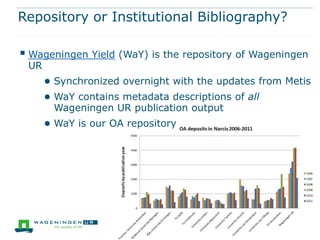
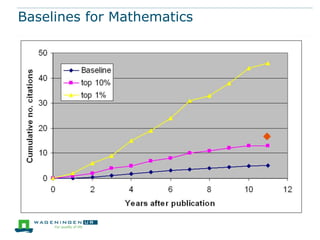
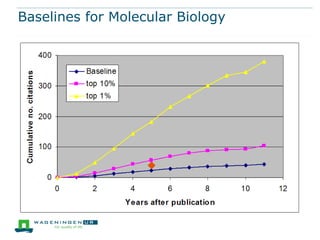
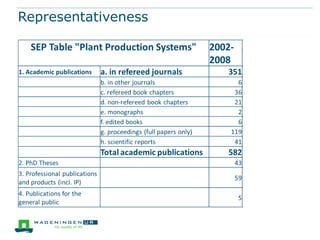
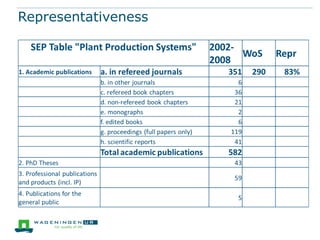
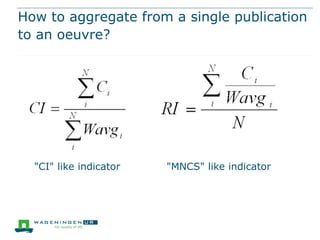
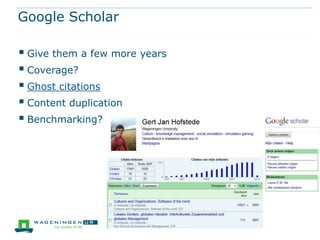
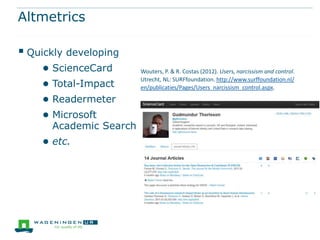
This document discusses the use of bibliometrics and citation analysis at Wageningen University. It provides context about the university's evaluation cycle and criteria. It then describes the current research information system (Metis) and institutional repository (Wageningen Yield) that provide publication data. The document discusses challenges in comparing citation metrics across fields and researchers. It also considers sources of citation data and developing altmetric tools. Finally, it argues that the university library is well-positioned to conduct bibliometric analyses using these local data systems.