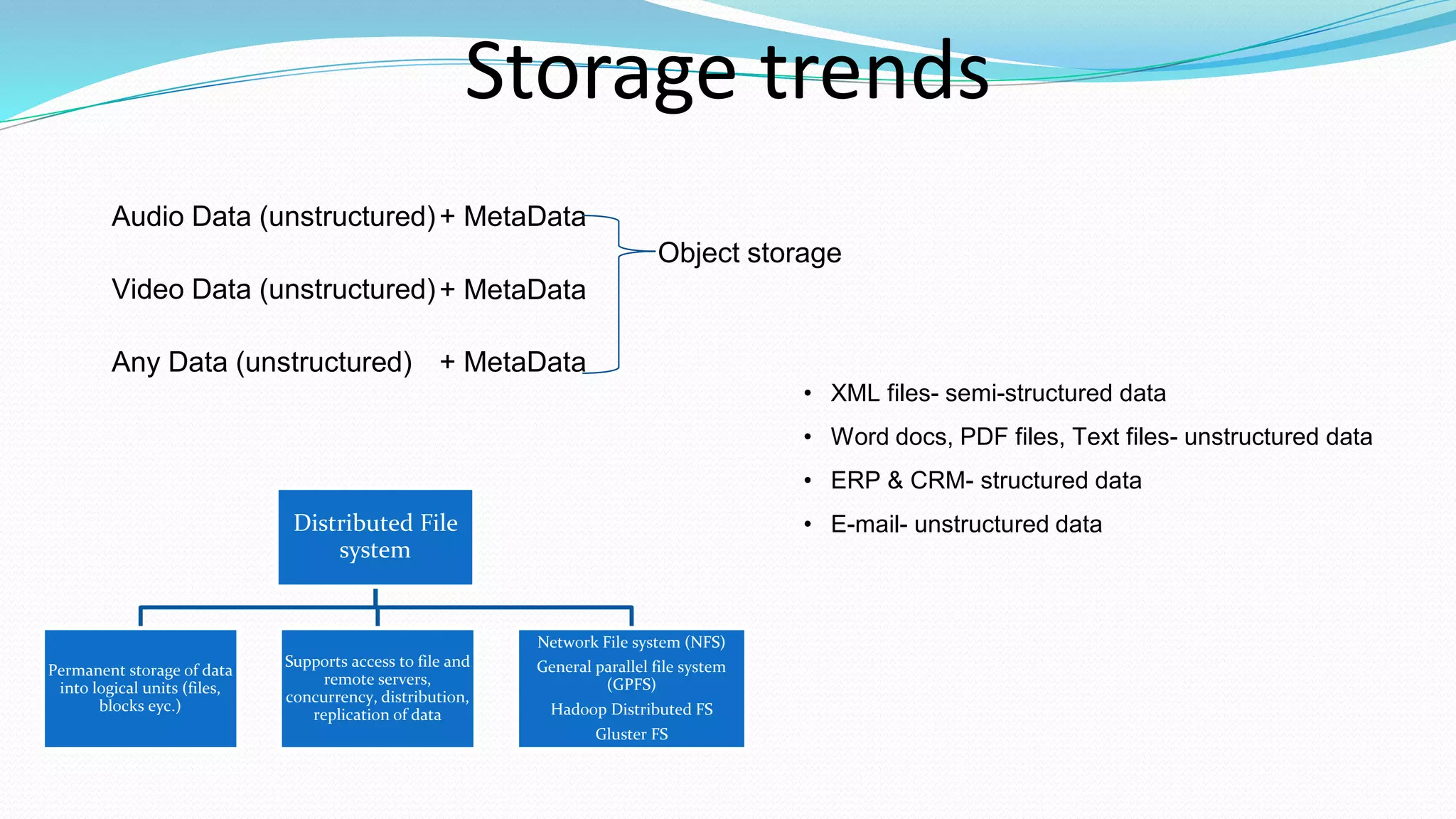
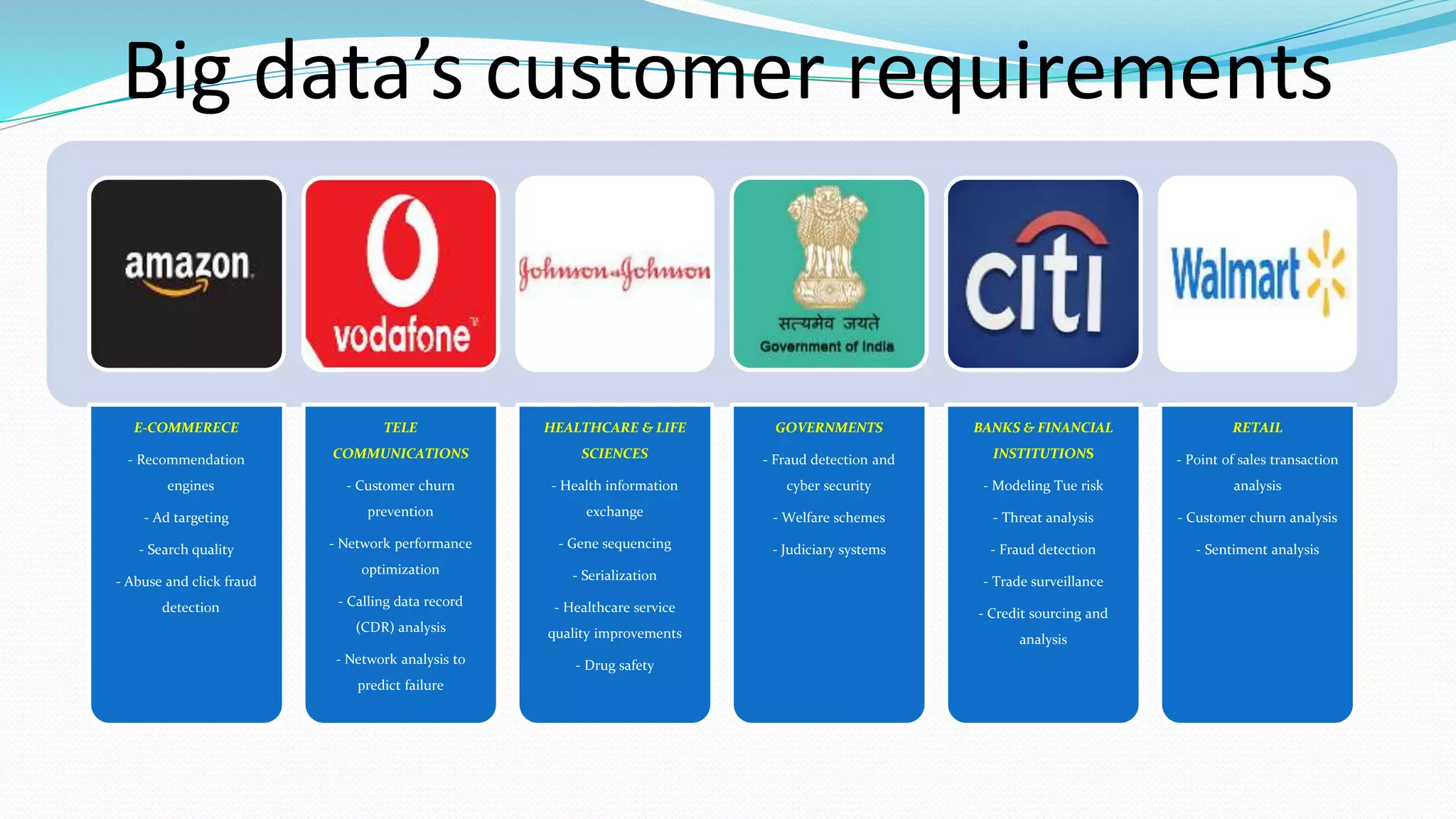
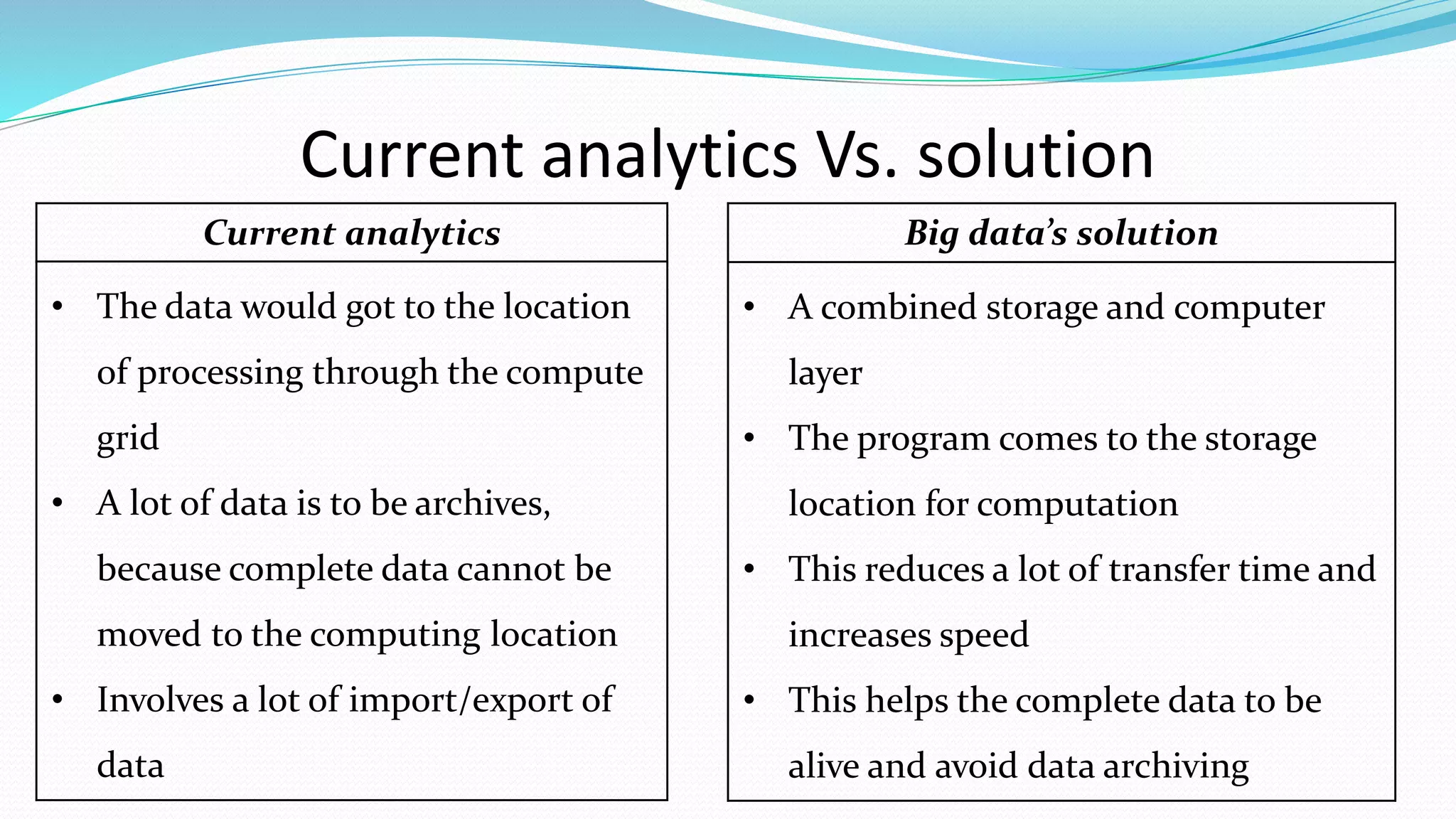
This document provides an overview of big data basics. It discusses how big data is not just about data size but also about analyzing large, diverse datasets from multiple sources. It describes how big data systems can efficiently process huge volumes of data in parallel from petabytes of data. Examples of big data applications include digital marketing, fraud detection, social media analysis, and machine-generated data analytics. Common sources of big data are also listed. The document then covers new analytics approaches for big data and different types of data warehouses. It concludes by discussing current and future trends in data storage and analytics for big data.