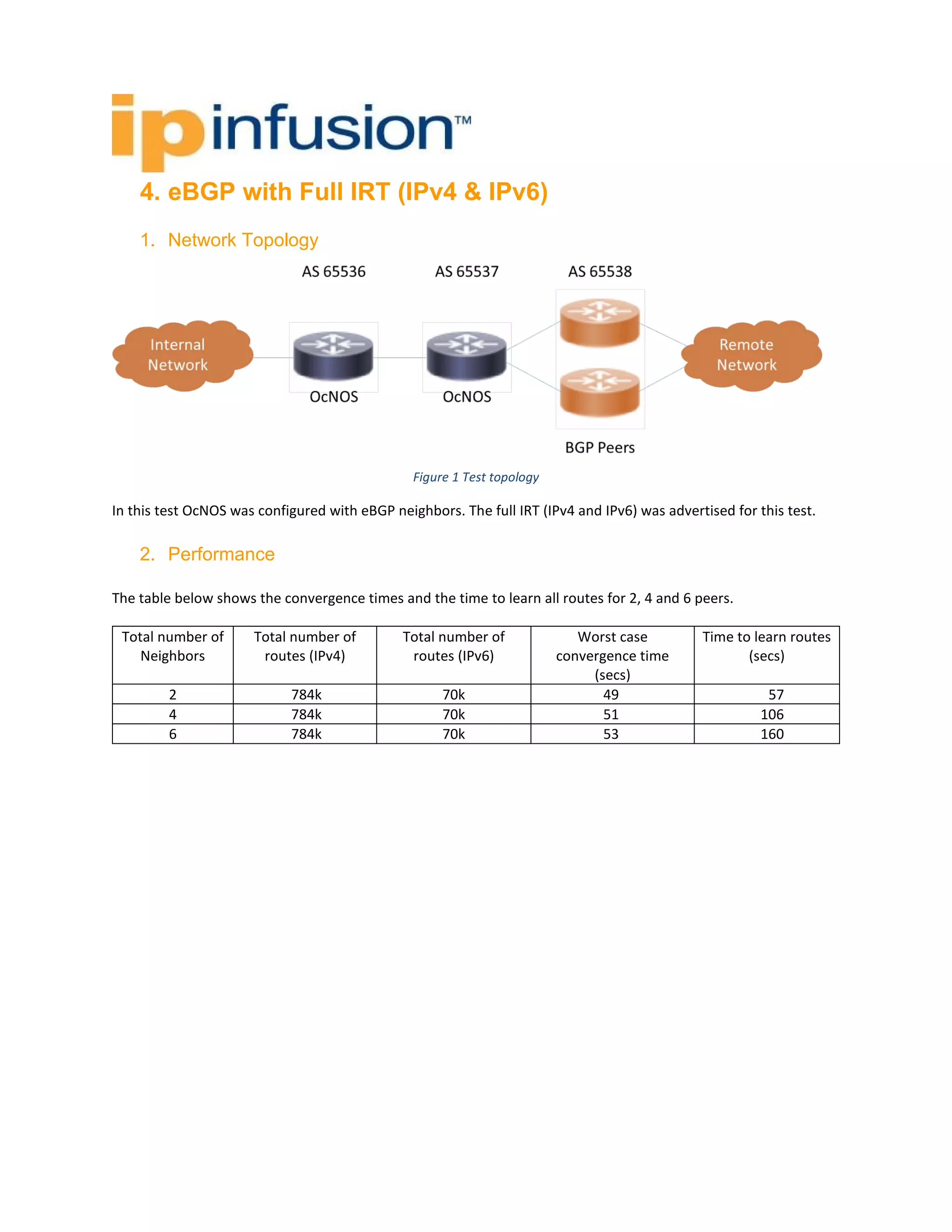
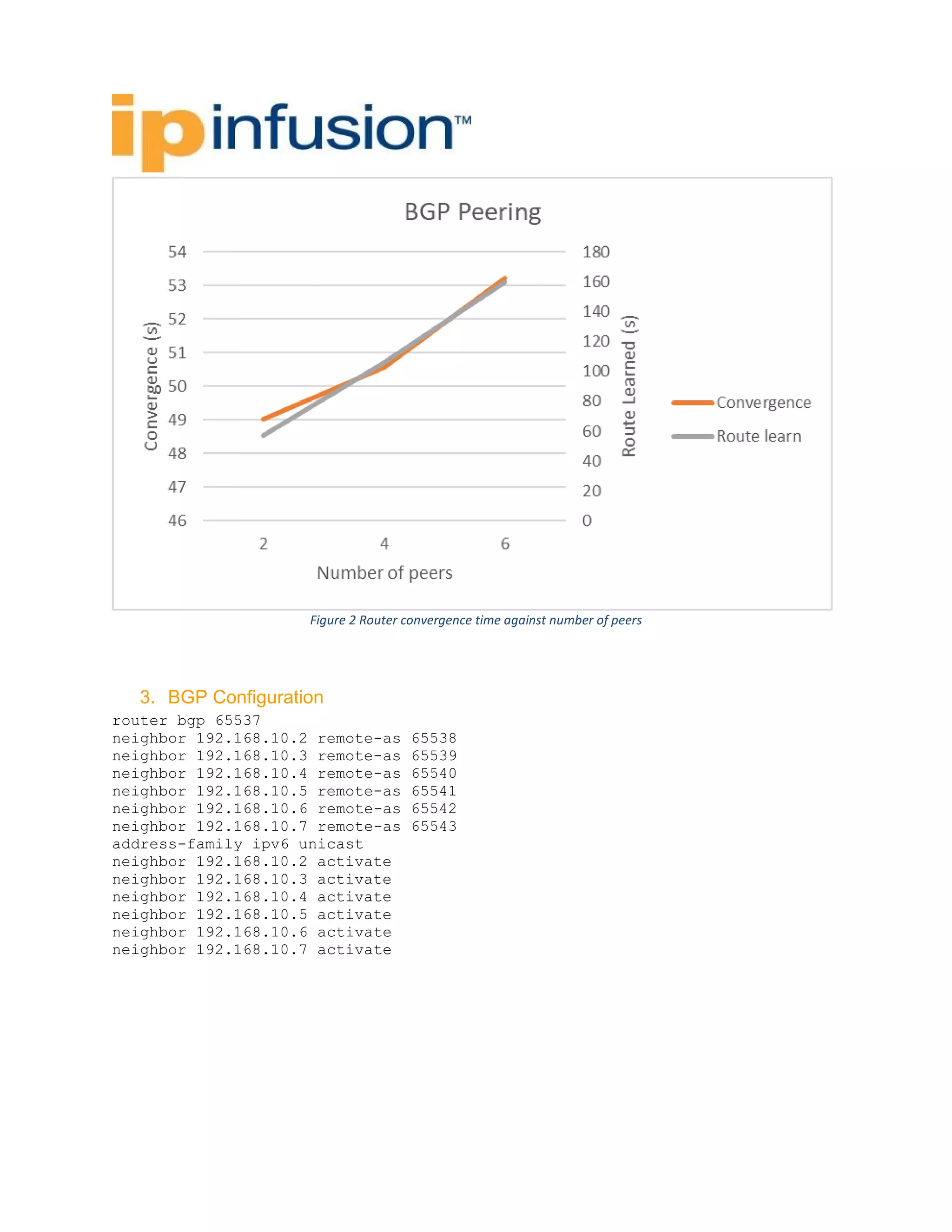
The BGP Peering Test Report evaluates the performance of the OCNOS routing software in supporting BGP peering with a full Internet routing table. The tests involved simulating internal network traffic across multiple BGP peers and measuring the convergence times and route learning periods. Results show varying performance metrics based on the number of peers, highlighting the behavior of the system under different network conditions.